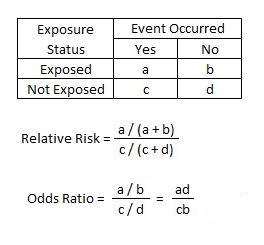
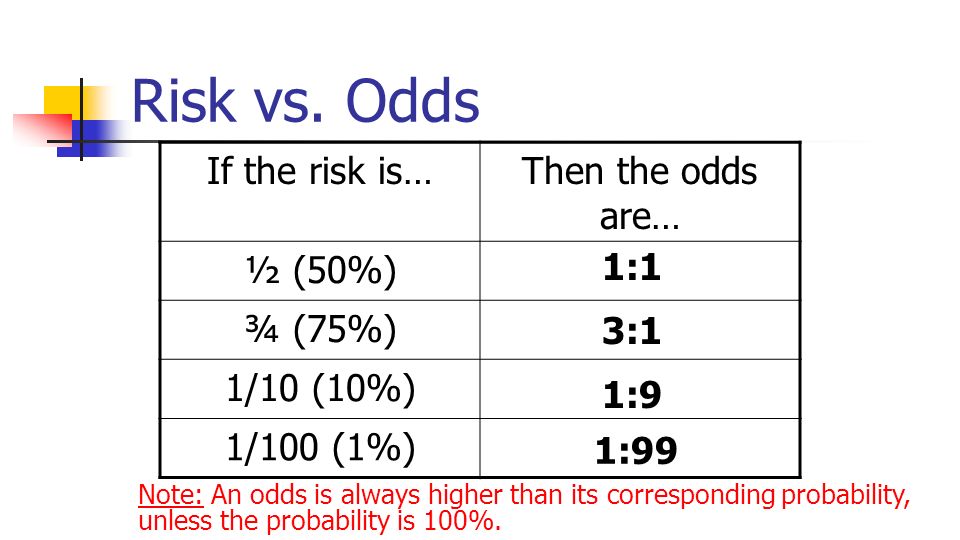
Even an odds ratio;RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO The relative risk (also known as risk ratio RR) is the ratio of risk of an event in one group (eg, exposed group) versus the risk of the event in the other group (eg, nonexposed group) The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds of the event in the other group09The effect could be beneficial (from a therapy) or harmful (from a hazard) Risk is the number of those having the outcome of interest (death, infection, illness, etc) divided by the total number exposed to the treatment Odds is the number having the outcome divided by the number not having the outcome
Relative Risk Article
What is the difference between odds and chances
What is the difference between odds and chances-Sometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR >About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy &




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)INTRODUCTION Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculatedThere can be substantial difference in the association of a risk factor with prevalent disease versus ;
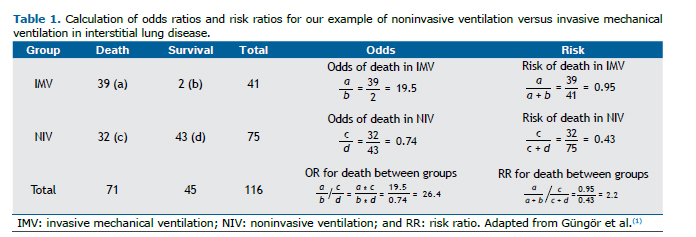
When the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative riskRisk is essentially the level of possibility that an action or activity will lead to lead to a loss or to an undesired outcome The risk may even pay off and not lead to a loss, it may lead to a gain A probability, on the other hand, is a measure or estimation of how likely is it that an event will come to pass, or that a statement is true In relation to risk, probability isThe odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the placebo group
Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsCommon pitfalls in statistical analysis Odds versus risk Priya Ranganathan 1, Rakesh Aggarwal 2, CS Pramesh 3 1 Department of Anaesthesiology, Tata Memorial Centre, Parel, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India 2 Department of Gastroenterology, Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India 3 Department of Surgical Oncology, Division of ThoracicRelative risks versus odds ratios Author Philip Sedgwick Created Date Z



Lecture3




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
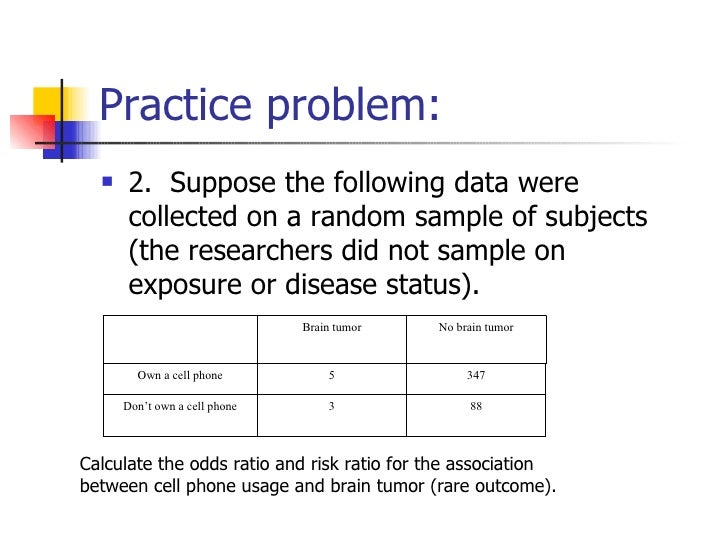
A rate ratio, ;Note that an odds ratio is a good estimate of the risk ratio when the outcome occurs relatively infrequently (<10%) Therefore, odds ratios are generally interpreted as if they were risk ratios Note also that, while this result is considered statistically significant, the confidence interval is very broad, because the sample size is small2) Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the nonobese Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect




Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney
The odds ratio will estimate the average change in odds (the average odds ratio) among exposed individuals only when all individual odds ratios are equal and all individual outcome risks without exposure are equal 1;We see that the 'relative risk' is now different, but the odds ratio does not change if we change the ratio of cases versus controls Until now we have learned the following 1 we can calculate relative risk IF we can estimate probabilities of an outcome in EACH group 2Common pitfalls in statistical analysis Odds versus risk In biomedical research, we are often interested in quantifying the relationship between an exposure and an outcome Odds and Risk are the most common terms which are used as measures of association between variables



Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsrisk




Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download
Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk Published on December 14, 15 by Howard Herrell, MD Many great things have been written about the difference between Odds Ratios (OR) and Relative Risks (RR) Every medical student at some point has been taught the differenceThat is one of the attractive features of the odds ratio — when the health outcome is uncommon, the odds ratio provides a reasonable approximation of the risk ratio Another attractive feature is that the odds ratio can be calculated with data from a casecontrol study, whereas neither a risk ratio nor a rate ratio can be calculatedOdds Ratio versus Relative Risk Since it is a ratio of ratios, the odds ratio is very difficult to interpret The relative risk is easier to interpret, so the odds ratio alone is not very helpful However, there are certain commonly occurring situations in which the estimate of the relative risk is not very good,



Plos One Different Depths Of Sedation Versus Risk Of Delirium In Adult Mechanically Ventilated Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis




Odds Ratio Relative Risk
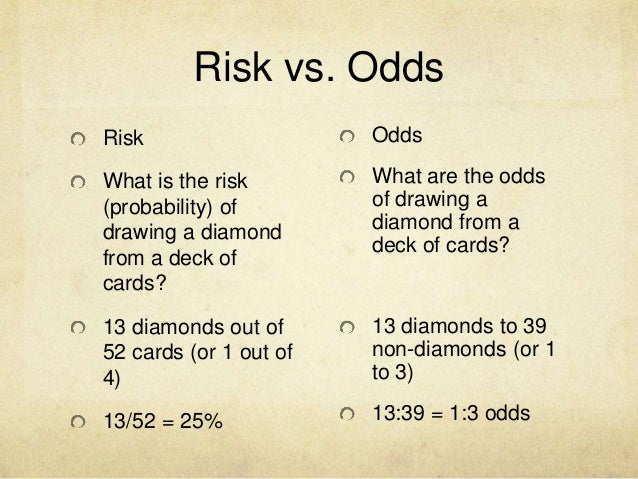
Everyone's choice is different weighing up the risk of potential side effects against the chance of contracting coronavirus and perhaps becoming seriously ill, or even dyingThis implausible scenario is shown in Table 5, where collapsed counts for low (or high) risk subjects only produce a 2 ×The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
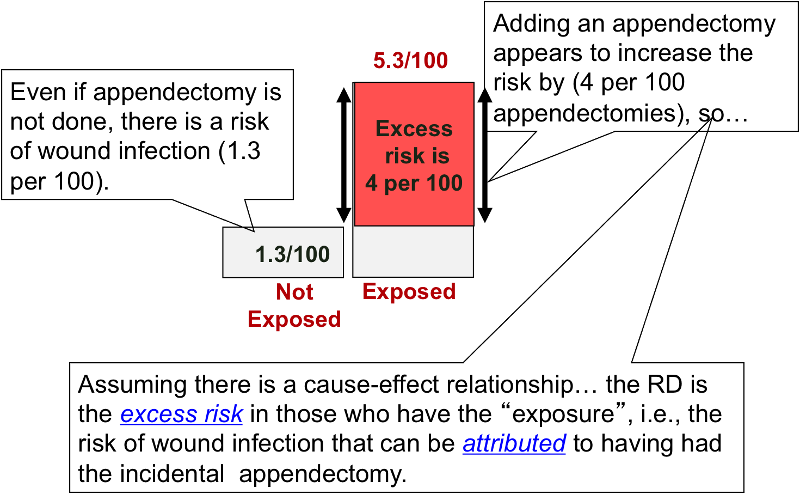
In finer terms, odds is described as the probability that a certain event will happen or not Odds can range from zero to infinity, wherein if the odds is 0, the event is not likely to happen, but if it is ∞, then it is more likely to happen For example Suppose, there are marbles in a bag, eight are red, six are blue, and six are yellowA prevalence ratio, or ;Risk and Odds Risk vs odds The terms 'risk' and 'odds' are often used interchangeably but they actually have quite different CER = 02 EER = 01 RR = 01 / 02 ARR = 02 – 01 ARR = 01 RRR = 01 / 02 RRR = 05 NNT = 1 / 01 Dr Marc Barton qualified from Imperial College School




Risk Versus Chance What Are The Odds Health And Communications



Jornal Brasileiro De Pneumologia Estimando Risco Em Estudos Clinicos Razao De Chances E Razao De Risco
The difference between odds and risk is small when the event is rare (as illustrated in the first example above where a risk of 0091 was seen to be similar to an odds of 01) When events are common, as is often the case in clinical trials, the differences between odds and risks are largeCollapsibility Odds Ratios versus Risk Ratios Ask Question Asked 8 years, 3 months ago Active 3 years, 1 month ago Viewed 4k times 7 2 $\begingroup$ It is known that odds ratios enjoy a certain symmetry For exampleThe odds ratio and the relative risk will not always disagree by this much Large effects on groups with high initial risk seem to cause the most problems See Davies et al (1998) for some useful guidelines for when the odds ratio and relative risk are likely to differ When they do differ, the relative risk represents the typical interpretation




Believability Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios In Abstracts Cross Sectional Study The Bmj




Relative Risk Wikipedia
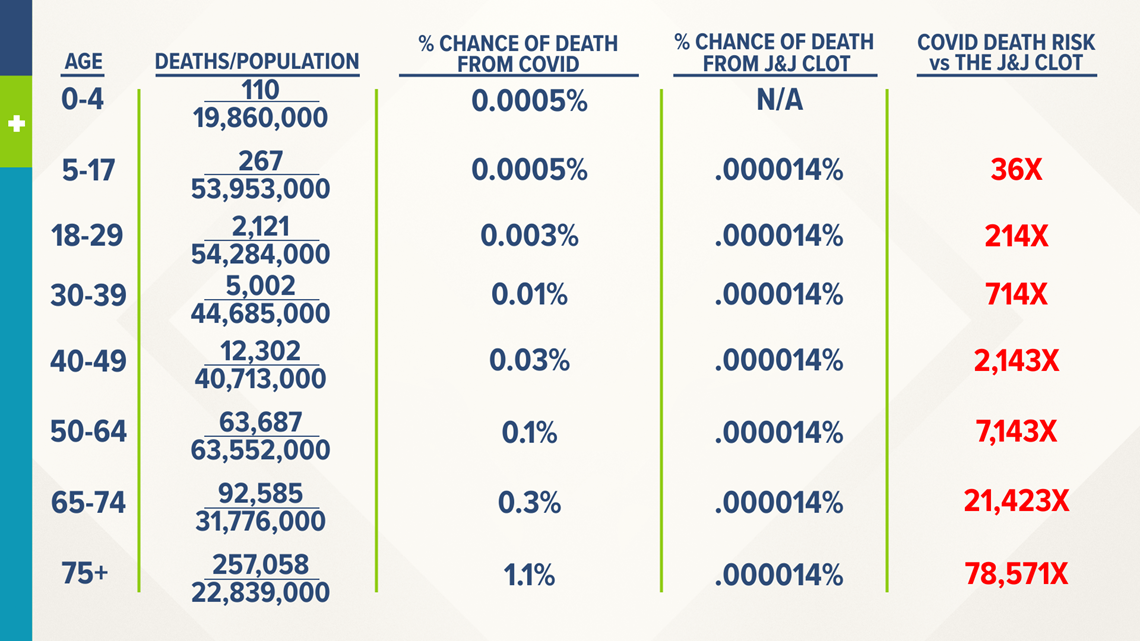
Odds The National Safety Council compiled an oddsofdying table for 08, which further illustrates the relative risks of flying and driving safety It calculated the odds of dying in a motorKnowing the odds is the first step in beating them But, not all risks faced in life can be accurately estimated Many people would like to know their odds of dying in the current COVID19 pandemic Please see the infographic to understand why odds of dying estimates are not yet available2 table with an odds ratios of 400




What Are The Odds The Annals Of Thoracic Surgery




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
In the general medical literature, rate is often incorrectly used for prevalence measuresThe relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population,0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR <



Odds Ratio Plots With A Logarithmic Scale In Sas The Do Loop




Relative Risk Article
Safety of COVID19 vaccine by AstraZeneca explained Blood clot cause, risks, chance of death and benefits Nine days after getting an AstraZeneca jab, a young and otherwise healthy NSW woman died2600Odds ratios While risk reports the number of events of interest in relation to the total number of trials, odds report the number of events of interest in relation to the number of events not of interest Stated differently, it reports the number of events to nonevents• The risk of sexual dysfunction with venlafaxine is 24 times that with placebo • The risk of sexual dysfunction with venlafaxine is 240% that with placebo • Venlafaxine is associated with a 14fold increase in the risk of sexual dysfunction • Venlafaxine is associated with a 140% increase in the risk of sexual dysfunction




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence
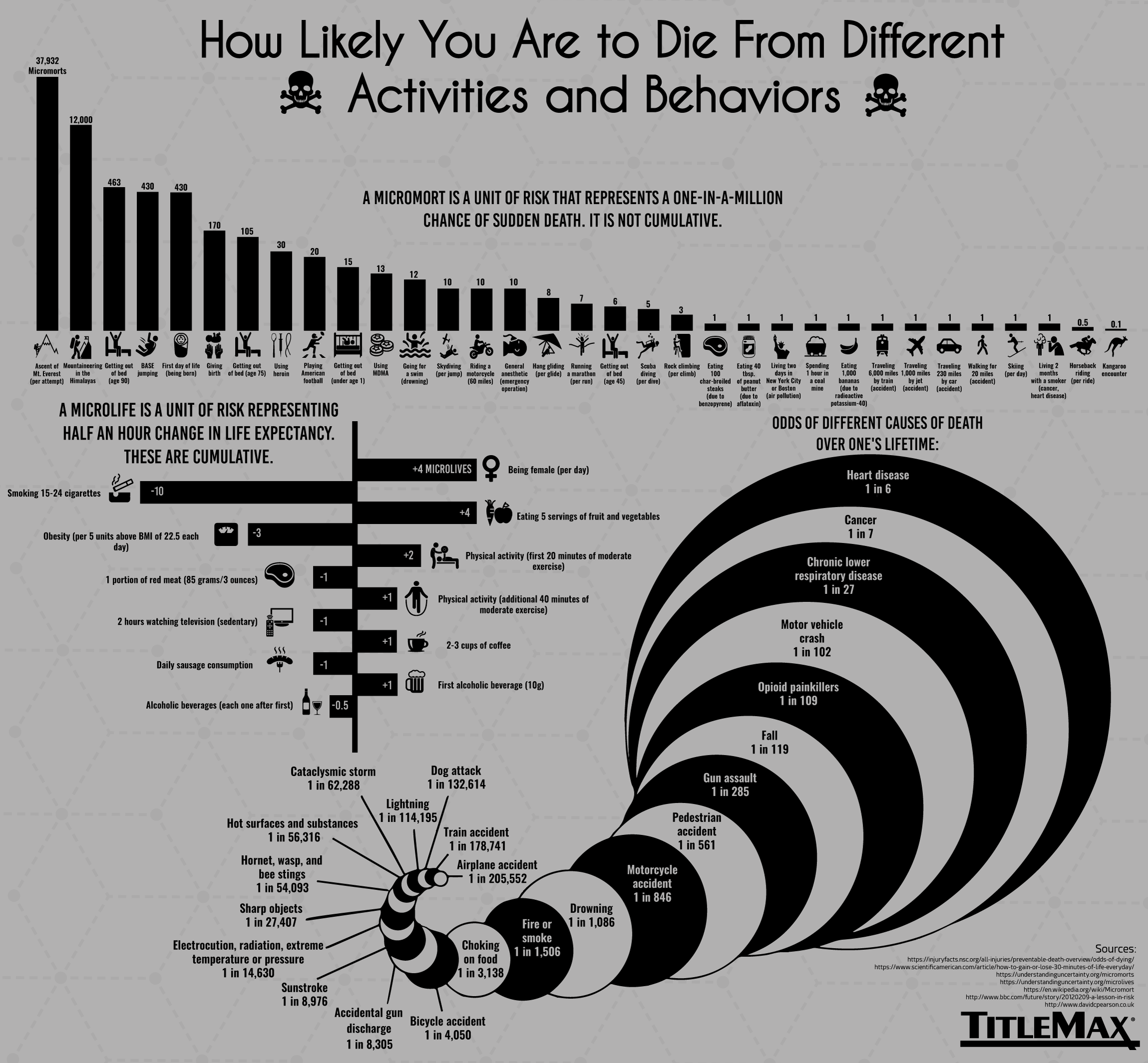
Hard to quantify the risk of being hit in your home by a plane falling out of the sky In Thursday's edition of its London Playbook newsletter, POLITICO quoted figures from the British Medical Journal (BMJ), which states that there's a one in 250,000 chance of being hit in your home by a plane falling out of the skyThe relative risk of losing weight by choosing diet A over diet B is 1125, while the odds ratio is about 225 The reasons a medical article might choose one method of reporting over the other are complex, but the message here is that sorting that out starts by being clear about the difference between probability and oddsYou know the difference between risk and odds A risk is the proportion of subjects with an event in a total group of susceptible subjects Thus, we can calculate the risk of having a heart attack among smokers (infarcted smokers divided by the total number of smokers) and among nonsmokers (the same, but with nonsmokers)




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training




Risk Versus Chance What Are The Odds Health And Communications Communications Probability Health
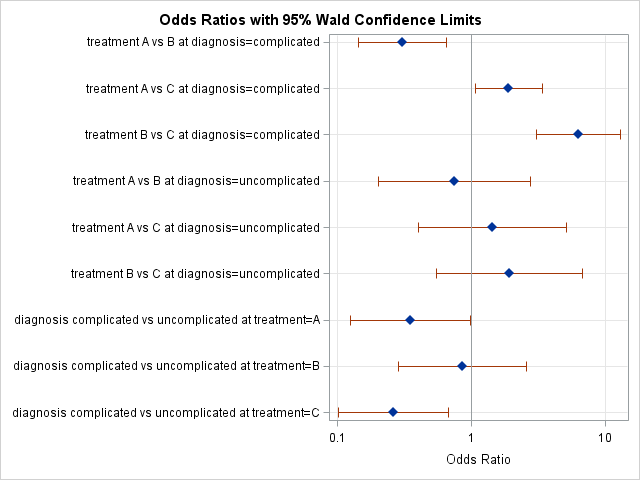
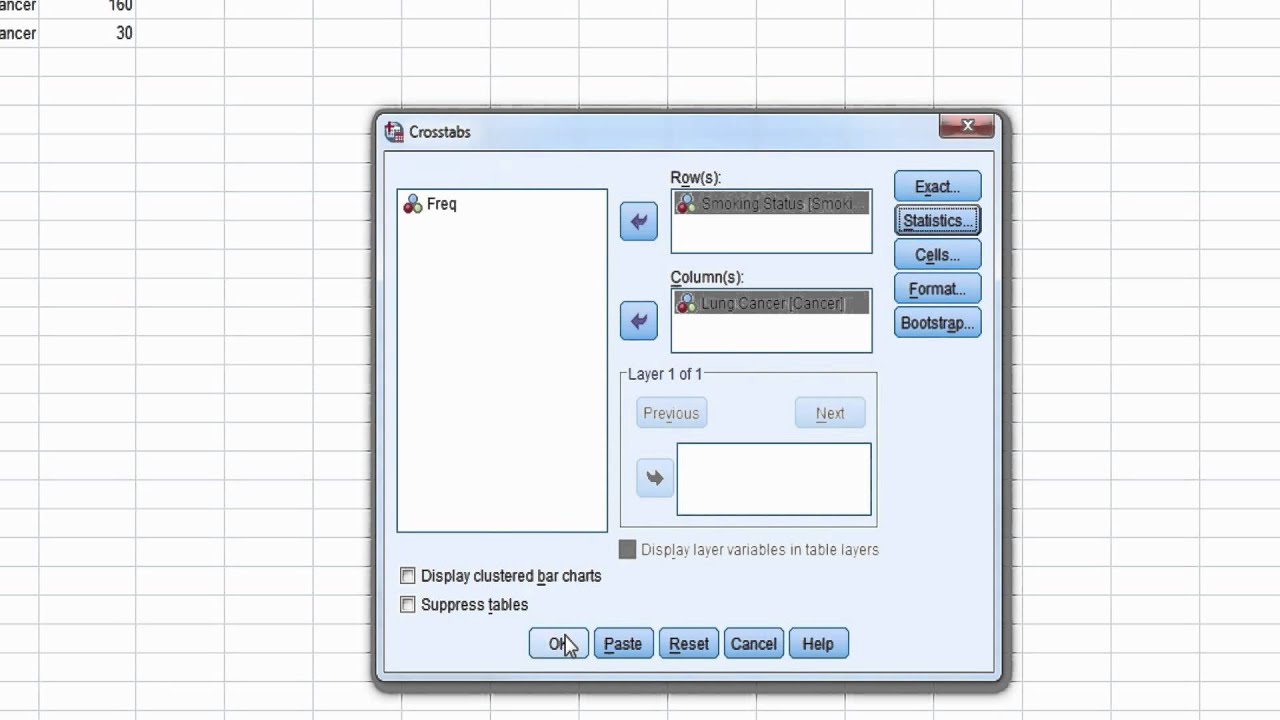
RR Relative risk or RR is very common in the literature, but may represent a risk ratio, ;This video demonstrates how to calculate odds ratio and relative risk values using the statistical software program SPSSSPSS can be used to determine odds r0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056




Odds Ratio Article
Comparing AstraZeneca vaccine bloodclot risk to odds of dying in a car crash unhelpful, experts say Downplaying the risk with inappropriate comparisons will not build coronavirus vaccineOdds ratio versus relative risk The relative risk is easier to interpret, so the odds ratio alone is not very helpful However, there are certain commonly occurring situations in which the estimate of the relative risk is not very good and the odds ratio can be used to approximate the relative risk of the event of interest2410Odds can be expressed as a ratio of the probability an event will happen divided by the probability an event won't happen Odds in favor of A = A / (1 A), usually simplified to lowest terms, For instance, if the probability of an event occurring is 075, then the odds for it happening are 075/025 = 3/1 = 3 to 1 for, while the probability that it doesn't occur is 1 to 3 against




Forest Plots Of Odds Ratio With 95 Ci For Apoe Polymorphism And Proximal Crn A E2 Versus B E4 Versus And Distal Crn Risk C E2 Versus D E4




Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To
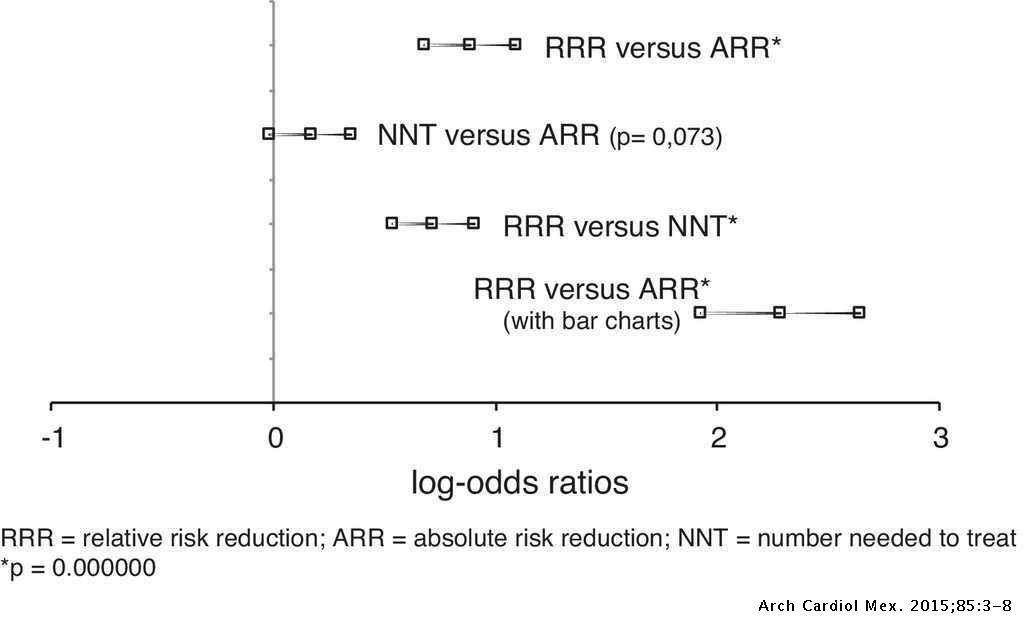
Each researcher provides a different method for comparing treatments For example, when the end point is binary, such as disease versus no disease, the common measures are odds ratios, relative risk, relative risk reduction, absolute risk reduction, and theRelative risk can only be used in prospective studies – note the wording above is all in terms of "contracting" the disease It is often used to compare the risk of developing a disease in people not receiving a new medical treatment (or receiving a placebo) versus people who are receiving an established treatment Odds ratio vs relative riskThe simple relative risk is 055 and the simple odds ratio is 025Clearly the probability of fathering a child is strongly dependent on a variety of demographic variables, especially age (the issue of marital status was dealt with by a separate analysis) The control group was 84 years older on average (435 years versus 351), showing the need to adjust for this variable



Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download



Pdf Common Pitfalls In Statistical Analysis Odds Versus Risk




Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk




Based On This Chart The Top Of This Question Is P Chegg Com




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Pdf Common Pitfalls In Statistical Analysis Odds Versus Risk




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor



Clinical Epidemiology Bootcamp




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine




Odds Ratio Relative Risk




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Risk Ratio Vs Relative Risk



Risk Of Covid 19 Not Increased In Ms Patients Medical Conferences




Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute




Measures Of Disease Association Ppt Download




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Common Pitfalls In Statistical Analysis Odds Versus Risk Abstract Europe Pmc




Lecture3



Spss Video 10 Obtaining Odds Ratio Relative Risk In Spss Youtube




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Simple Rules On When And How To Use Them Mckenzie European Journal Of Clinical Investigation Wiley Online Library




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Single Workplace Factor Odds Ratios Between High Risk Versus Low Risk Download Table




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Plos One Paper And Pencil Versus Computerized Administration Mode Comparison Of Data Quality And Risk Behavior Prevalence Estimates In The European School Survey Project On Alcohol And Other Drugs Espad




Risk Estimates Relative Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio Analyses For Download Table




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




R Calculate And Interpret Odds Ratio In Logistic Regression Stack Overflow



The Odds Of Dying From A J J Vaccine Related Blood Clot Vs Dying From Covid 19 Newscentermaine Com




Risk Of In Hospital Morbidity Mortality In Log Odds Versus Vitamin D Download Scientific Diagram



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research



Risk Differences And Rate Differences




Retrospective Cohort Study Wikipedia



Plos One Different Depths Of Sedation Versus Risk Of Delirium In Adult Mechanically Ventilated Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis



How Likely You Are To Die From Different Activities And Behaviors Infographic Article




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research




Relative Risk Wikipedia



Effects Of Presenting Risk Information In Different Formats To Cardiologists A Latin American Survey Archivos De Cardiologia De Mexico




Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk




Measures Of Disease Association Measuring Occurrence Of New Outcome Events Can Be An Aim By Itself But Usually We Want To Look At The Relationship Between Ppt Download




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Risks Of And Risk Factors For Covid 19 Disease In People With Diabetes A Cohort Study Of The Total Population Of Scotland The Lancet Diabetes Endocrinology




Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge



Stats Guidelines For Logistic Regression Models September 27 1999




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download




Pdf Relative Risks Versus Odds Ratios




Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Handout



The Difference Between Probability And Odds




Forest Plot Showing Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio In Al In The Icg Group Download Scientific Diagram




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
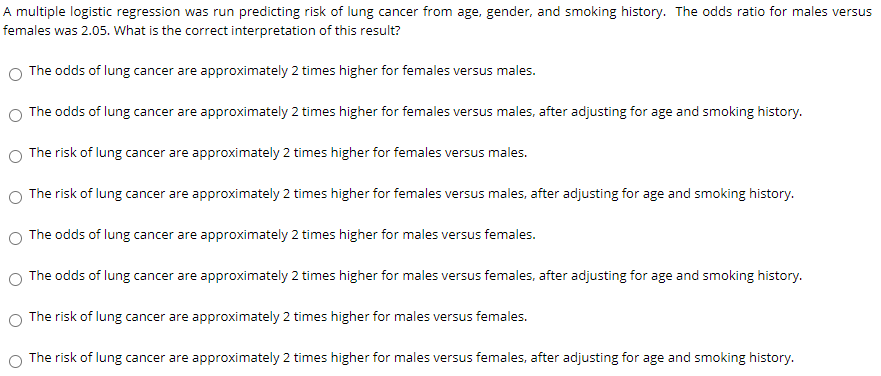



Solved A Multiple Logistic Regression Was Run Predicting Chegg Com




Power Calculations For Gwass The Smallest Odds Ratio Case Control Download Scientific Diagram




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Risk Ratio Versus Odds Ratio Dr Journal Club




What Are The Odds Of Dying From Covid 19 Vs Lightning Wqad Com
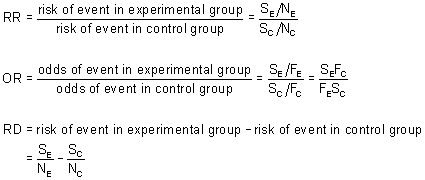



Box 9 2 A Calculation Of Rr Or And Rd
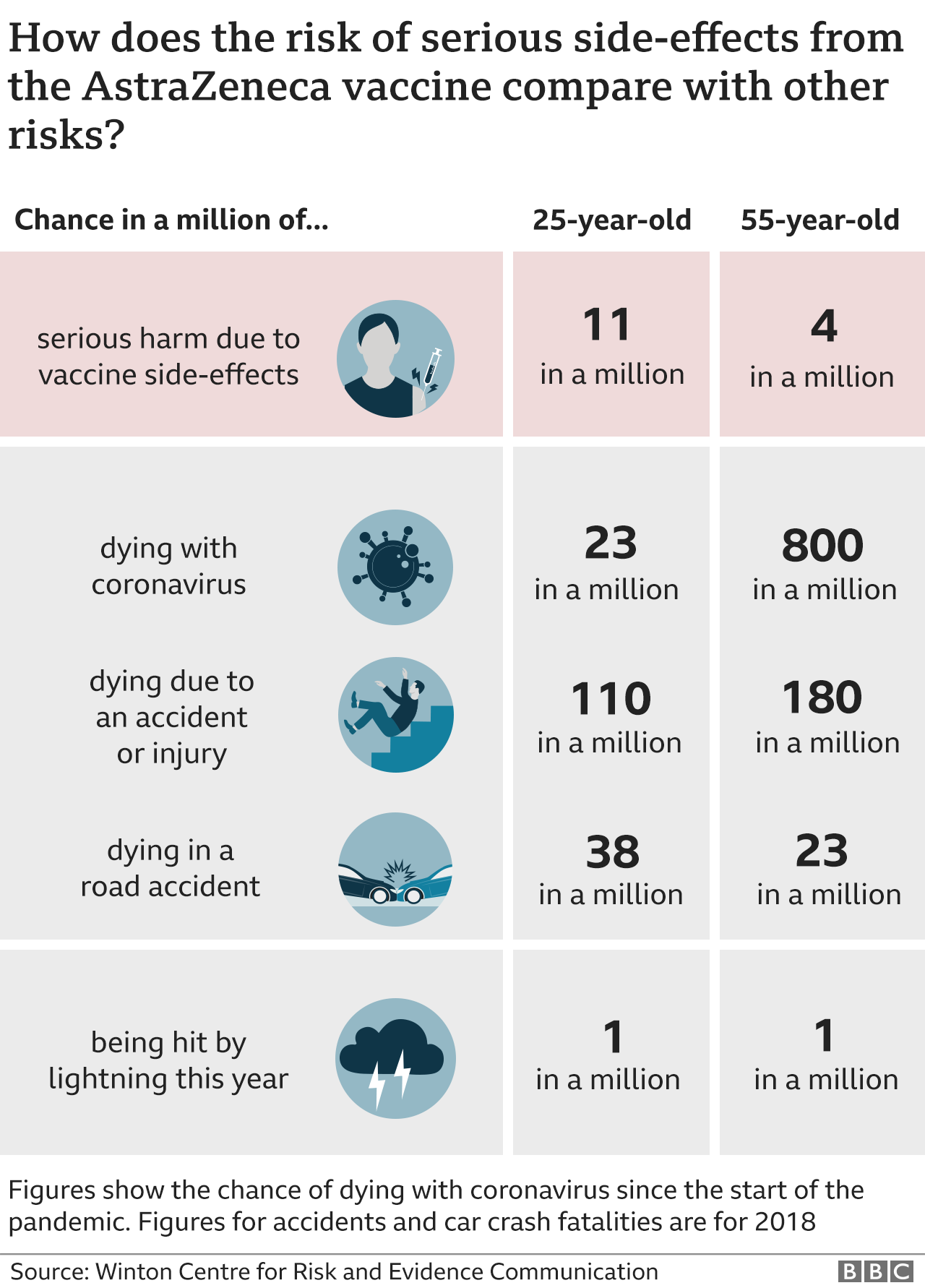



Astrazeneca Vaccine How Do You Weigh Up The Risks And Benefits c News




Image Result For Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio And Cohort Study And Case Study




Odds Ratio For The Risk Of Having A Prescription Pre Versus Download Table




Solved Select All Of The True Statements Regarding The Od Chegg Com
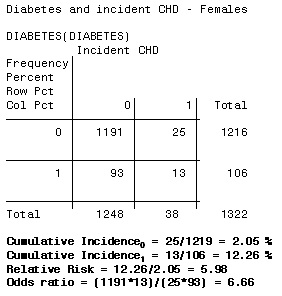



3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507




Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Youtube




Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases




Lecture3




Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿