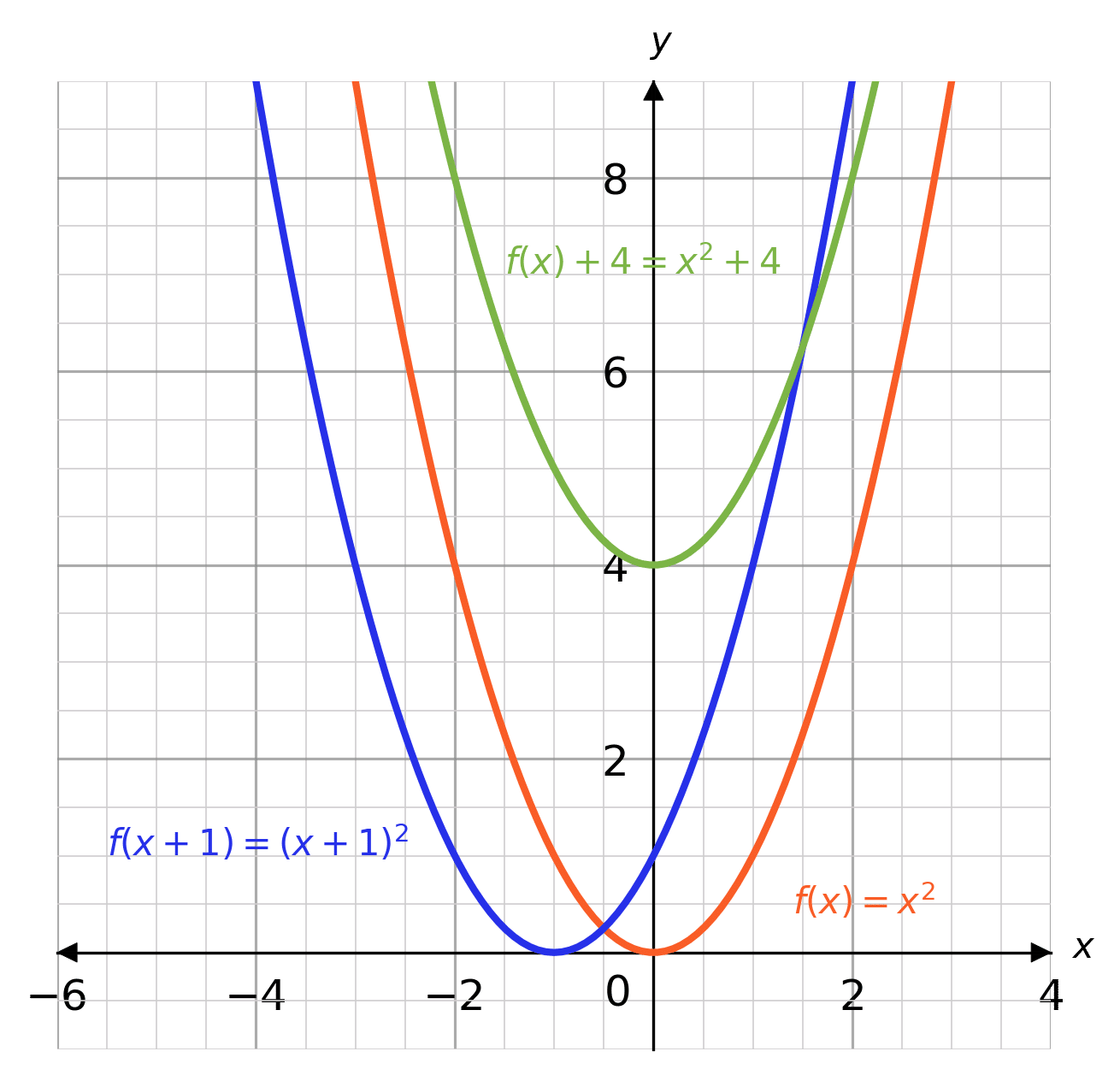
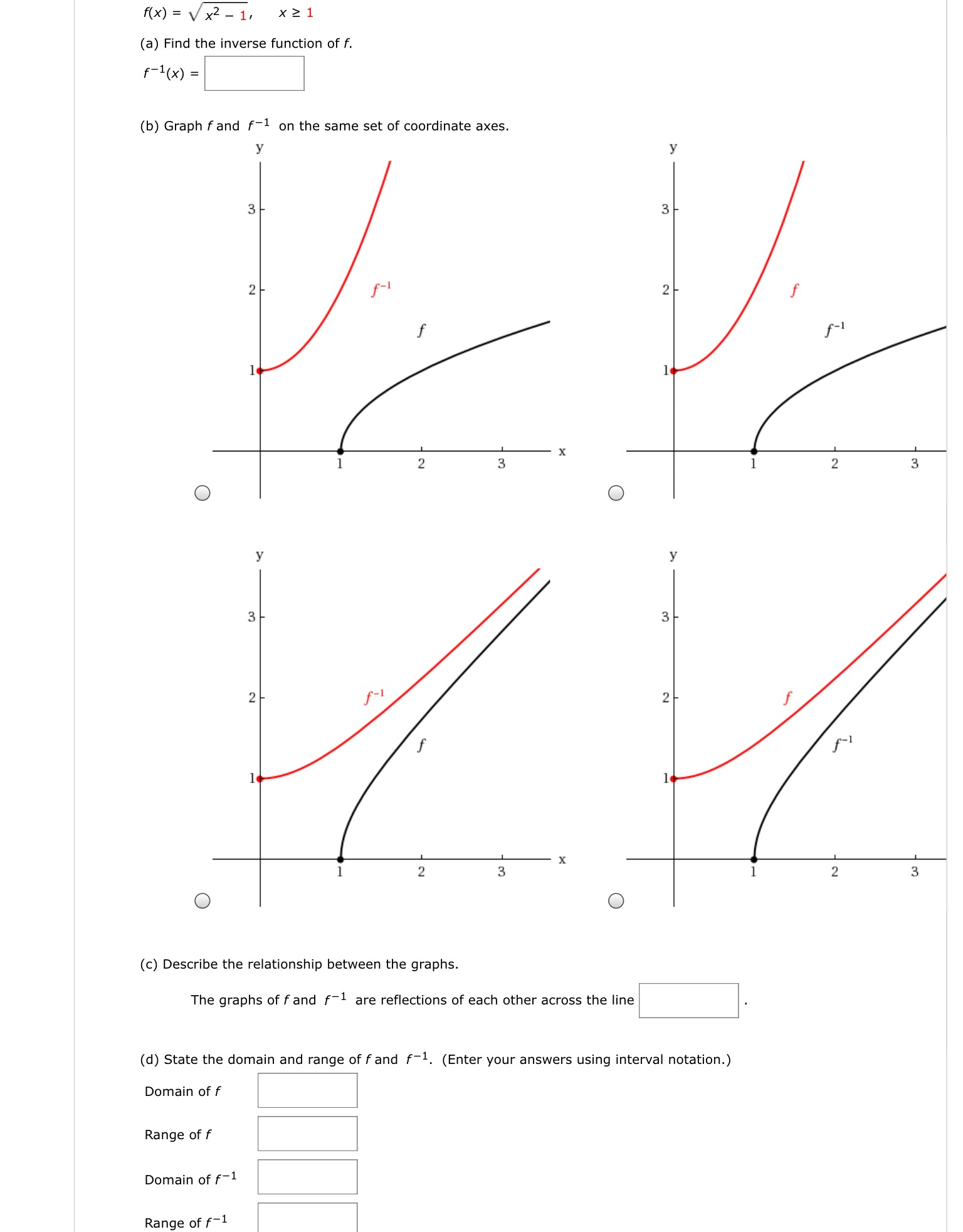
Use a graph of f(x) to determine the value of f(n), where n is a specific xvalueTable of Contents0000 Finding the value of f(2) from a graph of f(x)002Graph the following function {eq}f(x) = 4^x {/eq} Exponential Functions Exponential functions are the ones in which the variable of interest is the exponent of some other termF ( x) = x2 A function transformation takes whatever is the basic function f (x) and then "transforms" it (or "translates" it), which is a fancy way of saying that you change the formula a bit and thereby move the graph around For instance, the graph for y = x2 3 looks like this This is three units higher than the basic quadratic, f (x) = x2
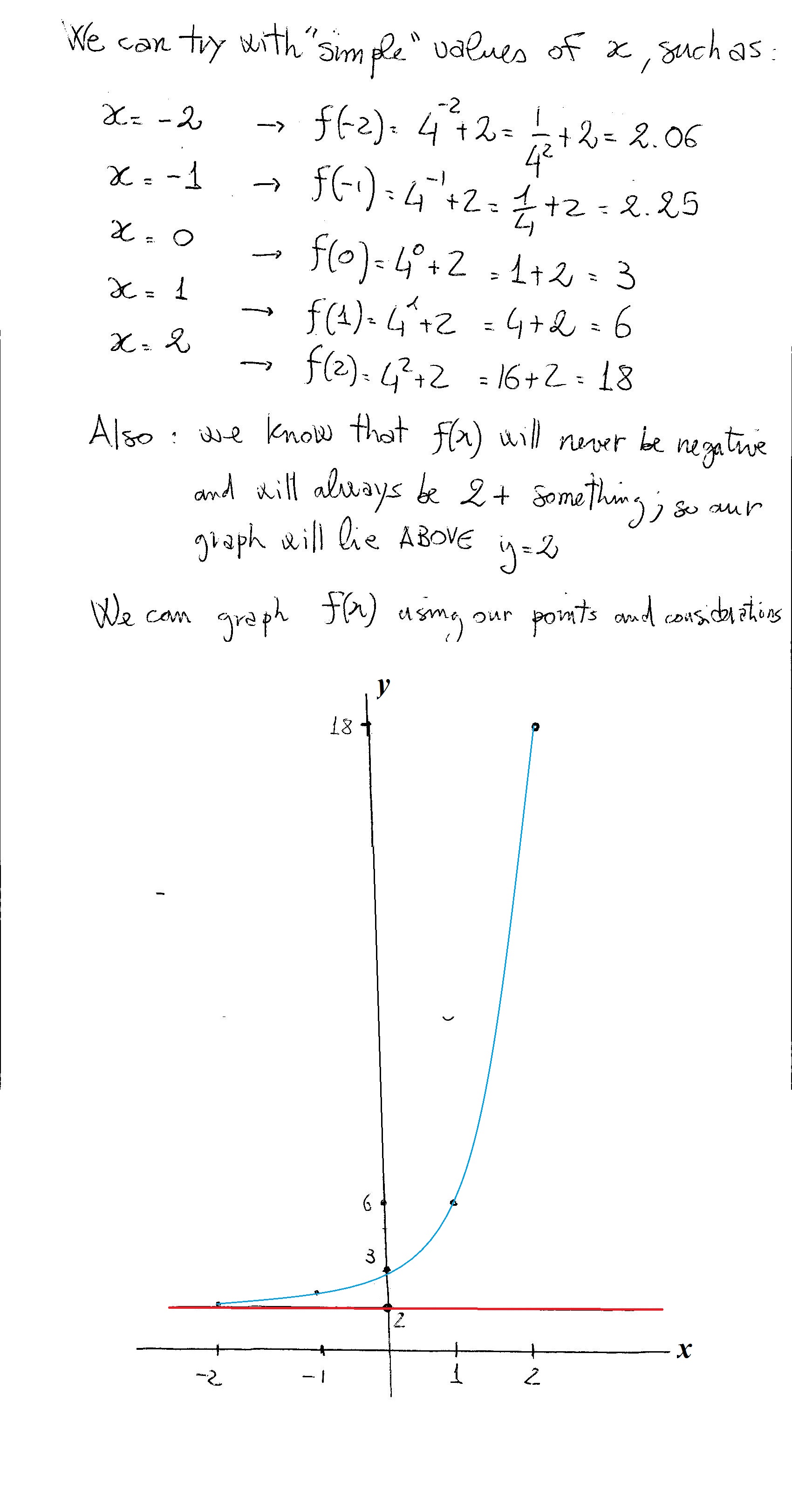
How Do You Graph The Exponential Function F X 4 X 2 Socratic
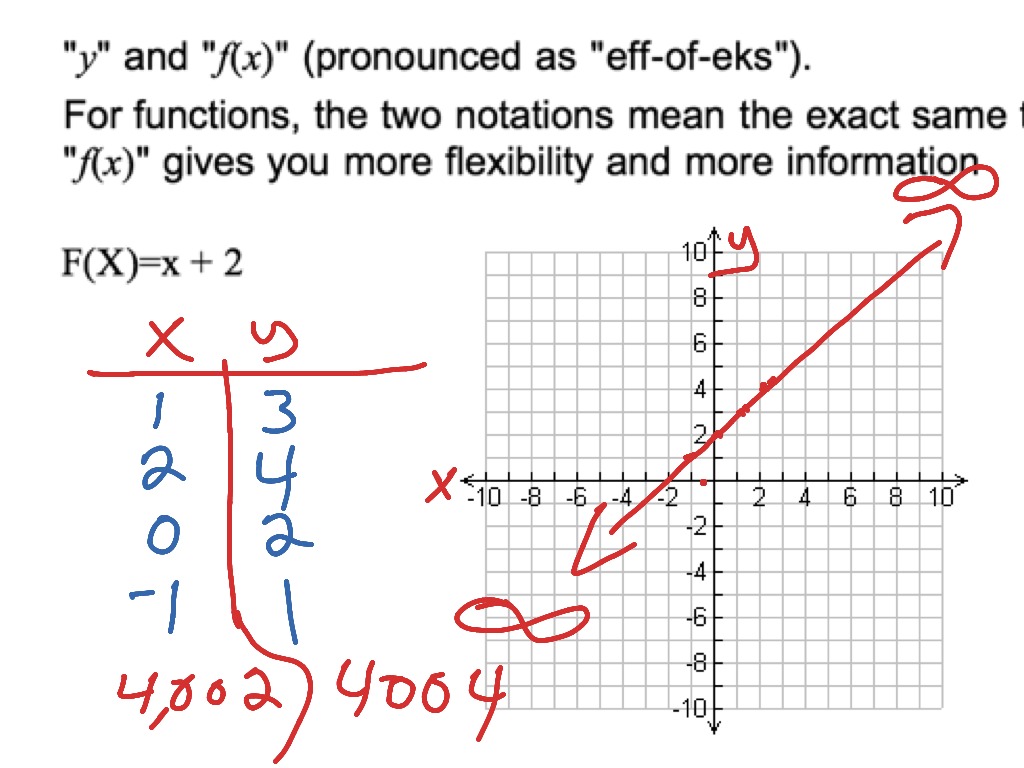
Y=f(x) graph
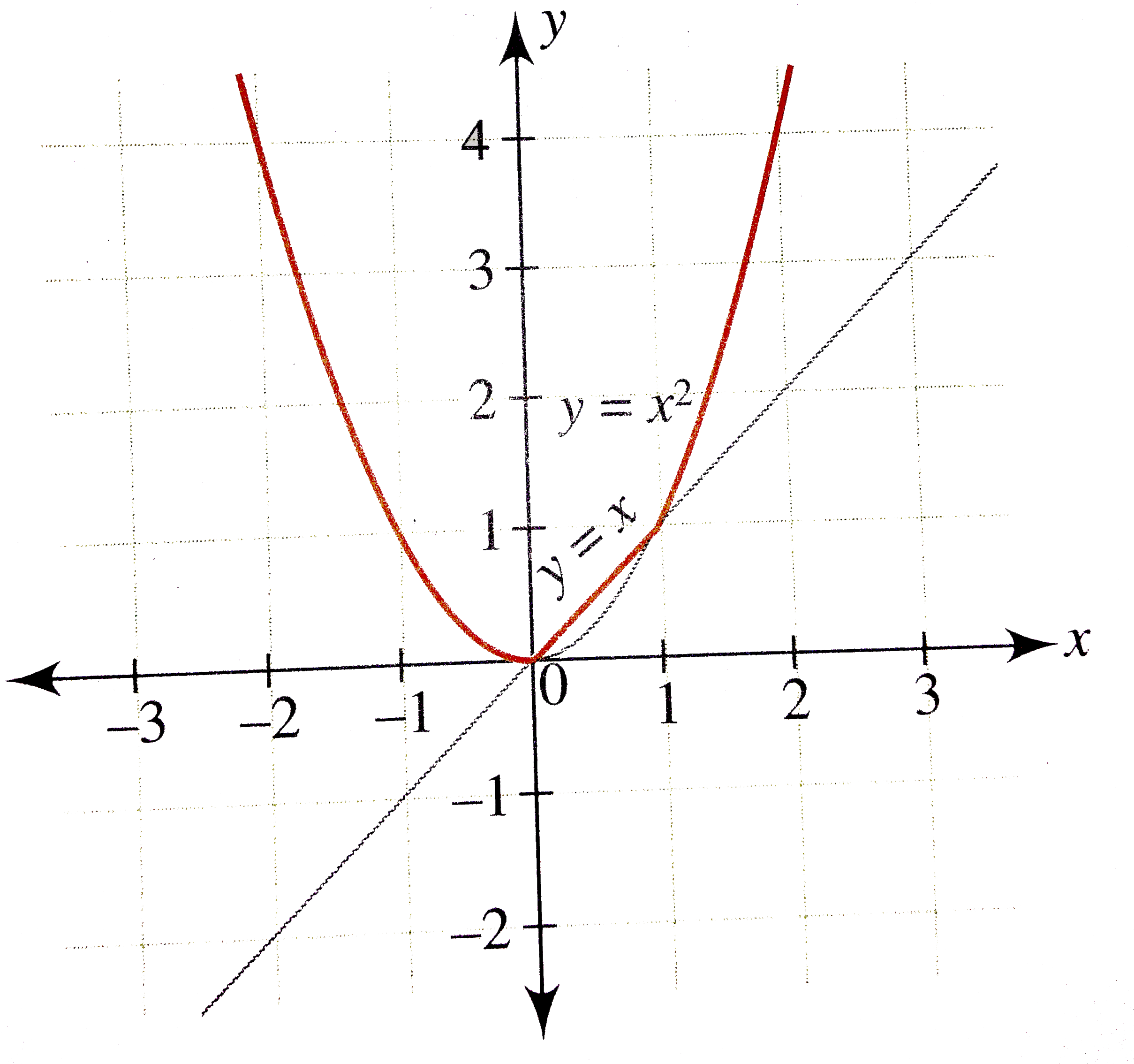
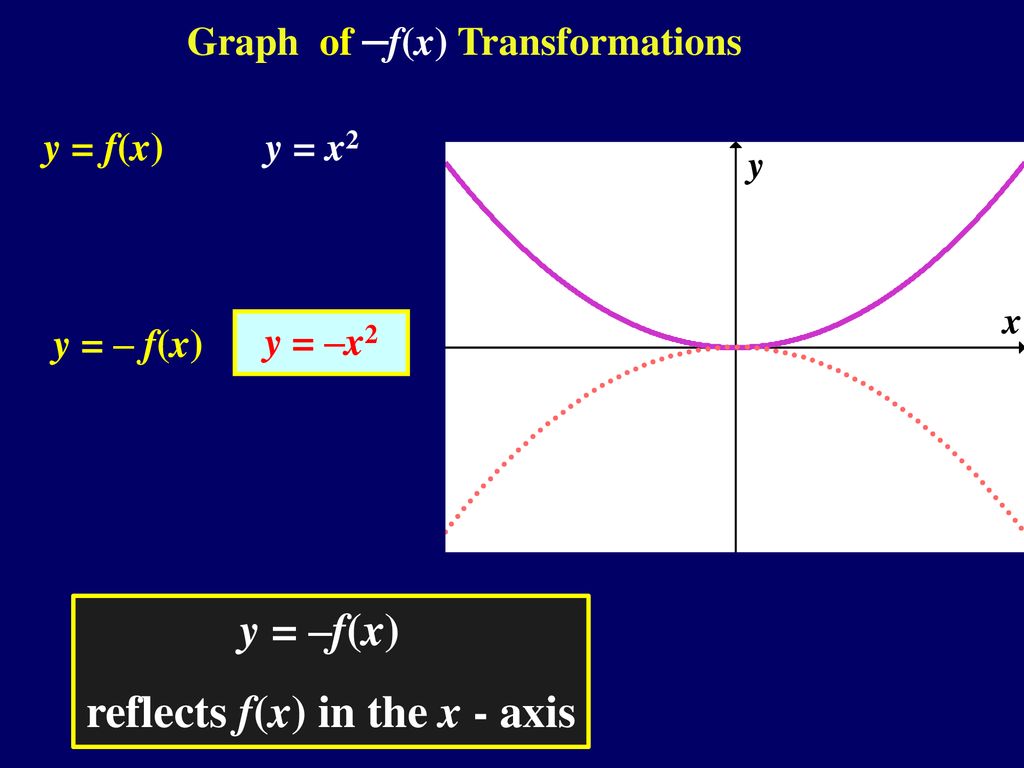
Y=f(x) graph-Explanation In the relation , there are many values of that can be paired with more than one value of for example, To demonstrate that is a function of in the other examples, we solve each for can be rewritten as can be rewritten as can be rewritten as need not be rewrittenPurplemath The last two easy transformations involve flipping functions upside down (flipping them around the xaxis), and mirroring them in the yaxis The first, flipping upside down, is found by taking the negative of the original function;
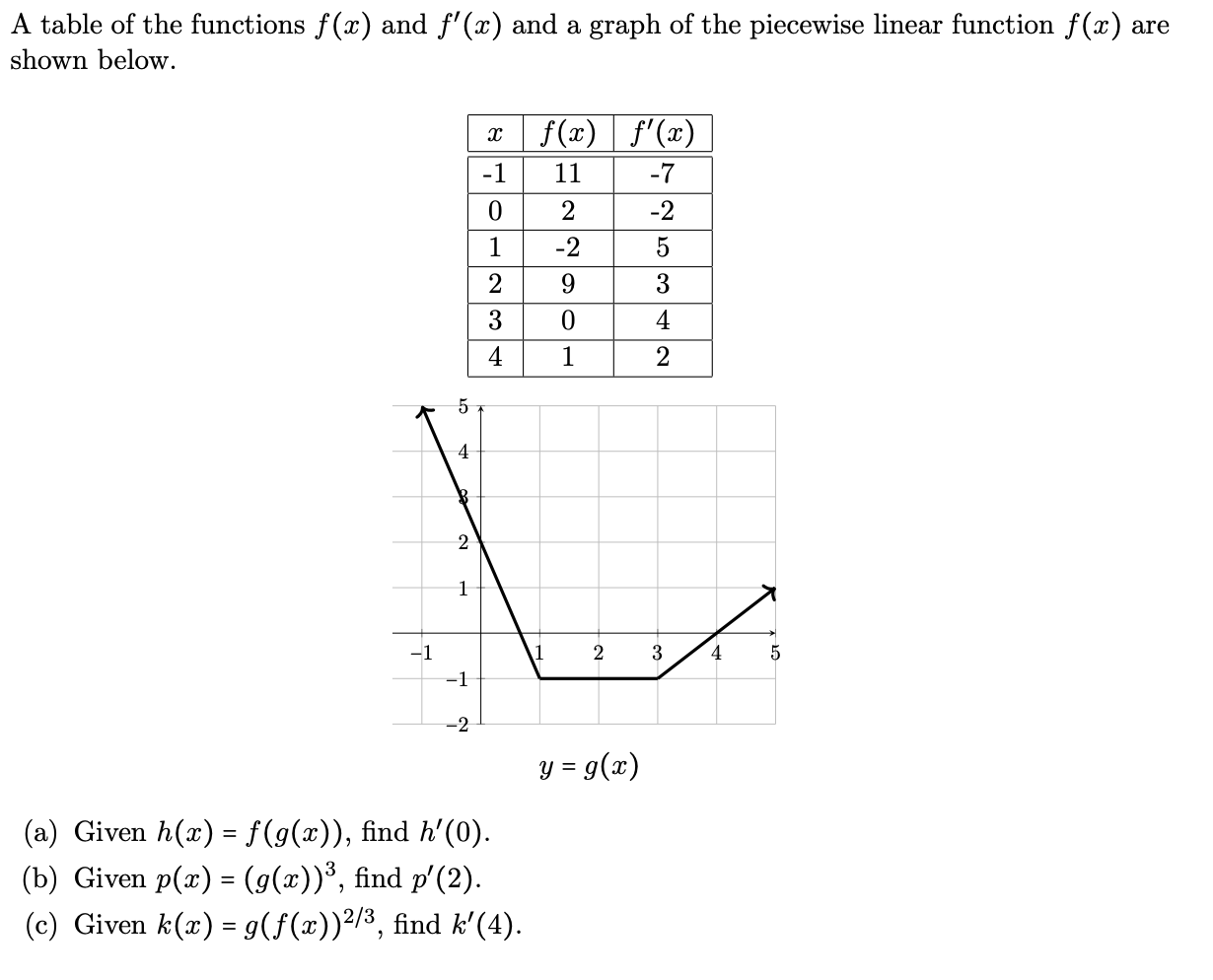



A Table Of The Functions F X And F X And A Graph Chegg Com
Absolute value of an integerINTERPRETING GRAPHS OF f(x)The graph of the function f (x) is shown belowAccording to this graph we havef'a is (positive, equal to zero, or negative)f'b is (positive, equal to zero, or negative)f
For every value of x, y takes the value it would have at kx It is the graph of y = f(x) stretched by a factor of 1/k on the xaxisThe output f (x) is sometimes given an additional name y by y = f (x) The example that comes to mind is the square root function on your calculator The name of the function is \sqrt {\;\;} and we usually write the function as f (x) = \sqrt {x} On my calculator I input x for example by pressing 2 then 5 Then I invoke the function by pressingOn the graph of a line, the slope is a constant The tangent line is just the line itself So f' would just be a horizontal line For instance, if f (x) = 5x 1, then the slope is just 5 everywhere, so f' (x) = 5
Free graphing calculator instantly graphs your math problems Mathway Visit Mathway on the web Download free on Google Play Download free on iTunes Download free on Amazon Download free in Windows Store get Go Graphing Basic Math PreAlgebra Algebra Trigonometry Precalculus Calculus Statistics Finite Math Linear AlgebraCalculates a table of the given functions f(x) and g(x) and draws the chart f(x) g(x) range (a, b) partitions n Customer Voice Questionnaire FAQ Chart drawing f(x),g(x) 15 /5 DispNum 1 0454 / 60 years old level or over / A teacher / A researcher / Useful /Graph of f (x)=1/x3 Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving process If it's not what You are looking for, type in into the box below your own function and let us find the graph of it The graph of f (x)=1/x3 is a visual




How To Find F 23 Given Part Of The Graph And That F X F X 6 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Which Graph Best Represents The Function F X 2 1 5 X Brainly Com
C < 0 moves it down We can move it left or right by adding a constant to the xvalue g(x) = (x · In order to find what value (x) makes f (x) undefined, we must set the denominator equal to 0, and then solve for x f (x)=3/ (x2); · The graph of #f(x)=x^2# is called a "Parabola" It looks like this One of the ways to graph this is to use plug in a few xvalues and get an idea of the shape Since the x values keep getting squared, there is an exponential increase on either side of the yaxis



What Is The Graph Of F X X 5 Socratic



Graph Transformations Discovering Manipulating Functions Geogebra
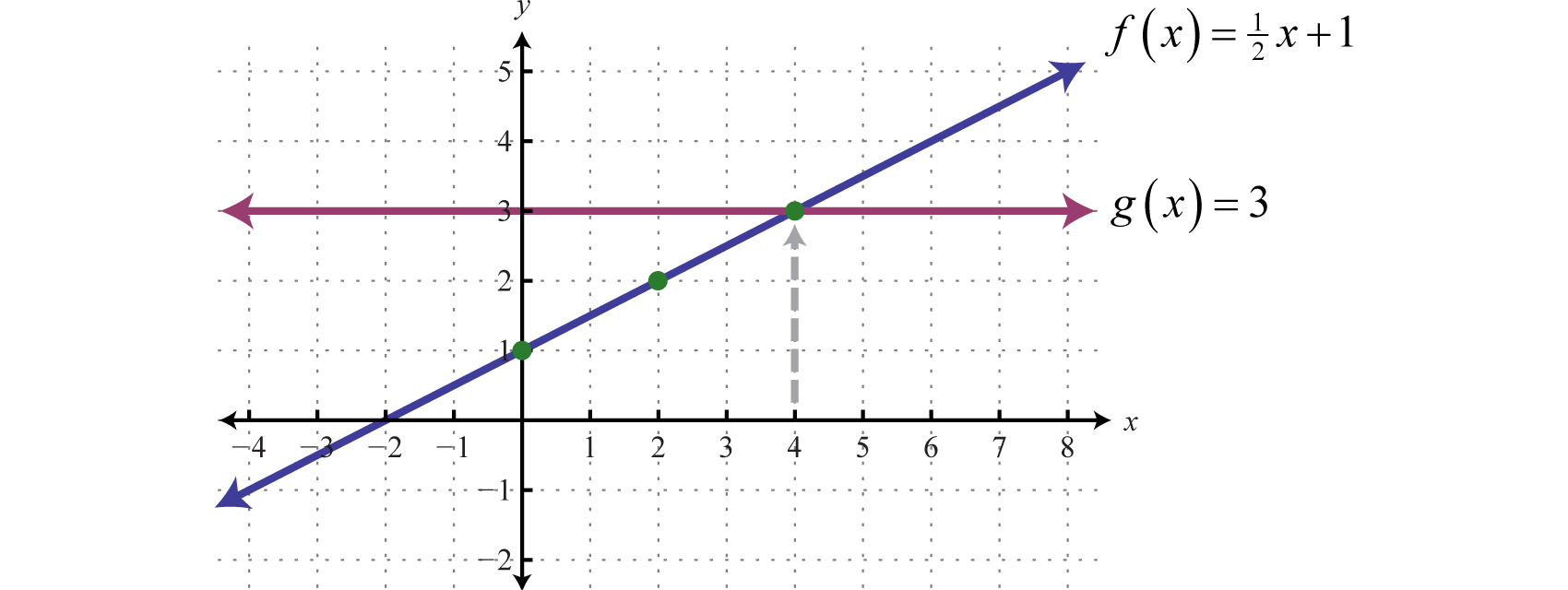
· Gió Dec 14, 14 This function is a constant so that for every value of x has always the same value of y, that is 4 A general straight line has the following form as a function y = f (x) = axb where a is the slope of the line and b the intercept with the y axis Now your function has the form f (x) = 0x 4CH11 Functions and Their Graphs Ex36數學系卡安很閒 所以決定拯救沒辦法用slader和chegg的莘莘學子To find f(x) you delete the decimal or fractional portion of x, leavingAbout Beyond simple math and grouping (like "(x2)(x4)"), there are some functions you can use as well Look below to see them all They are mostly standard functions written as you might expect




From The Graph Of The Derivative F X Make A Sketch Of The Original Function F X And Of The Second Derivative F X Mathematics Stack Exchange



Draw The Graph Of The Function F X Max X X 2 And Write
We set the denominator,which is x2, to 0 (x2=0, which is x=2) When we set the denominator of g (x) equal to 0, we get x=0 So x cannot be equal to 2 or 0 Please click on the image for a better understandingReflections of graphs Graphs can be reflected in either the \ (x\) or \ (y\) axes Reflections in the xaxis If \ (f (x) = x^2\), then \ (f (x) = (x^2)\)Let us start with a function, in this case it is f(x) = x 2, but it could be anything f(x) = x 2 Here are some simple things we can do to move or scale it on the graph We can move it up or down by adding a constant to the yvalue g(x) = x 2 C Note to move the line down, we use a negative value for C C > 0 moves it up;



6 5 4 3 2 6 5 4 7 2 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 2 Chegg Com
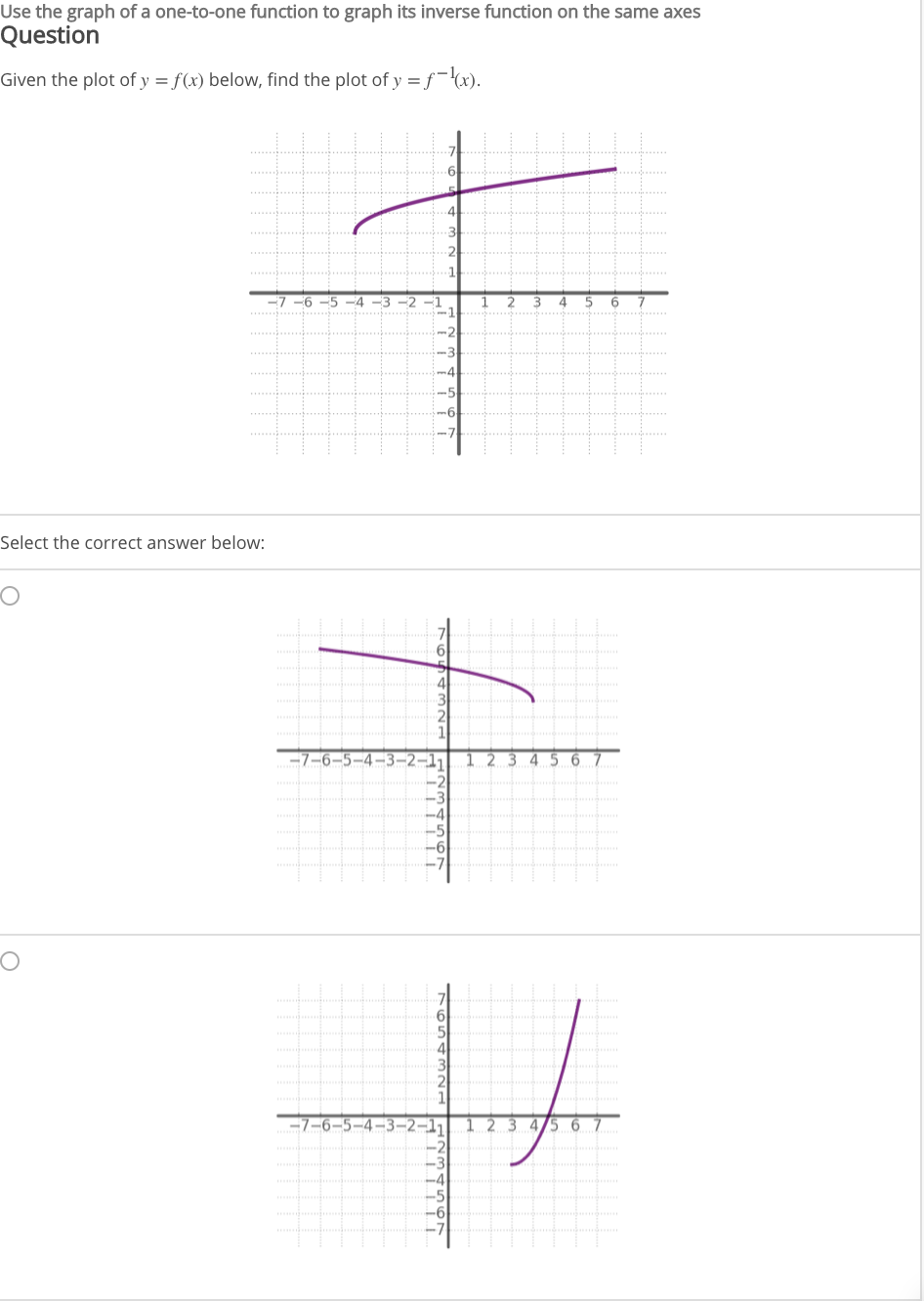



Given The Plot Of Y F X Below Find The Plot Of Chegg Com
Get the free "Surface plot of f(x, y)" widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle Find more Engineering widgets in WolframAlphaRemember f(x) reflects any part of the original f(x) graph that was below the xaxis in the xaxis In this video I show you how to draw graphs of the form y=f(x) using the modulus function and give you three graphs to try Examples in the video Sketch the following yThat is, the rule for this transformation is –f (x) To see how this works, take a look at the graph of h(x) = x 2 2x – 3



Graph Transformations Worksheets Questions And Revision Mme



Geogebra Tutorial Functions
Functions & Graphing Calculator \square!Mathf(x)=x/math Function is giving the absolute value of mathx/math whether mathx/math is positive or negative See the y axis of graph which is mathf(x)/math against mathx/math, as x axis It shows y axis values or mathf(x · To sketch y = 1/f(x) This should be obvious but note that the sign of f(x) is the same sign as 1/f(x) So for a given domain, no part of the graph of f(x) should suddenly switch to the other side of the xaxis when graphing 1/f(x)




2 Graph Of The Function Y D F X L For The Column Fixed At The Bottom Download Scientific Diagram



Understanding F X Function And How To Graph A Simple Function Math Algebra Graphing Functions F If 7 F If 4 Showme
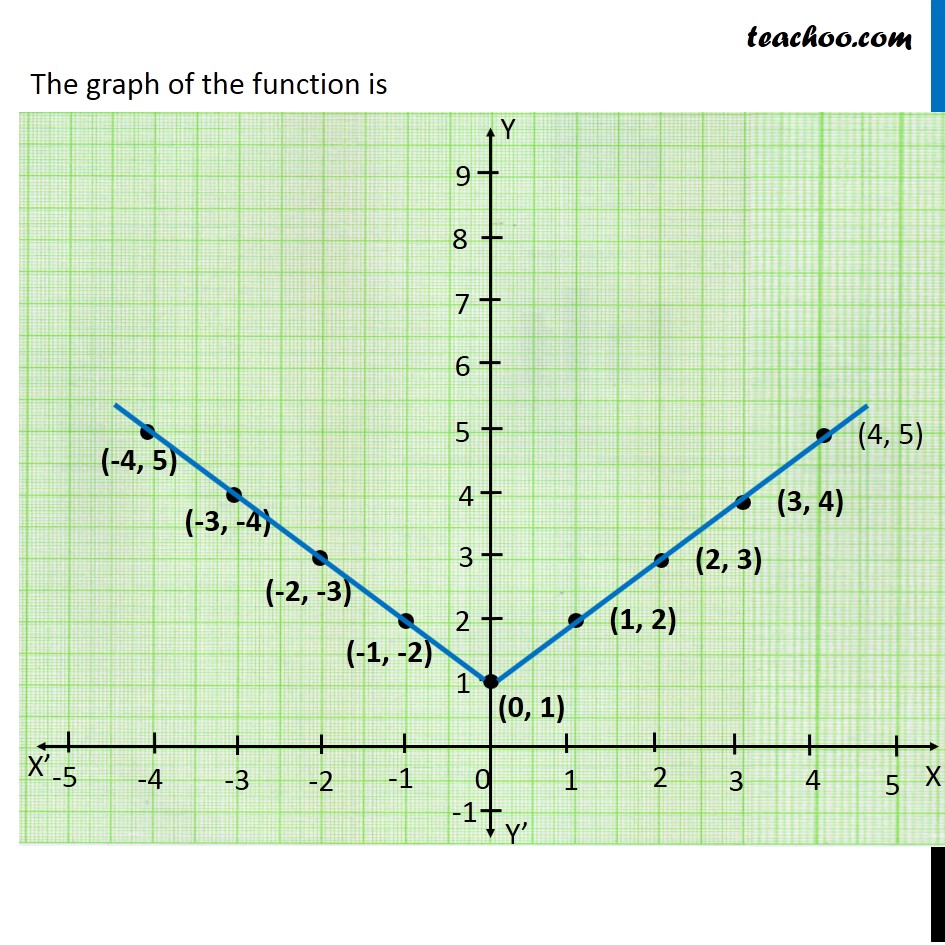
Graph Transformations A transformation is something that is done to a graph/function that causes it to change in some way This topic is about the effects that changing a function has on its graph There are two types of transformation translations and reflections, giving 4 key skills you must be familiar with Throughout this topic, we will use the notation f(x) to refer to a function andFirst graph f(x) Derivative Integral C Blue 1 Blue 2 Blue 3 Blue 4 Blue 5 Blue 6 Red 1 Red 2 Red 3 Red 4 Yellow 1 Yellow 2 Green 1 Green 2 Green 3 Green 4 Green 5 Green 6 Black Grey 1 Grey 2 Grey 3 Grey 4 White Orange Turquoise Violet 1 Violet 2 Violet 3 Violet 4 Violet 5 Violet 6 Violet 7 Purple Brown 1 Brown 2 Brown 3 Cyan Transp Self 1 Self 2 Self 3The graph of the function is the set of all points latex\left(x,y\right)/latex in the plane that satisfies the equation latexy=f\left(x\right)/latex If the function is defined for only a few input values, then the graph of the function is only a few points, where the x coordinate of each point is an input value and the y coordinate of each point is the corresponding output value
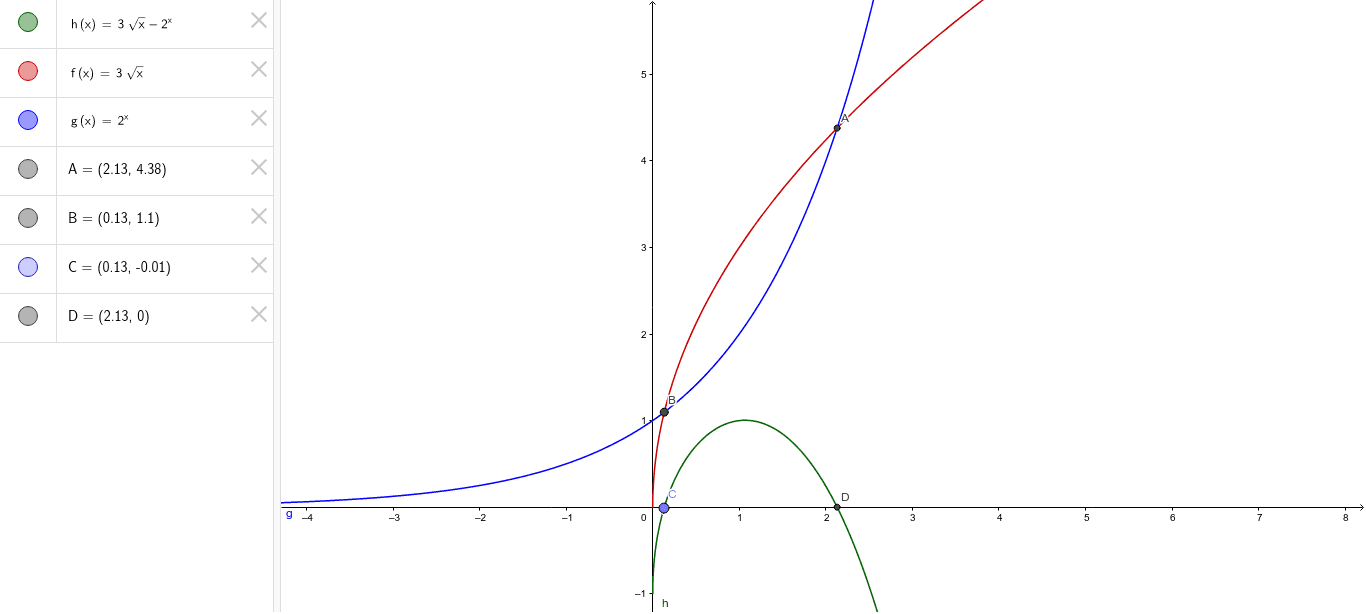



Graph Of F X G X F G X Geogebra
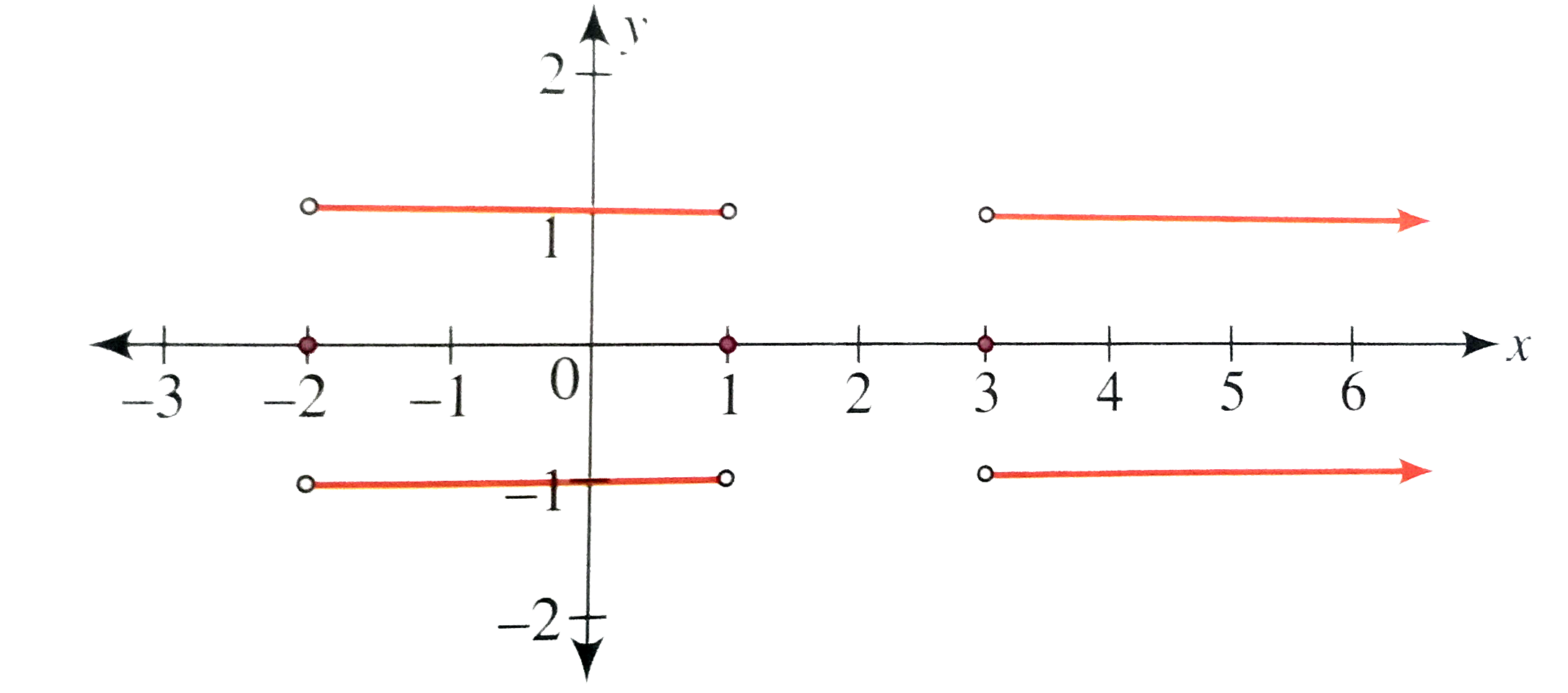



The Graph Of The Function Y F X Is As Shown In The Figure
For example, (3, 2) is on the graph of f (x), (3, 4) is on the graph of 2f (x), and (3, 1) is on the graph of f (x) Graphs of f (x), 2f (x), and f (x) To stretch or shrink the graph in the x direction, divide or multiply the input by a constant As in translating, when we change the input, the function changes to compensateAlgebra Graph f (x)=x f (x) = x f ( x) = x Find the absolute value vertex In this case, the vertex for y = x y = x is (0,0) ( 0, 0) Tap for more steps To find the x x coordinate of the vertex, set the inside of the absolute value x x equal to 0 0 In this case, x = 0 x = 0 x = 0 x = 0Graph of z = f(x,y) New Resources Untitled;
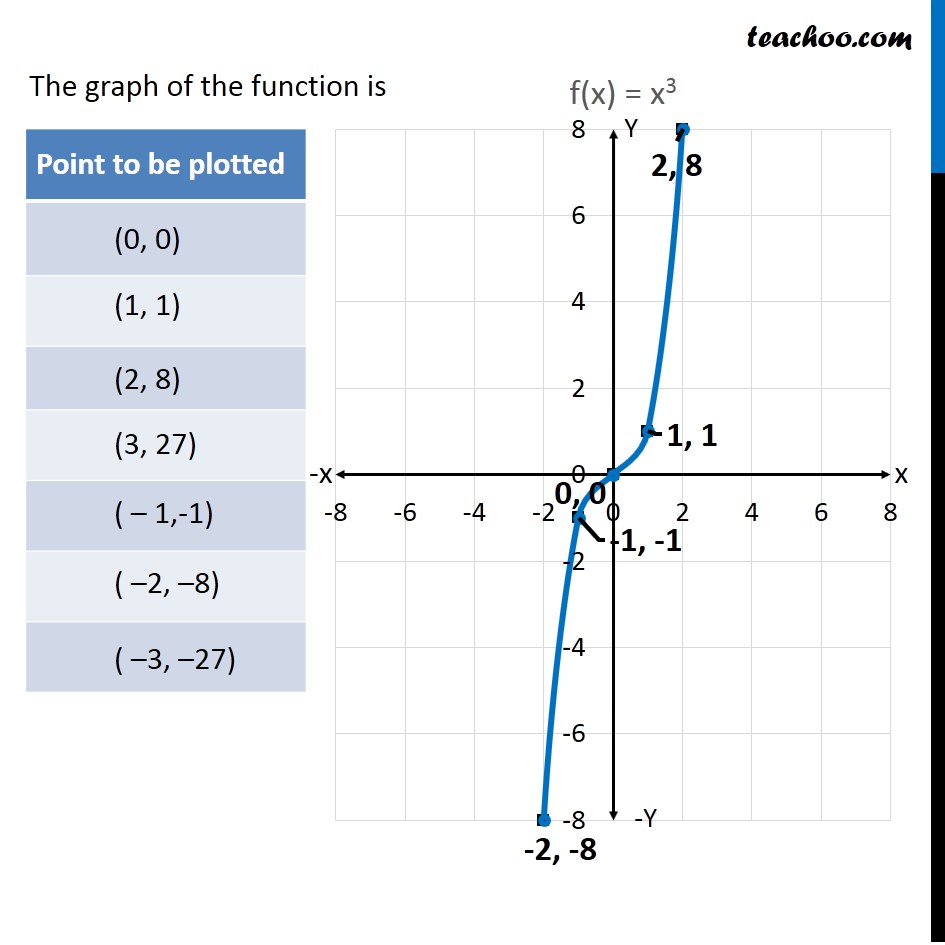



Example 14 Draw Graph Of F X X 3 Chapter 2 Class 11



How To Graph F X From F X
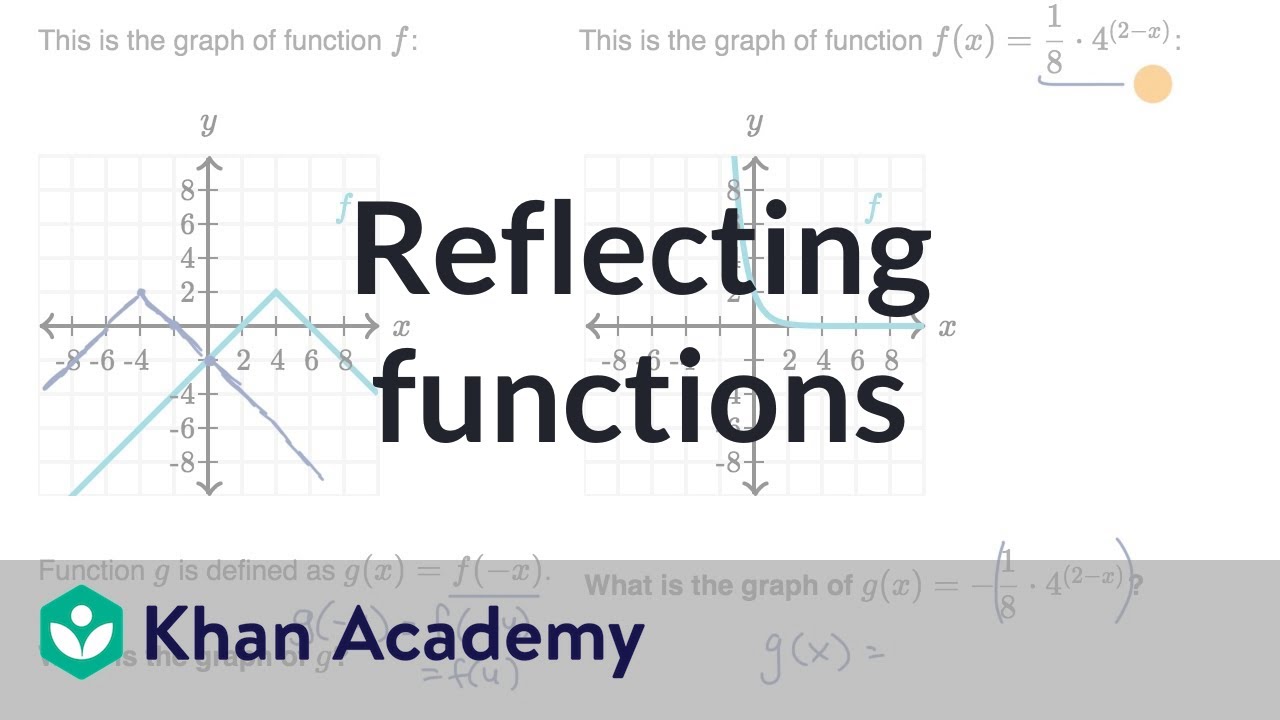
· Reflection y=f (x) will indicate that the graph has reflected about the xaxis y=f (x) will indicate that the graph has reflected about the yaxis y=f (x) will indicate that the graph has reflected about the origin14 The graph of f ( − x) is the mirror image of the graph of f ( x) with respect to the vertical axis The graph of − f ( x) is the mirror image of the graph of f ( x) with respect to the horizontal axis A function is called even if f ( x) = f ( − x) for all x (For example, cos ( x) )If y = f(x), the graph of y = f(x c) will be the graph of y = f(x) shifted c units to the left If y = f(x), the graph of y = f(x – c) will be the graph of y = f(x) shifted c units to the right If y = f(x), the graph of y = af(x) is ), parallel to the xaxis



Linear Functions And Their Graphs




How Do You Graph The Exponential Function F X 4 X 2 Socratic
· Graph and Formula of f(x) g(x) New Resources Pythagoras' Theorem Area dissection 2;As the graph of f'(x) is a straight line with equation y = c (degree = I), will be a quadratic function (degree = 2) The turning point at x = O {x x < O} gradient is negative (as the graph is Iccated telow the xaxis) and in magnitude {x x O} gradient is pcsitive and is increasing in magnitudeGraph of y = f (x) k Adding or subtracting a constant \ (k\) to a function has the effect of shifting the graph up or down vertically by \ (k\) units Graph of y = f (x) This has the effect of



Example 22 Function F Is Defined By F X 1 X 1 X 1




Graph F X To F X A Science
· To find the value of f (3) we need to follow the below steps Step 1 First plot the graph of f (x) Step 2 We need to find f (3) or the function value at x = 3 therefore, in the graph locate the point (3,0) Step 3 Draw a line parallel to Yaxis passing through the point (3,0)The graph is y=f(x) stretched along the yaxis by a the factor of k What is the connection between the graphs of y = f(x) and y = f(kx)?The graph of f, shifted 3 units to the left



Given The Graph Of F X Draw The Graph Each One Of The Followin
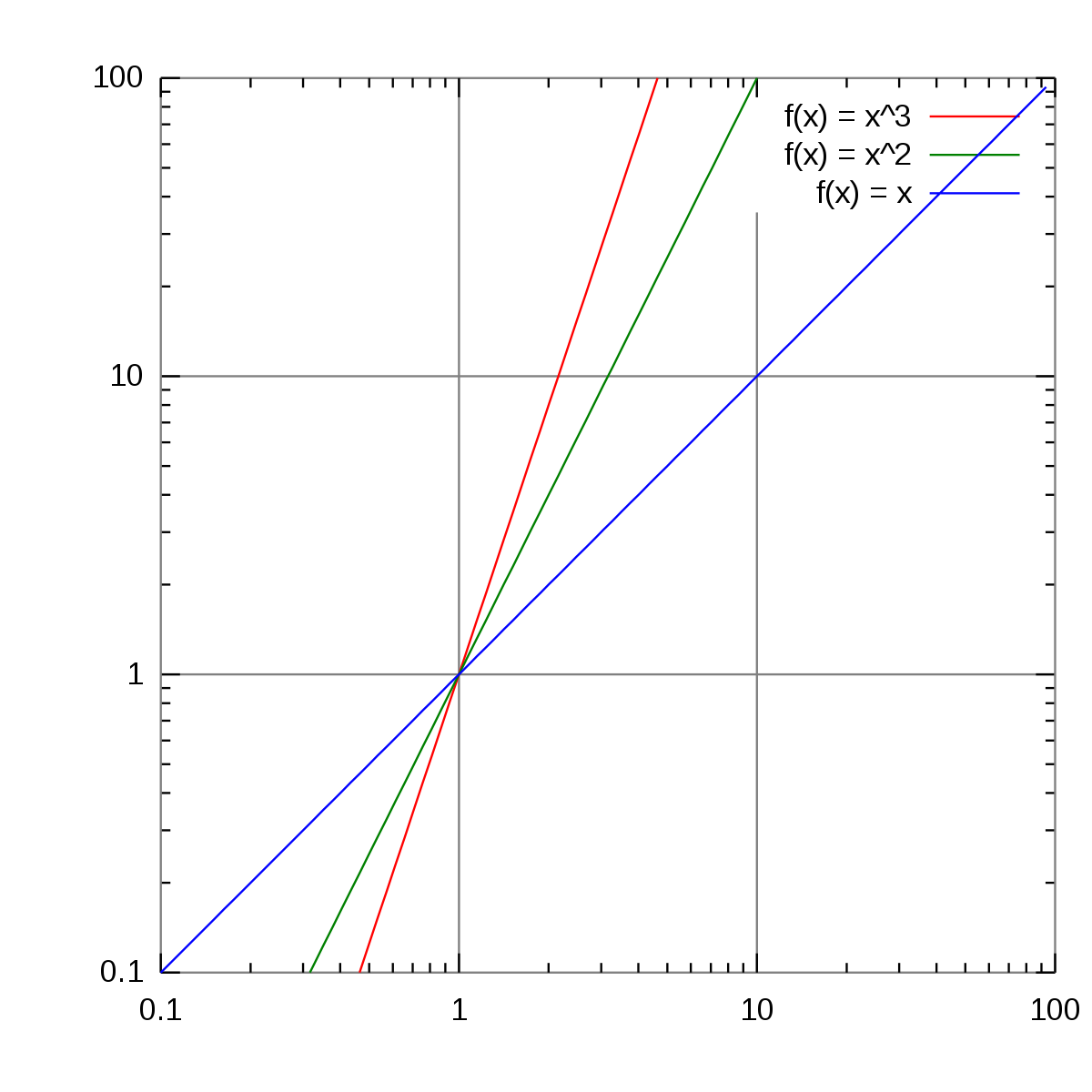



Log Log Plot Wikipedia
Graph {eq}f(x) = 3^x 1 {/eq} Graph The graph of an exponential function shows how rapidly the function increases as its input value increases Even for small changes in the input, the functionGet stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!FX Graph is amazingly versatile It can graph Cartesians, polars, parametrics, slope fields, volumes of rotation, 3D graphs, vector diagrams, linear programming questions and much, much more Most of the time you just type what you want and FX Graph will sort out how to graph it




4 F S And Corresponding U X Graphs Are As Shown In Figure Three Points A B
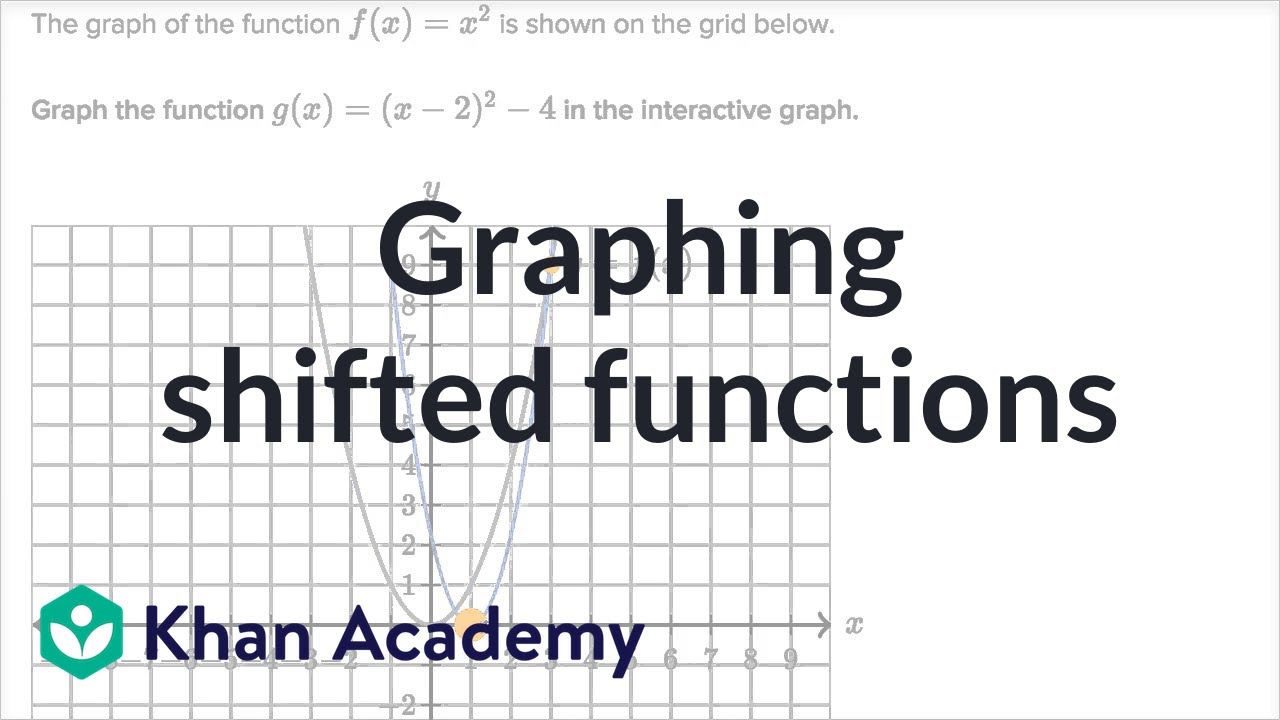



Graphing Shifted Functions Video Khan Academy
For the interval the depth of the graph will increase slightly, because as the values of x get greater the negative aspect of y= f (x) gets greater Basically x=1 graph doesn`t alter 0Relationships between graphs of f, f', f" Graph of f ()x f ()xyy== Decreasing Increasing Horizontal tangent line ('flat' spot) possible max or min, but could be terrace point Vertical tangent line Cusp ''() dy fx y dx == Negative ≤ 0 Positive ≥ 0 = 0 DNE, (but f (x) exists) Determine from other info DNE, (but f (x) exists) DetermineFrom the graph of f ' (x), draw a graph of f(x) f ' is negative, then zero, then positive This means f will be decreasing for a bit, and will then turn around and increase We just don't know exactly where the graph of f(x) will be in relation to the yaxisWe can figure out the general shape of f, but f we could take the graph of f that we just made and shift it up or down along the y
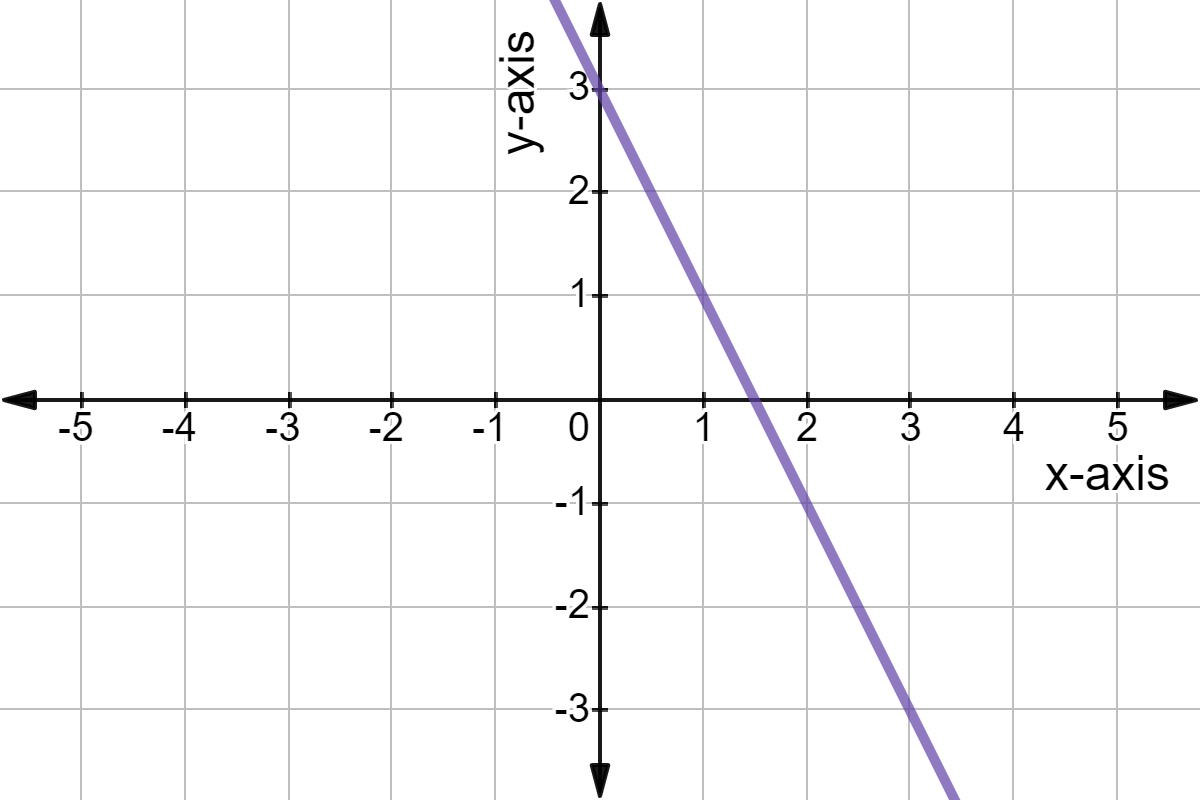



Graphing Linear Functions Expii




How To Graph F X And G X




2 4 Solving Equations And Inequalities By Graphing Mathematics Libretexts
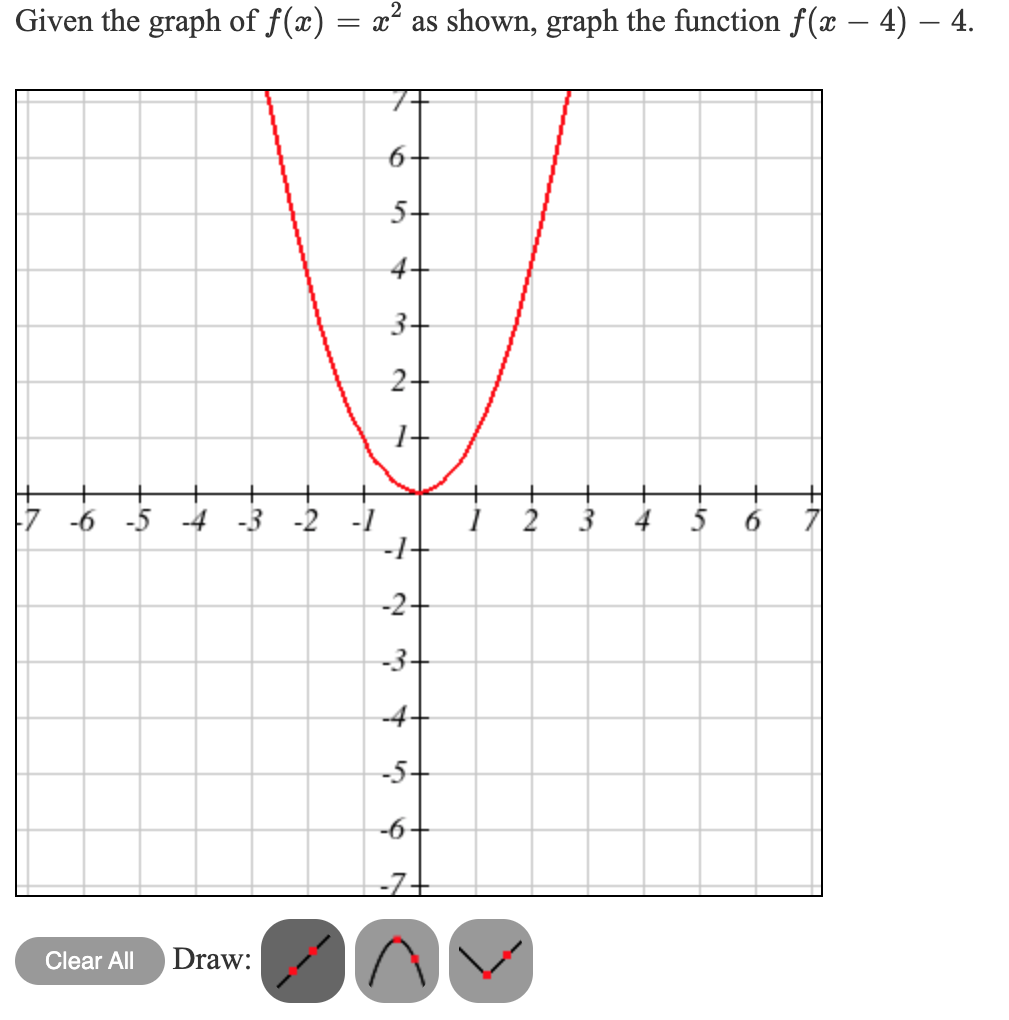



Solved Given The Graph Of F X X2 As Shown Graph The F Chegg Com



Answer In Calculus For Desmond
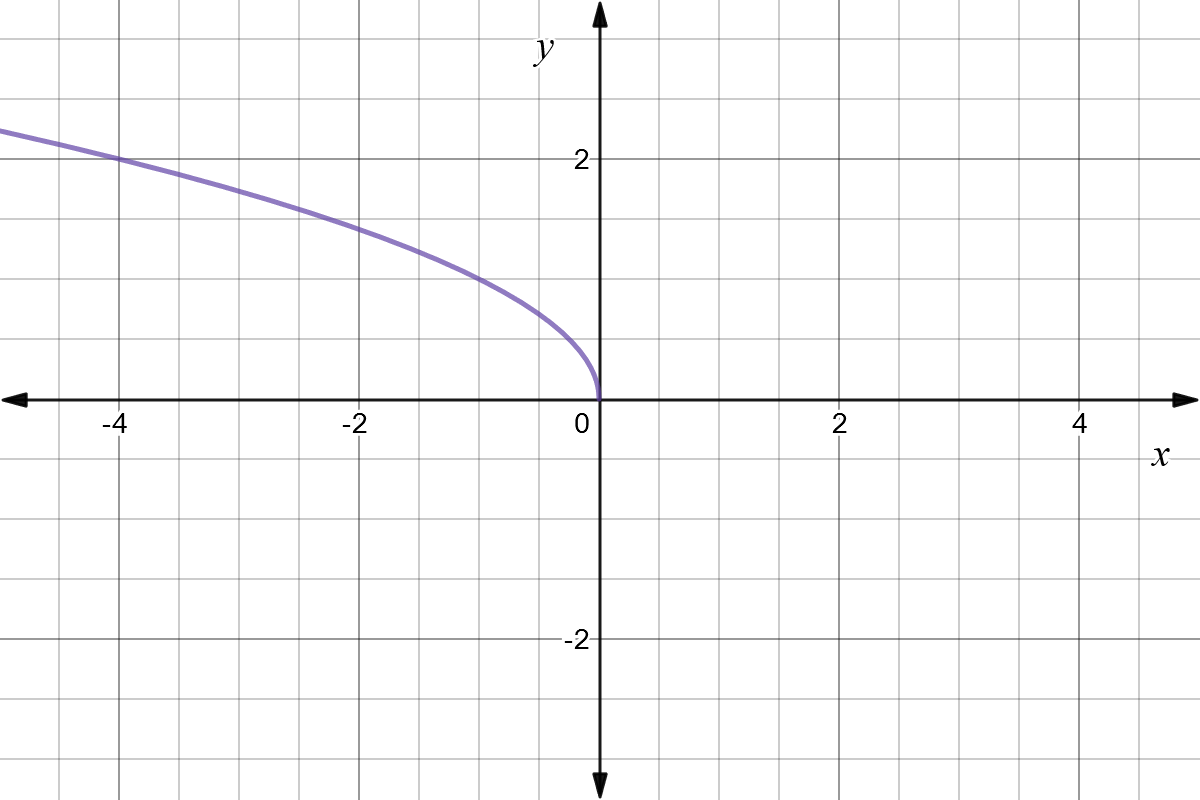



Reflect Function About Y Axis F X Expii
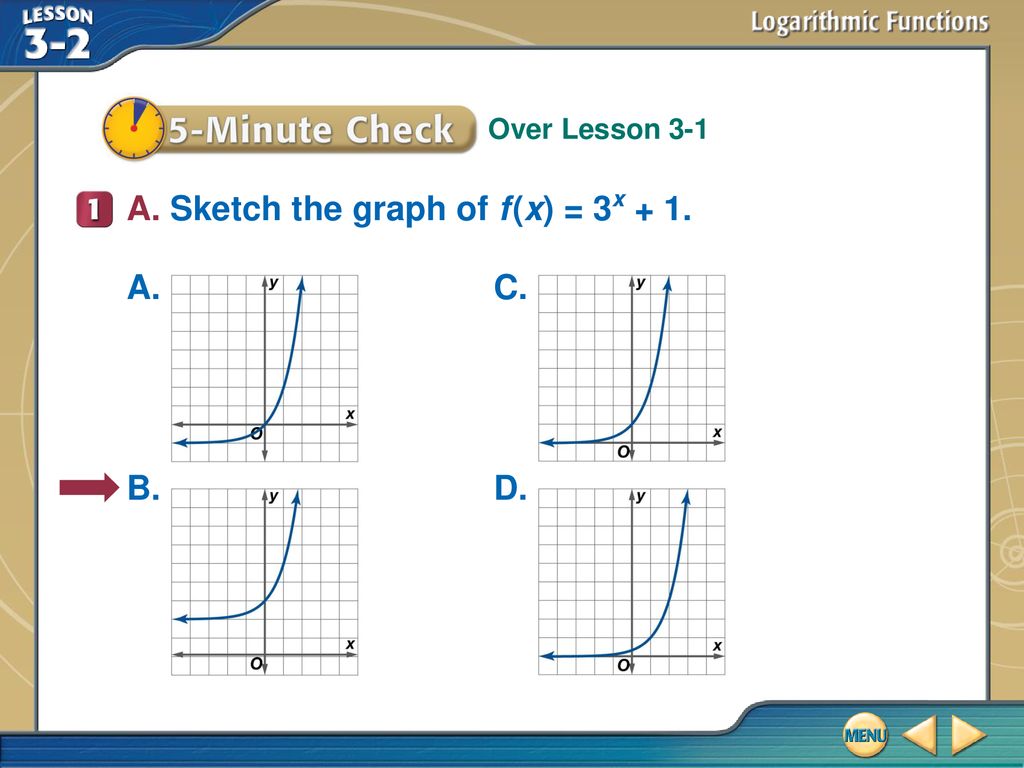



A Sketch The Graph Of F X 3x Ppt Download




Use The Graph Of F X X To Write An Equation For The Function Repesented By The Graph Brainly Com
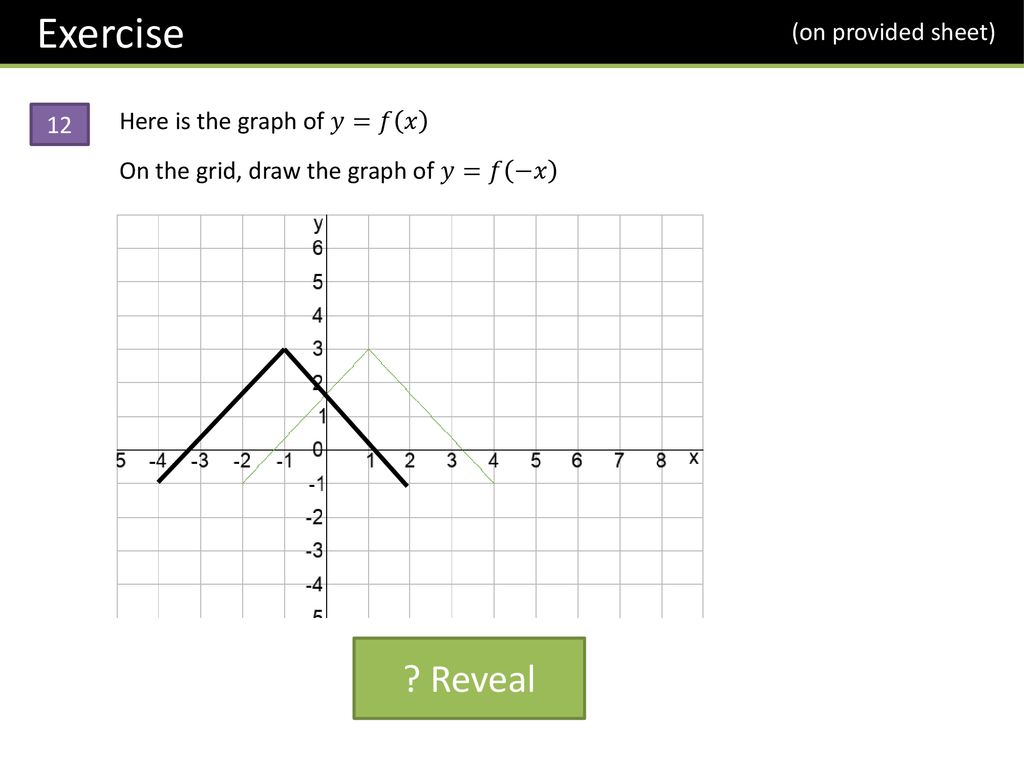



Gcse Graph Transformations Ppt Download
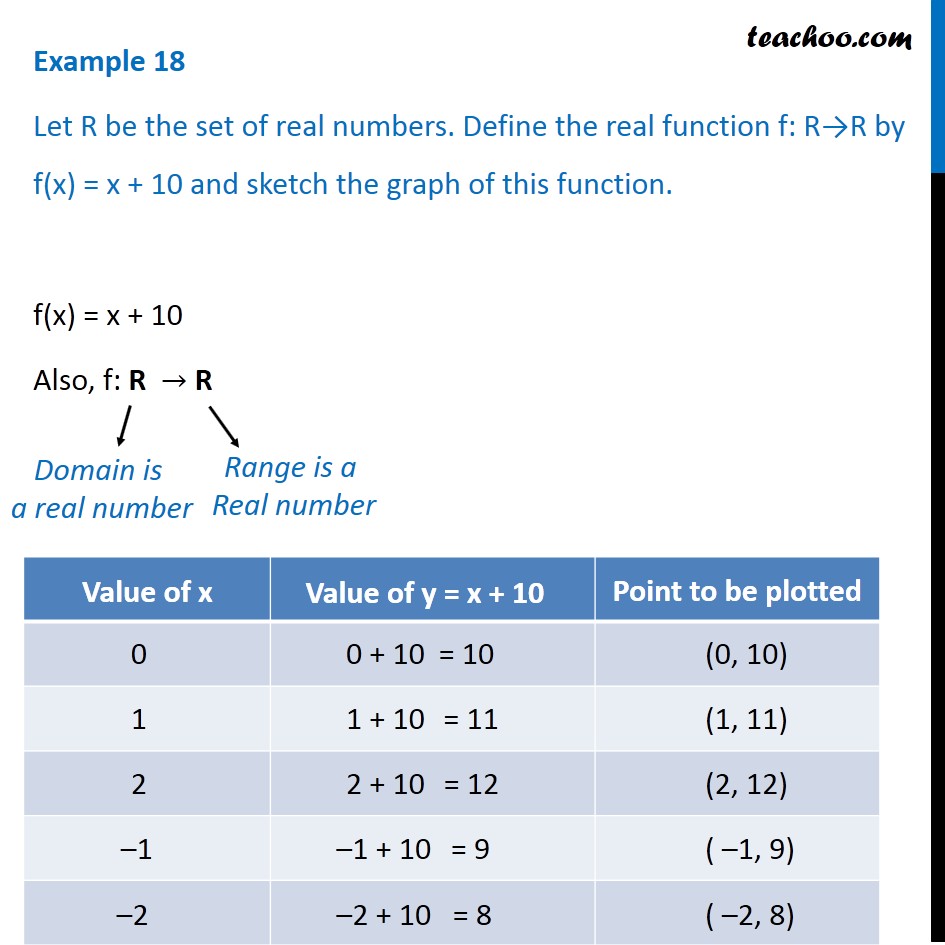



Example 18 Define F X X 10 And Sketch Graph Chapter 2
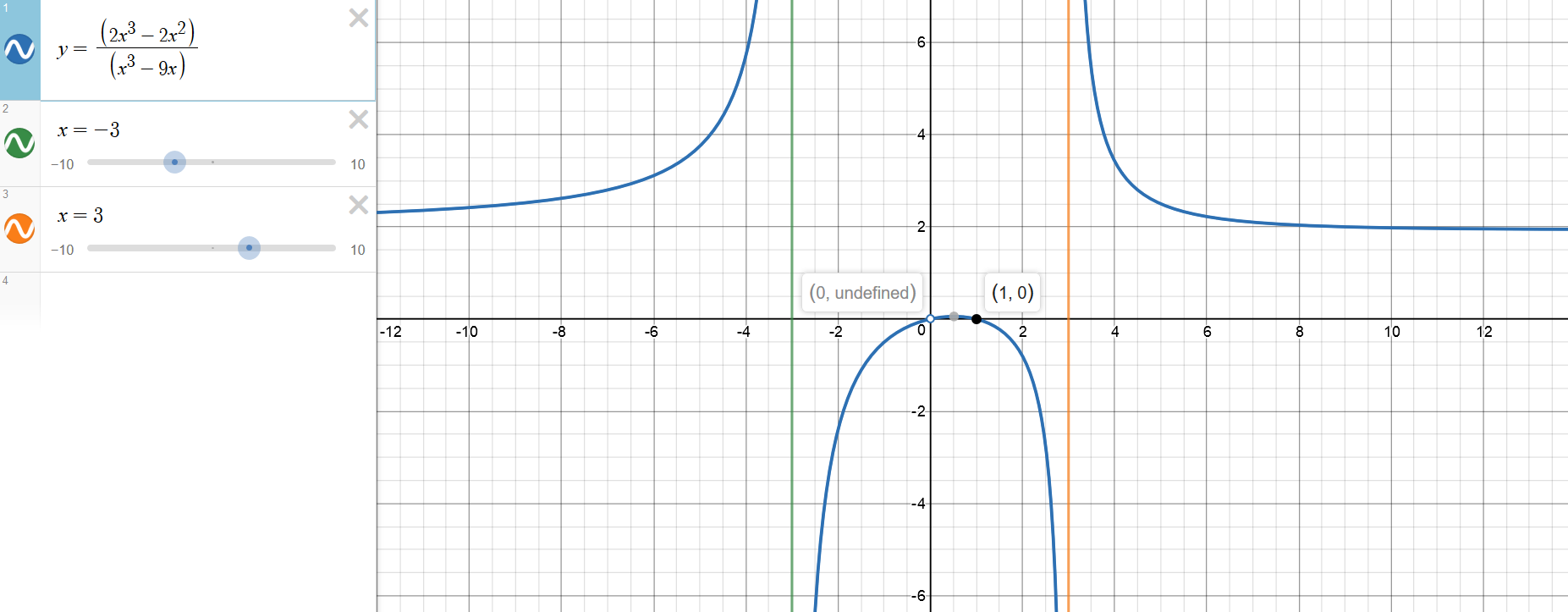



How Do You Graph F X 2x 3 2x 2 X 3 9x Using Holes Vertical And Horizontal Asymptotes X And Y Intercepts Socratic



2d Function Graphing In Fx Draw Fx Graph Youtube
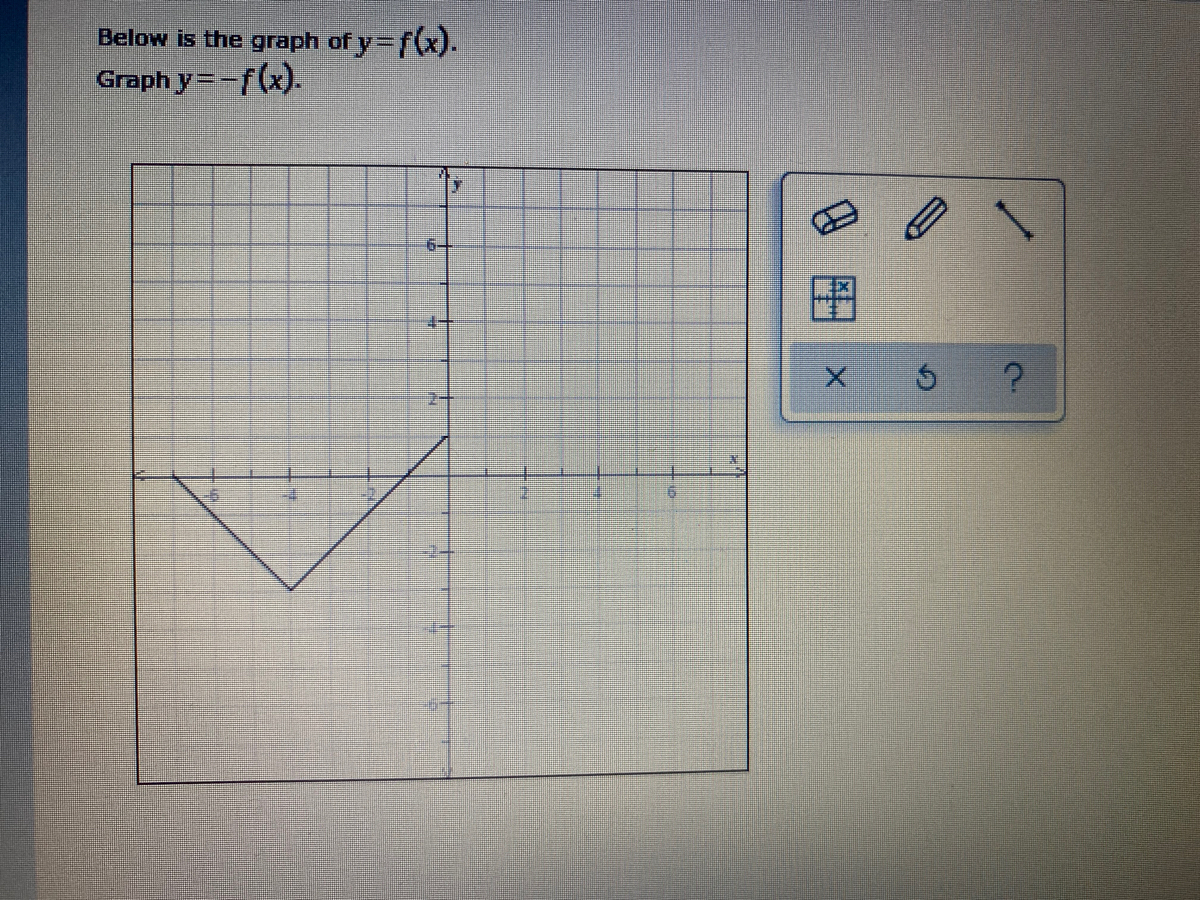



Answered Below Is The Graph Of Y F X Graph Bartleby
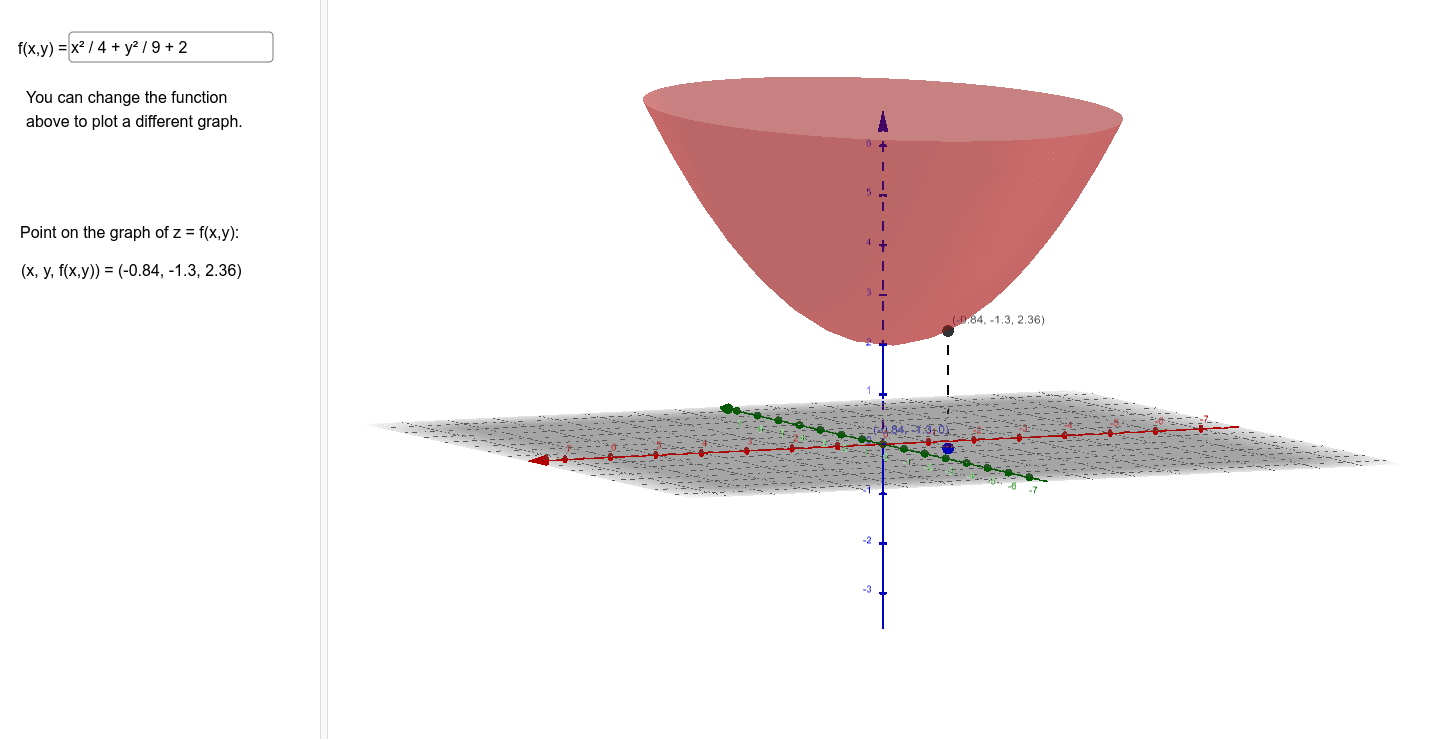



Graph Of Z F X Y Geogebra



Reading Inverse Values From A Graph Video Khan Academy
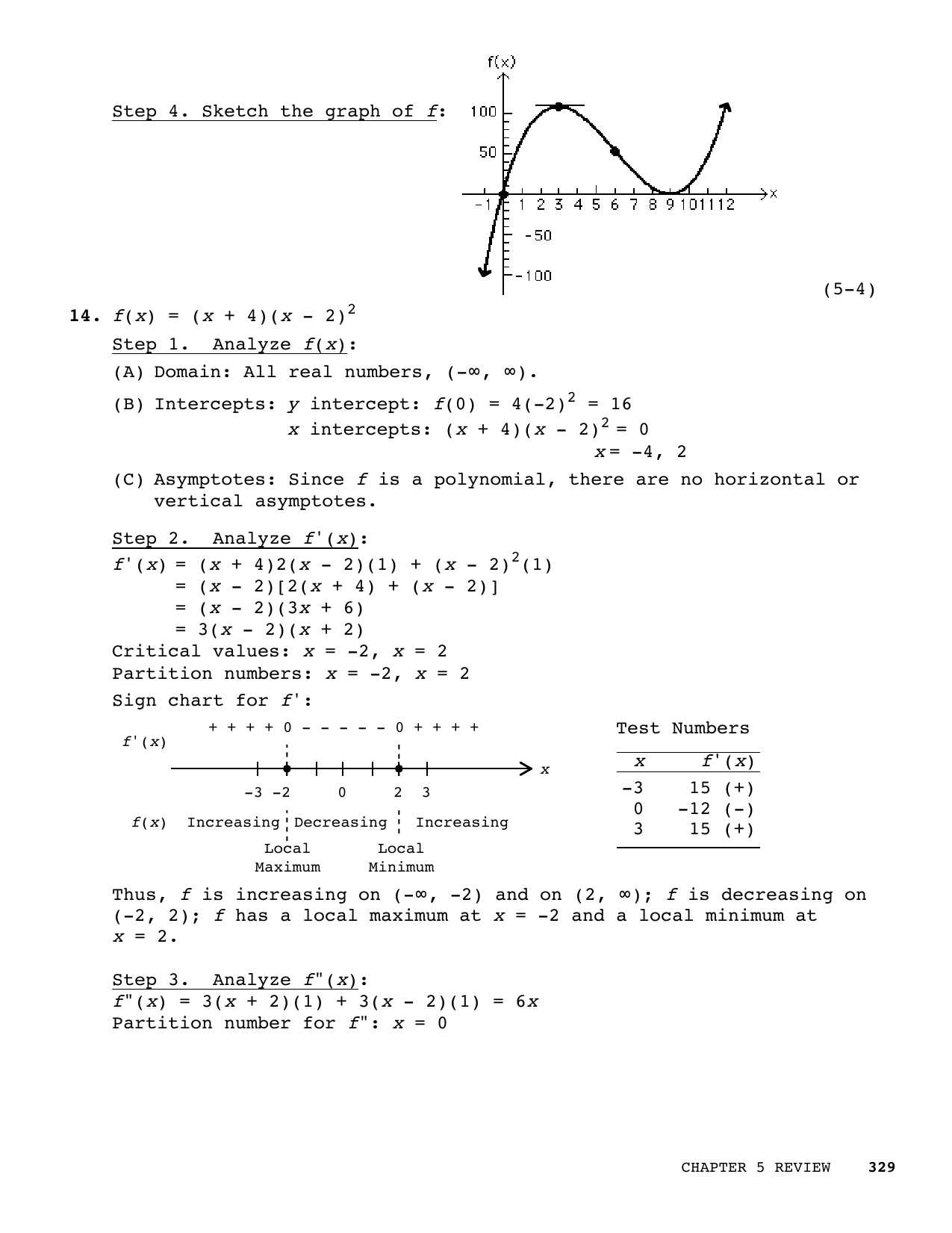



Step 4 Sketch The Graph Of F 5 4 14 F X X 4 X Manualzz




A Table Of The Functions F X And F X And A Graph Chegg Com
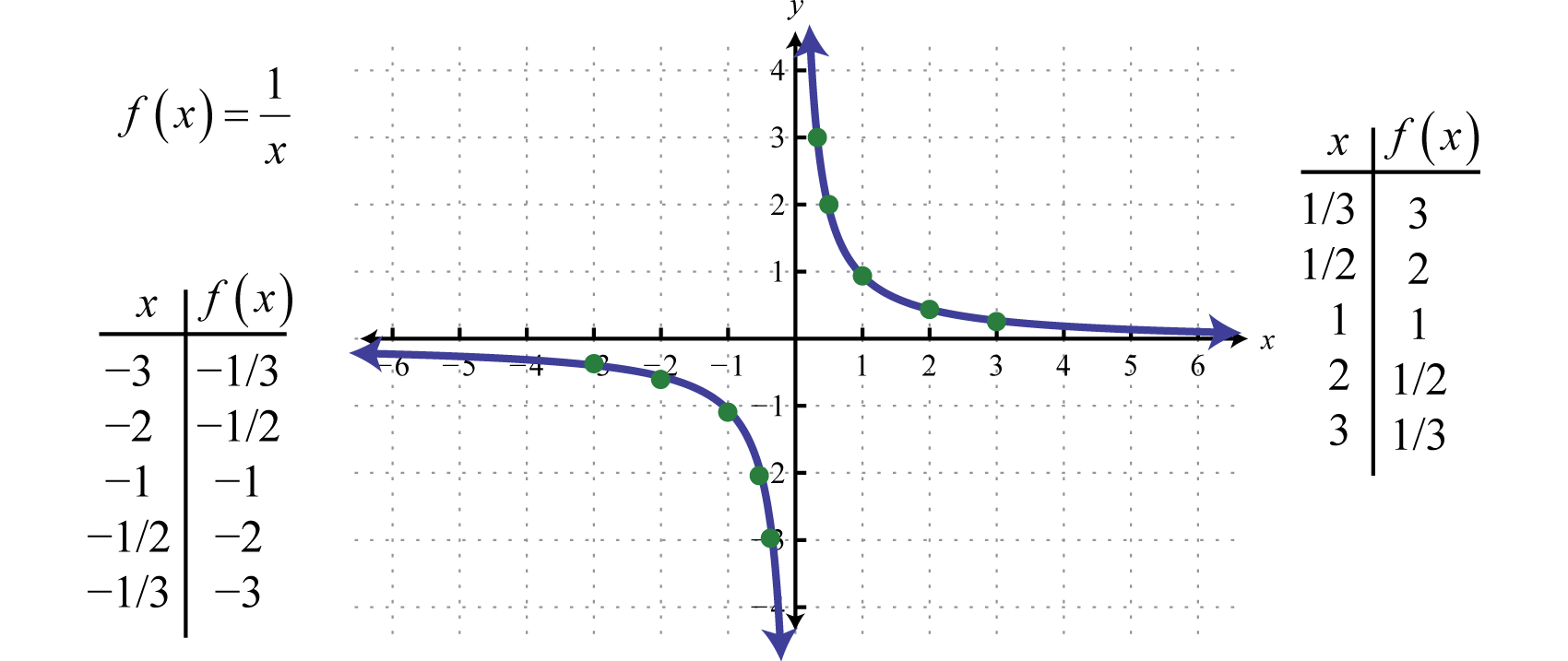



Graphing The Basic Functions




Given The Function Fx 3 2 X Graph The Function F Gauthmath




Fx Graph By Efofex Software Windows Apps Appagg
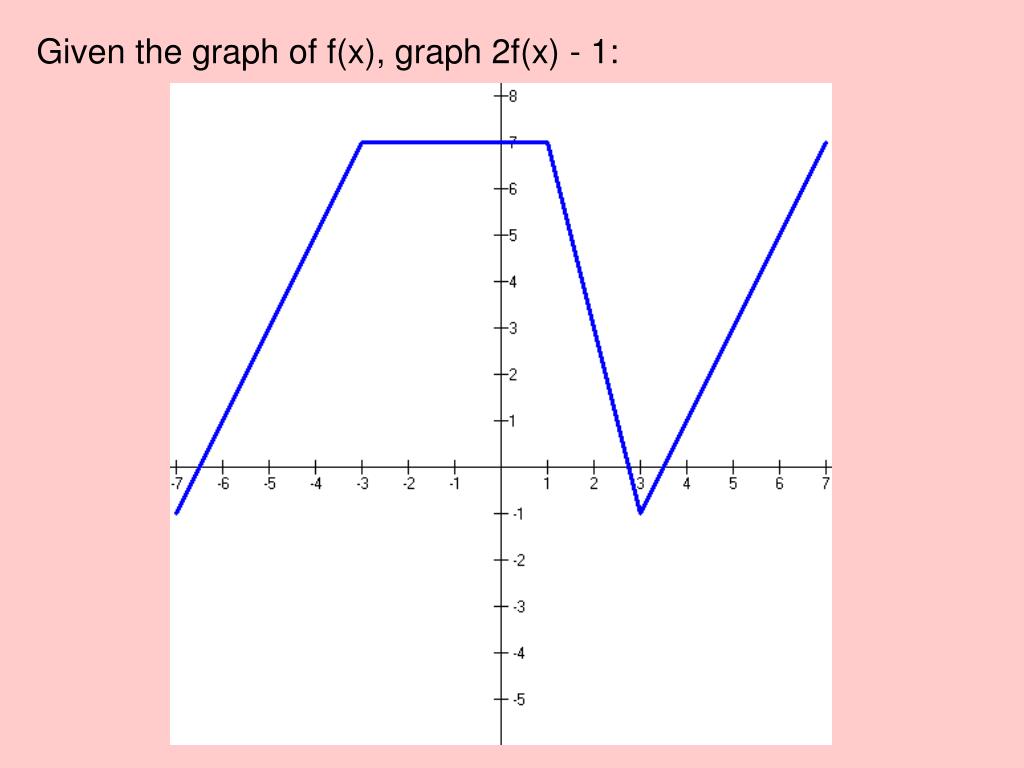



Ppt Section 1 4 Transformations And Operations On Functions Powerpoint Presentation Id




2 4 Solving Equations And Inequalities By Graphing Mathematics Libretexts
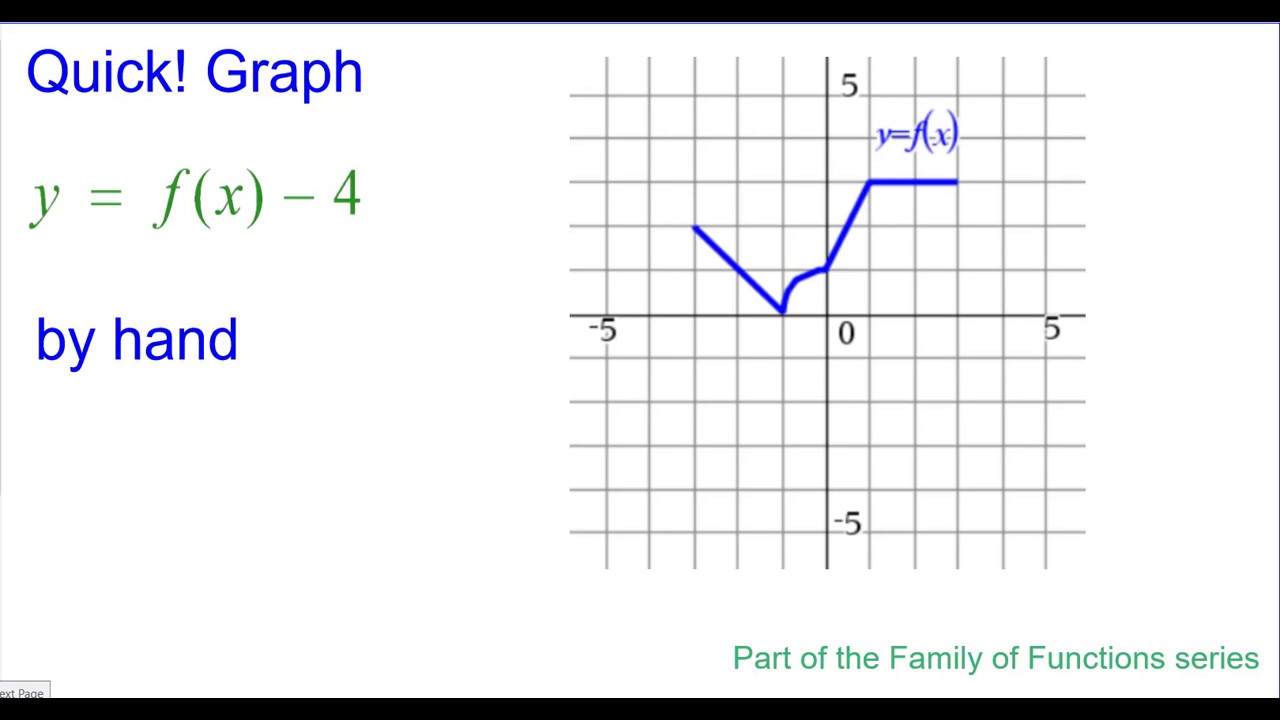



Quick Graph Y F X 4 Youtube




How To Determine The Graph Of F X By The F X E F X Graphics Askmath
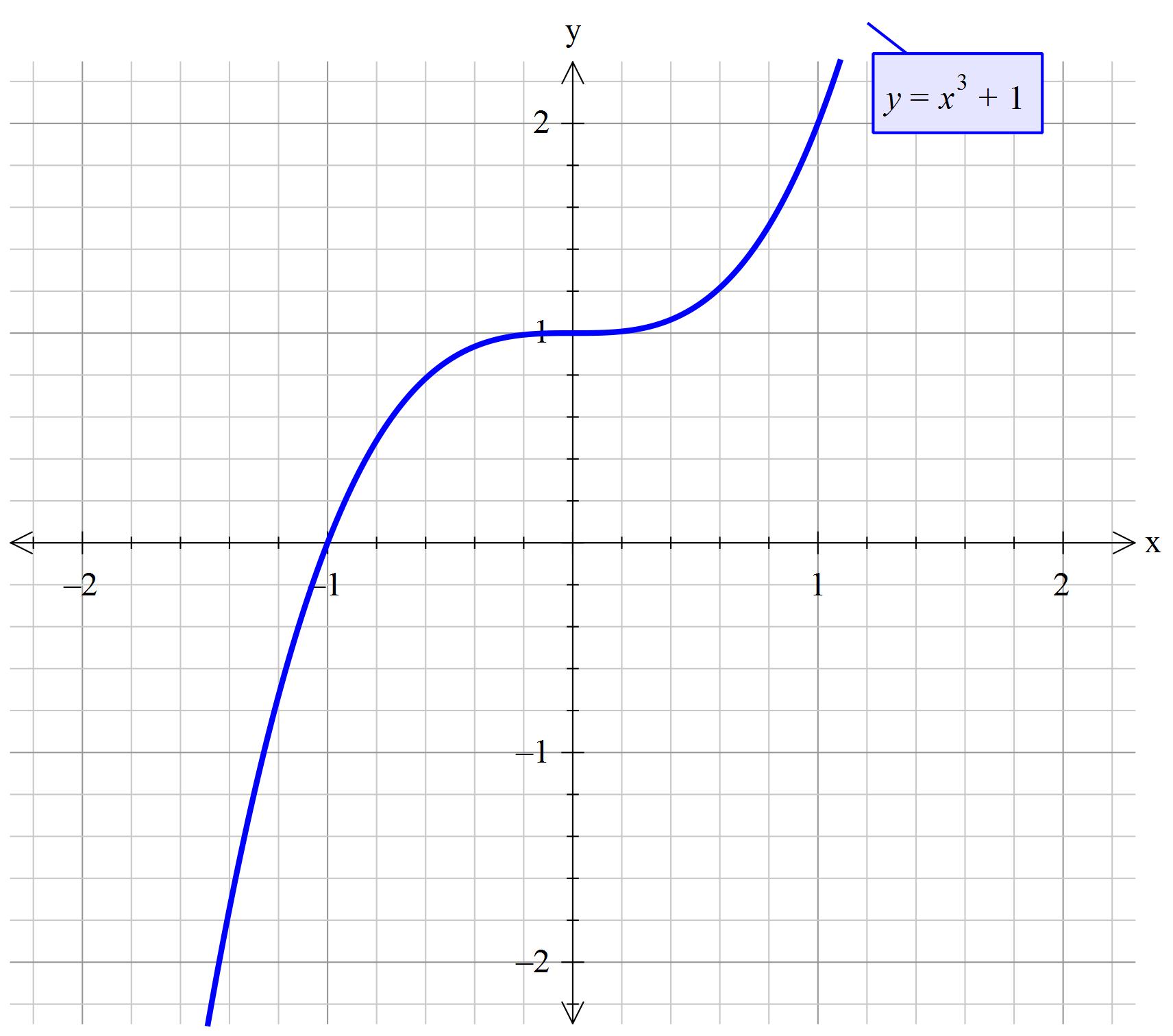



How Do You Sketch The Graph F X X 3 1 Socratic
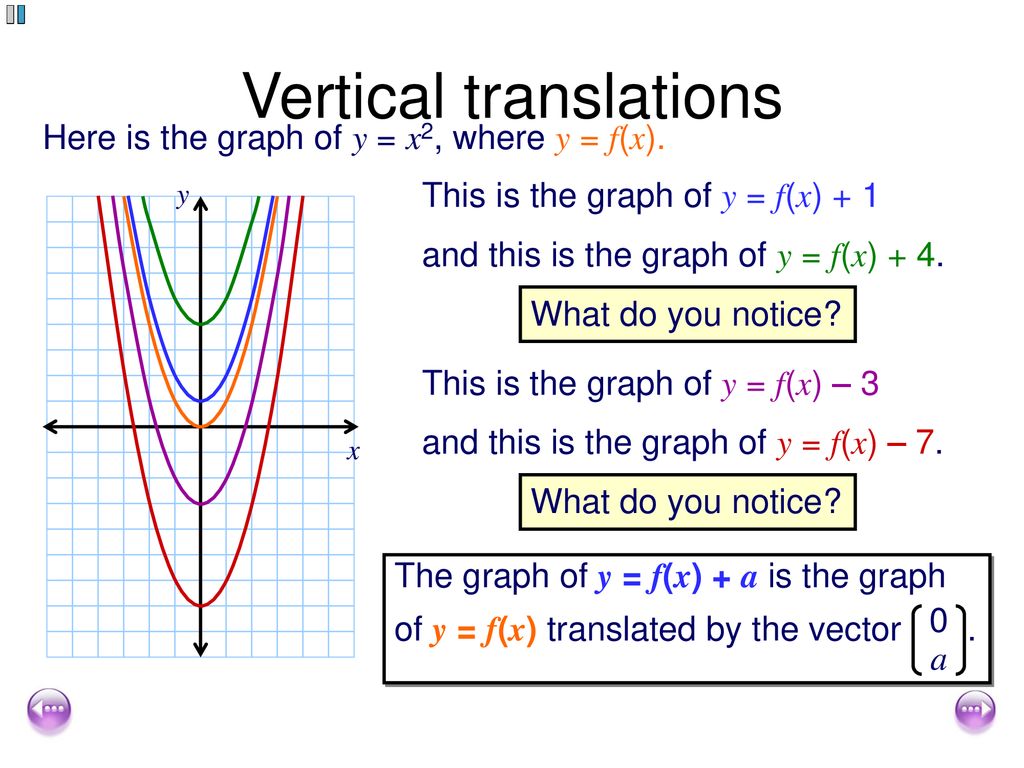



Transforming Graphs Of Functions Ppt Download
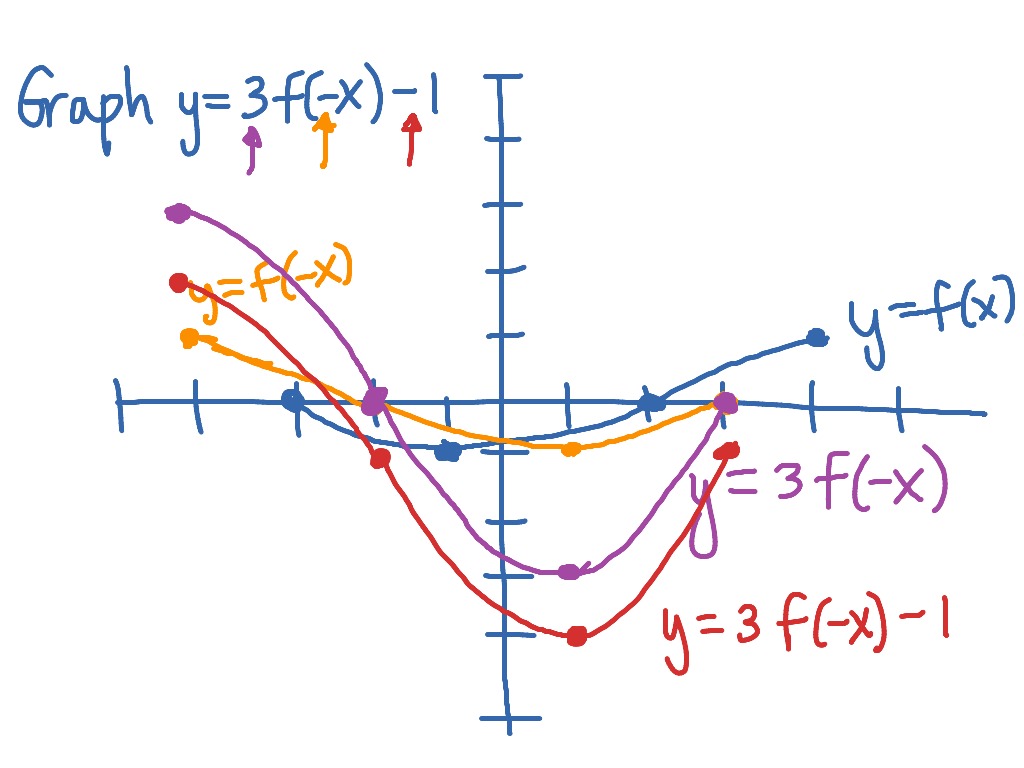



Graphing Y 3f X 1 From The Graph Of Y F X Math Showme



Solved The Graph Of F X Is Shown Below Suppose G X Has The Same Shape As The Graph Of F X But Is Shifted Down 3 Units And Left 2 Units Part O



Graphs Of Related Functions Ppt Download



Question Video Sketching Graphs Of Rational Functions Nagwa



Reflecting Functions Examples Video Khan Academy




Which Is The Graph Of F X Square Root Of X Brainly Com
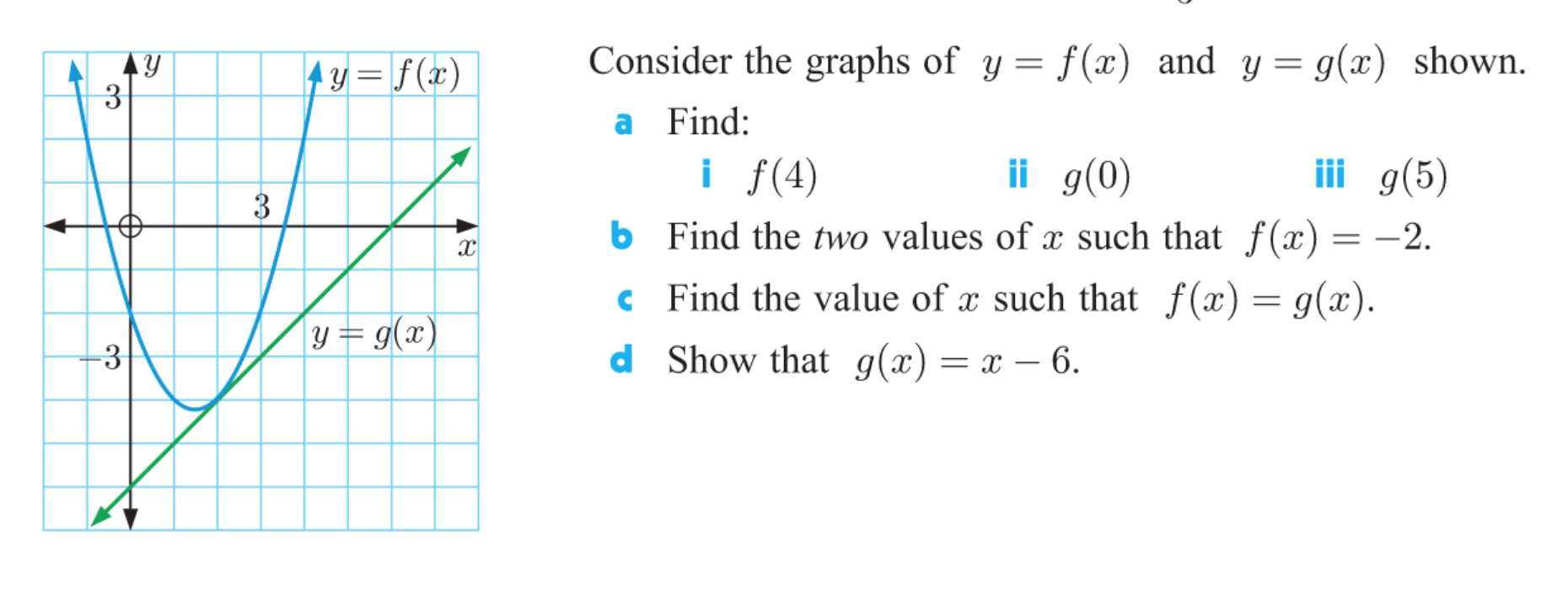



Answered Consider The Graphs Of Y F X And Y Bartleby
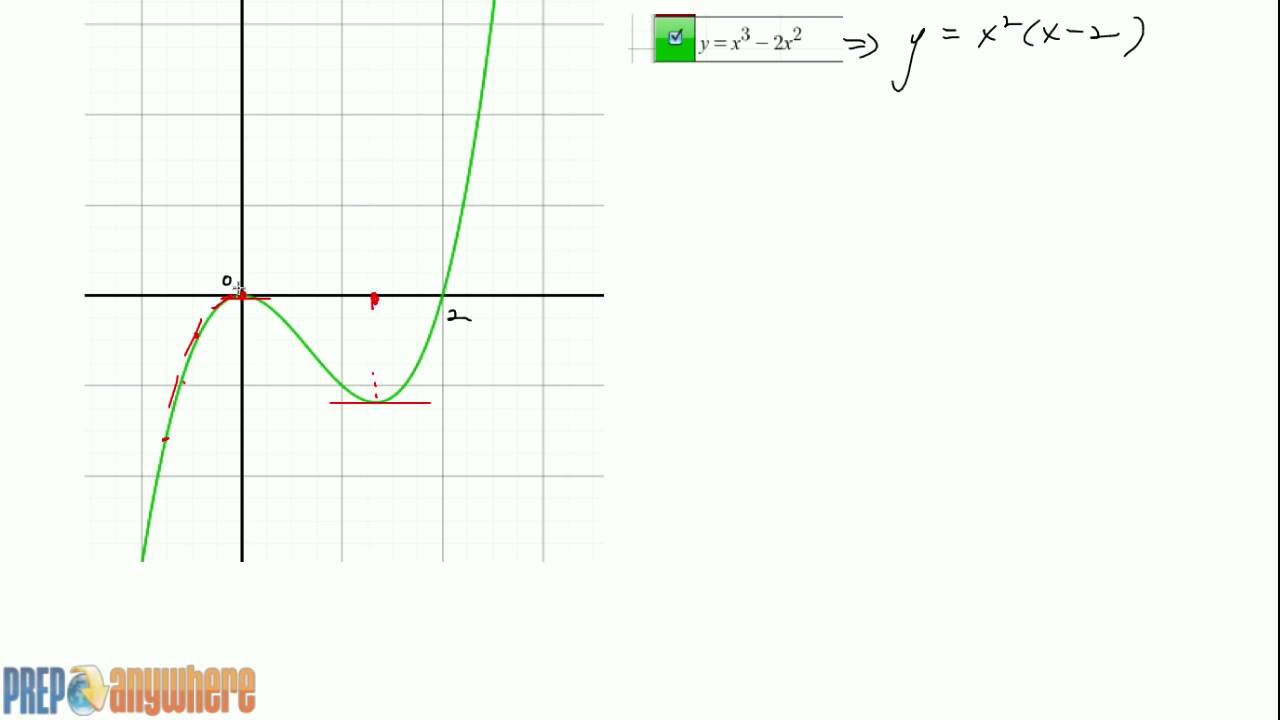



Sketching F X From Given F X Graph Youtube
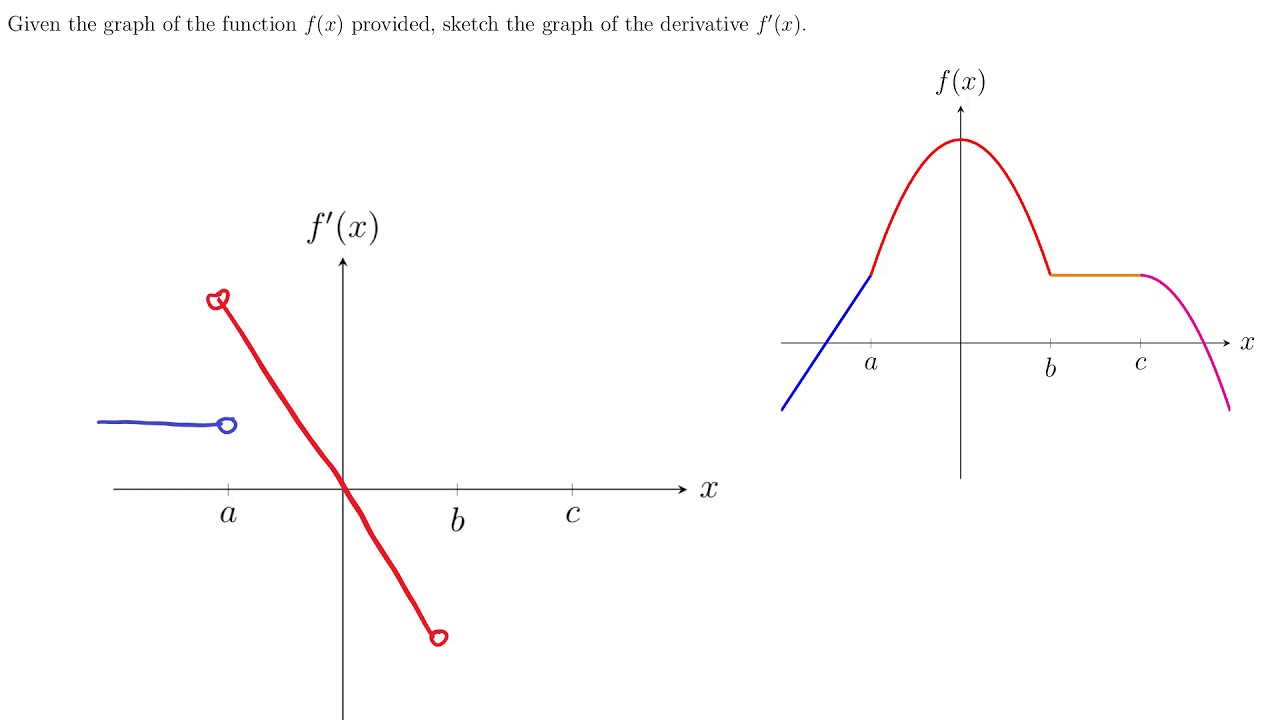



The Derivative Function




Efofex Software
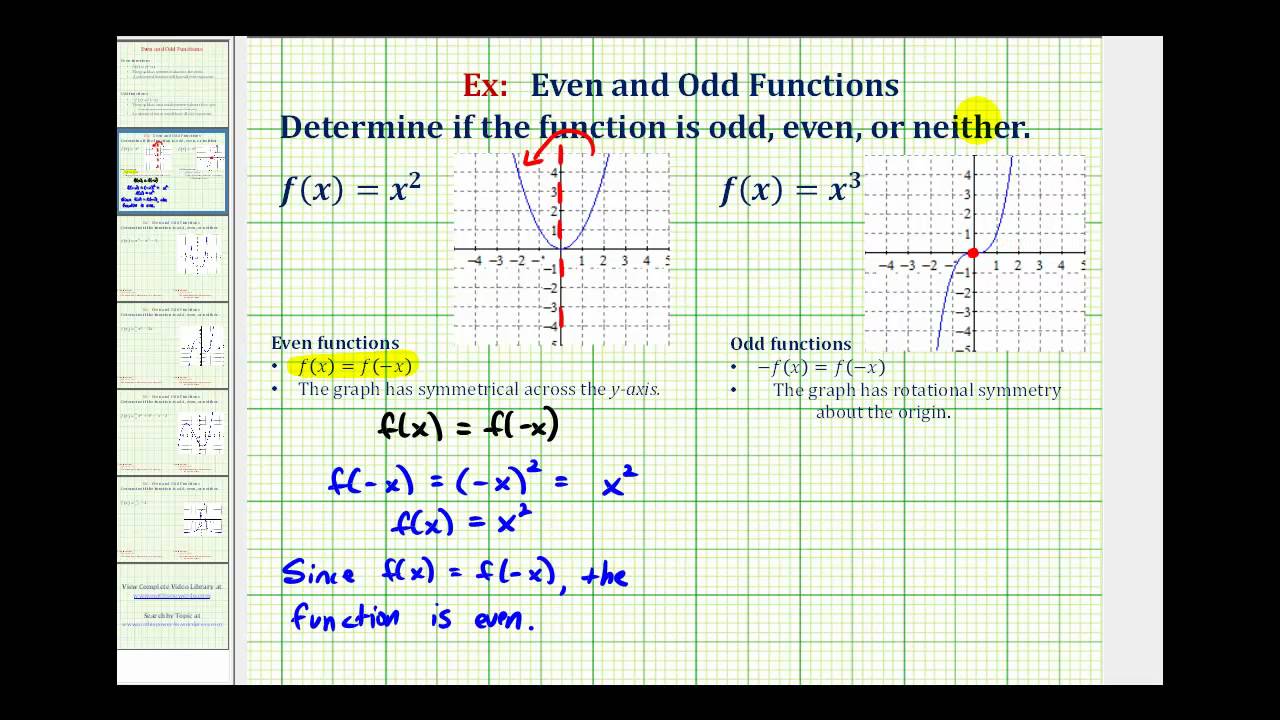



Transformations Of Functions College Algebra




Transformations Of Graphs Edexcel Igcse Maths Revision Notes




Sketch The Graph Of The Following Functions F X X X




Consider The Function F X X 3 Draw The Graph Of F X Maths Relations And Functions Meritnation Com
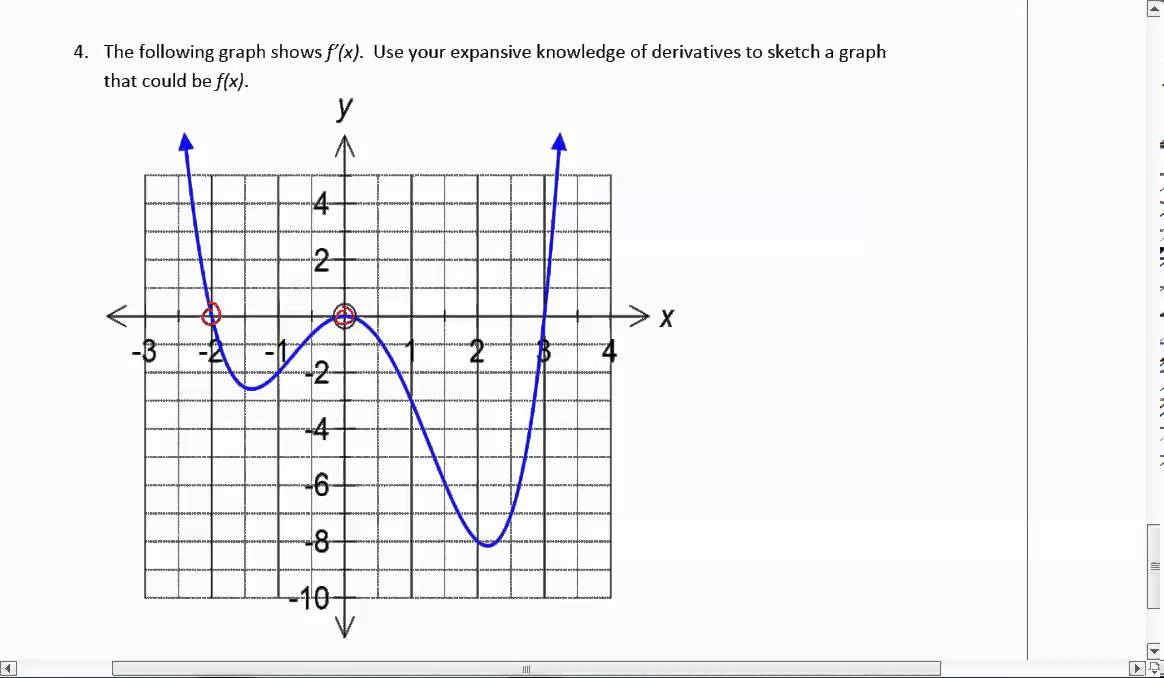



Creating Derivative Graph From The Graph Of F X Youtube




Finding Values Of Derivative Given F Graph Mathematics Stack Exchange




How Do Plot F X E X 4x 3 1 In Python With Matplotlib Stack Overflow
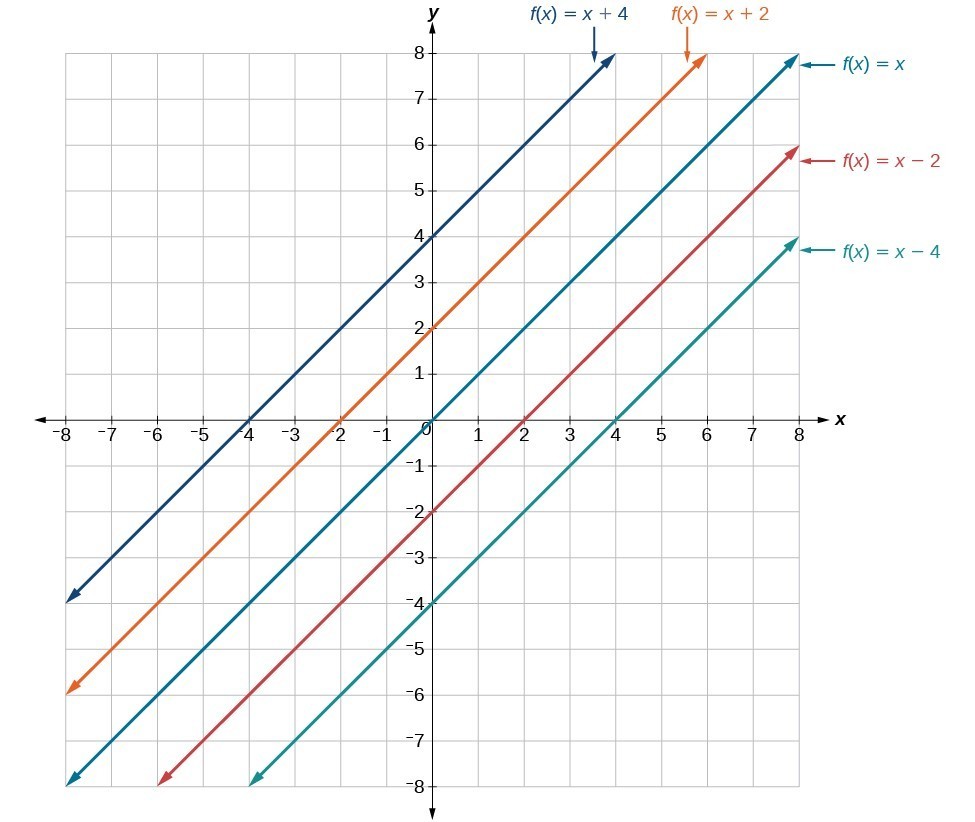



Graphing Linear Functions College Algebra
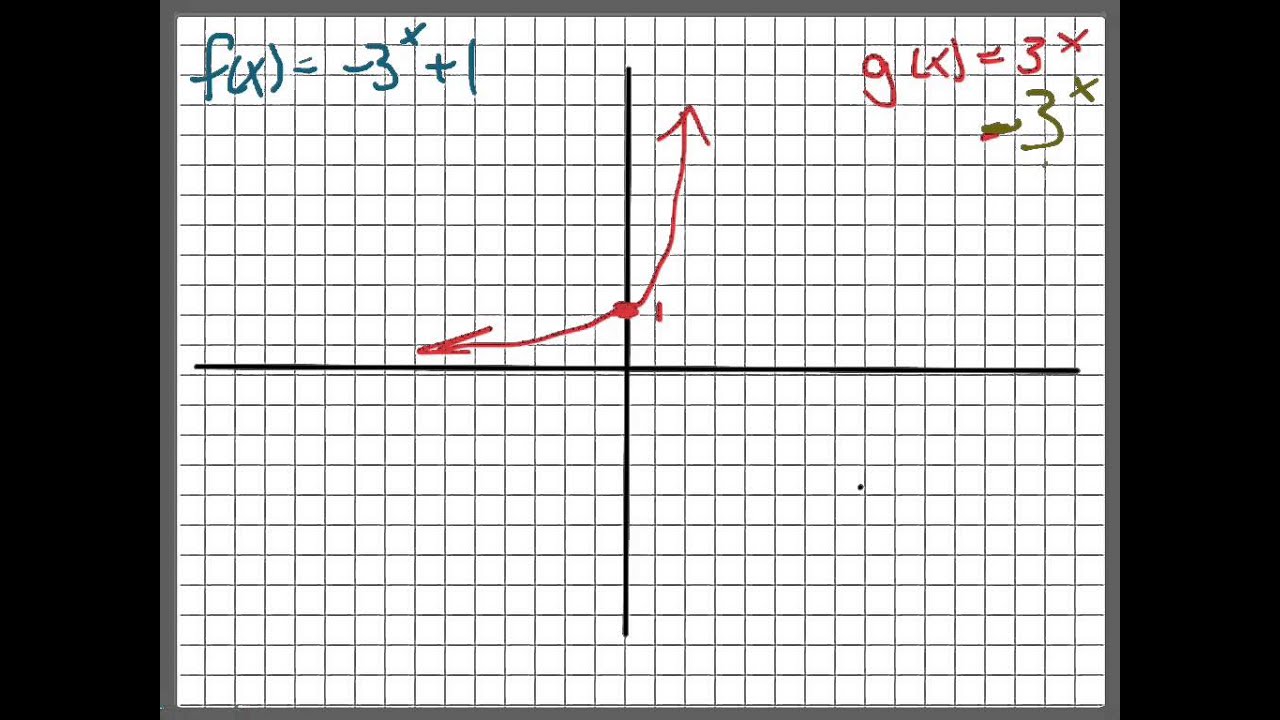



Graph F X 3 X 1 Youtube




The Function F X 3g X Which Of The Following Shows Possible Graphs Of F X And G X Brainly Com
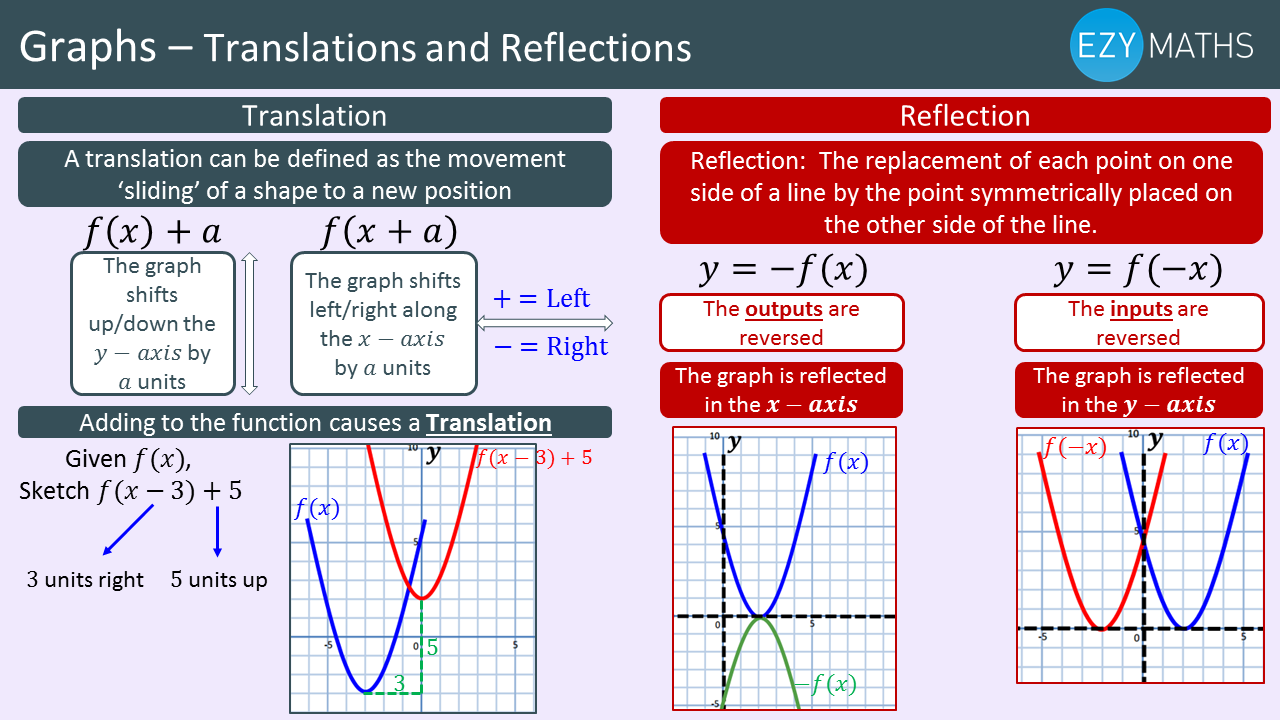



Maths Gcse Exam Revision Translations And Reflection Of Graphs Ezyeducation




Answered For Problems 29 31 Use The Given Graph Bartleby




2b7kutwk2s0ccm
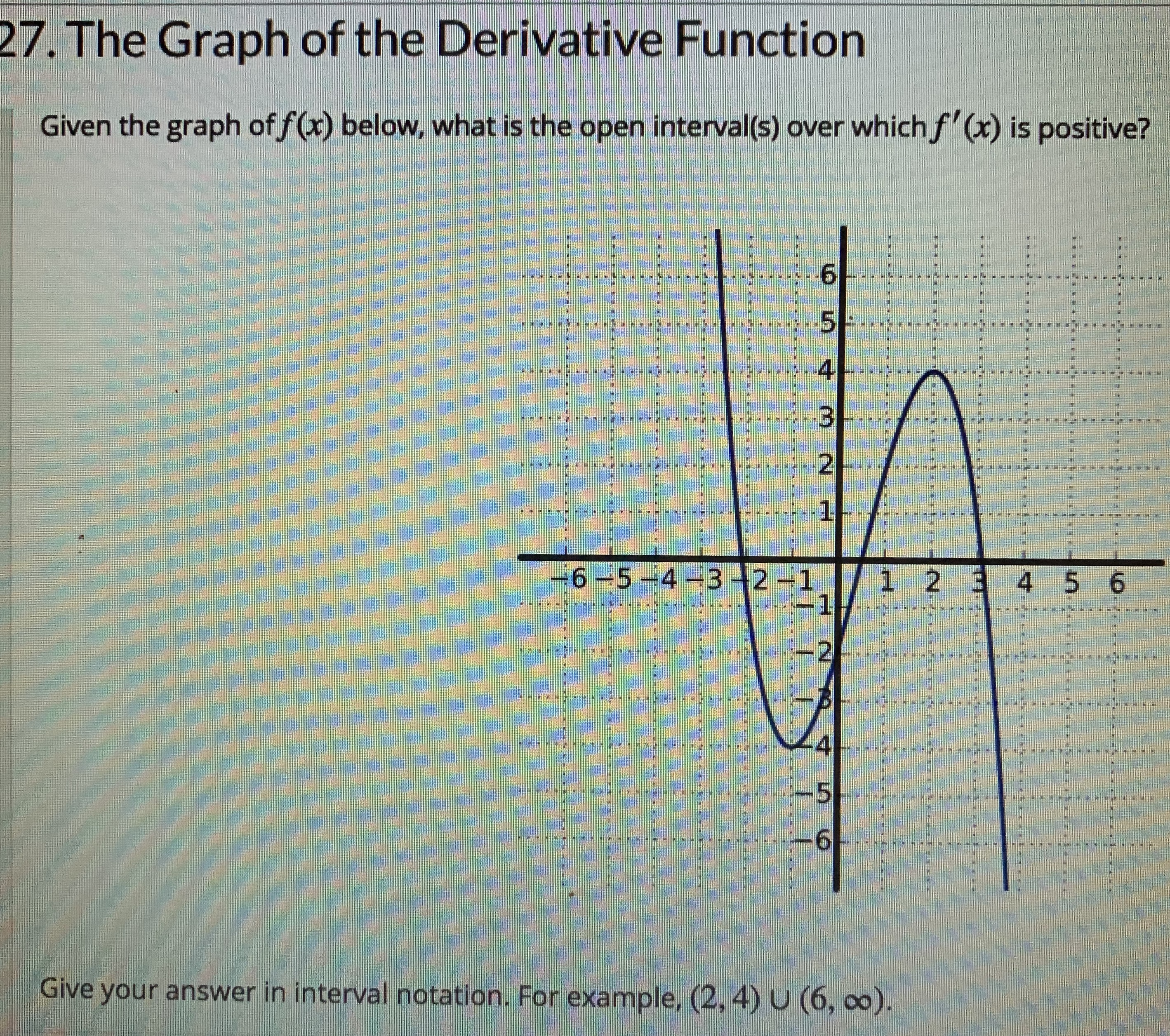



Answered 27 The Graph Of The Derivative Bartleby
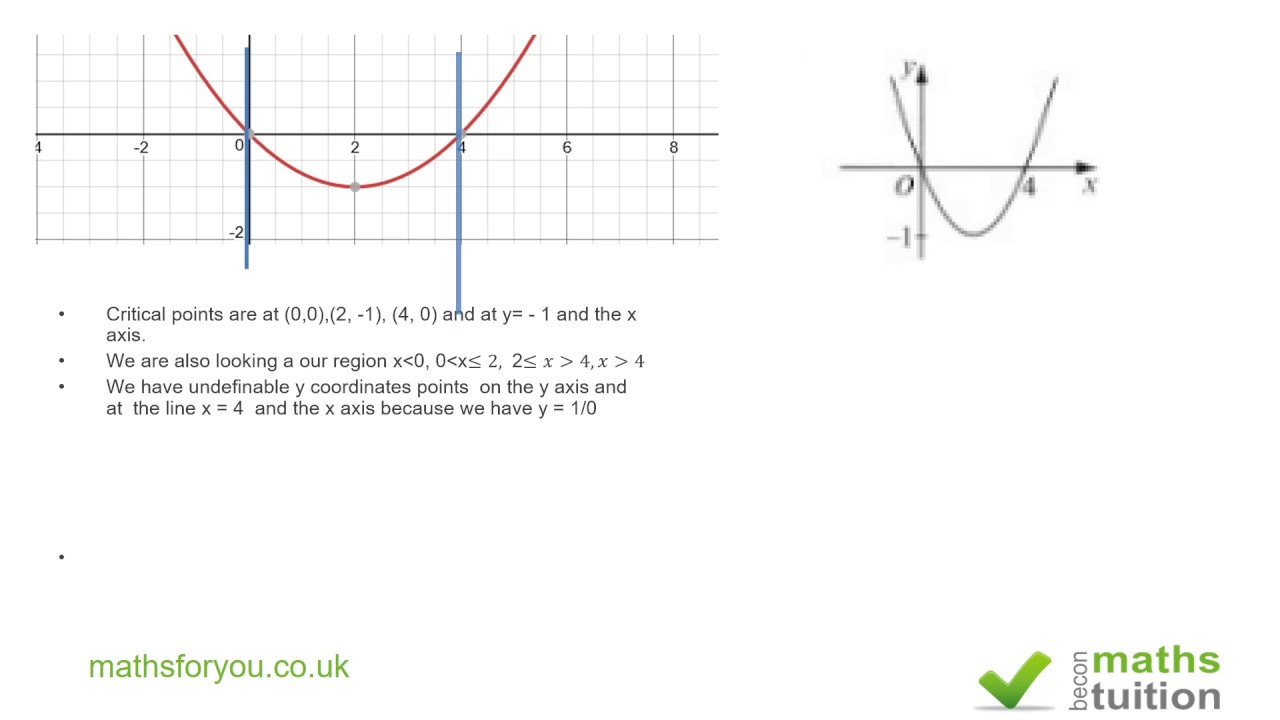



Sketching The Graph Of 1 F X Additional A Level Maths Youtube
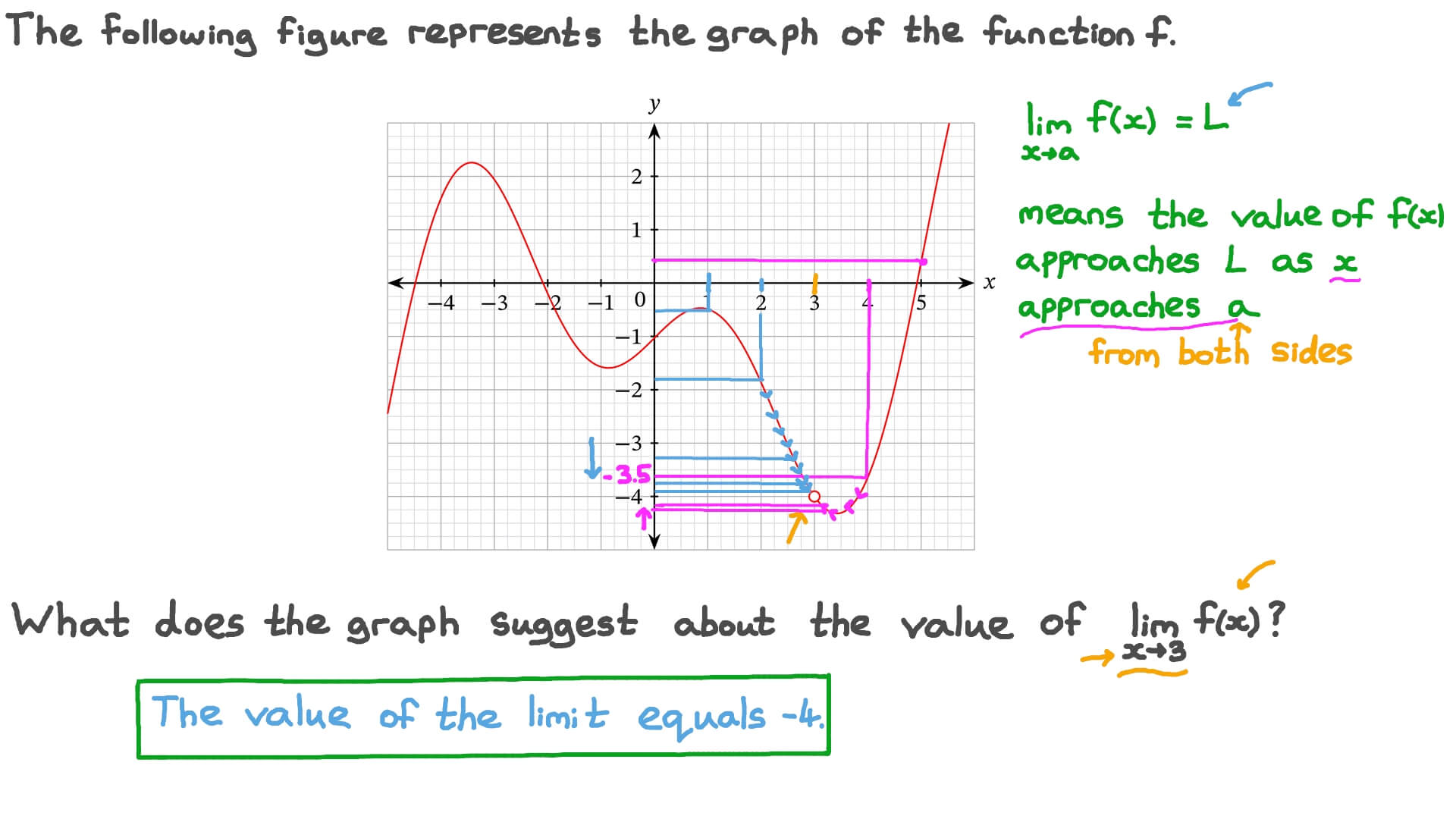



Question Video Finding The Value Of A Limit From A Graph Nagwa




Efofex Software



Solved Use The Given Graphs To Sketch The Graph Of F X G X Explain Your Process Course Hero
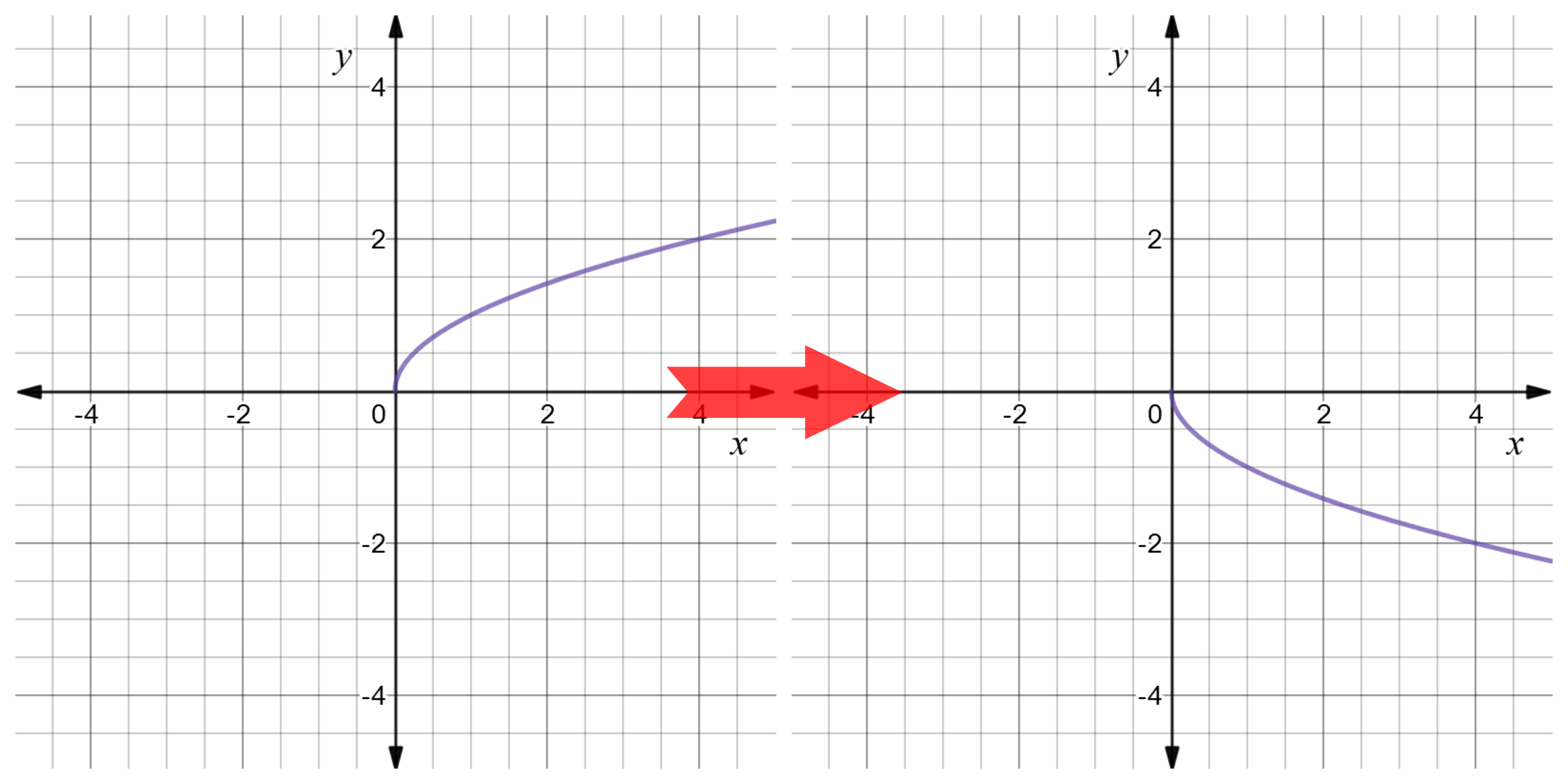



Reflect Function About Y Axis F X Expii
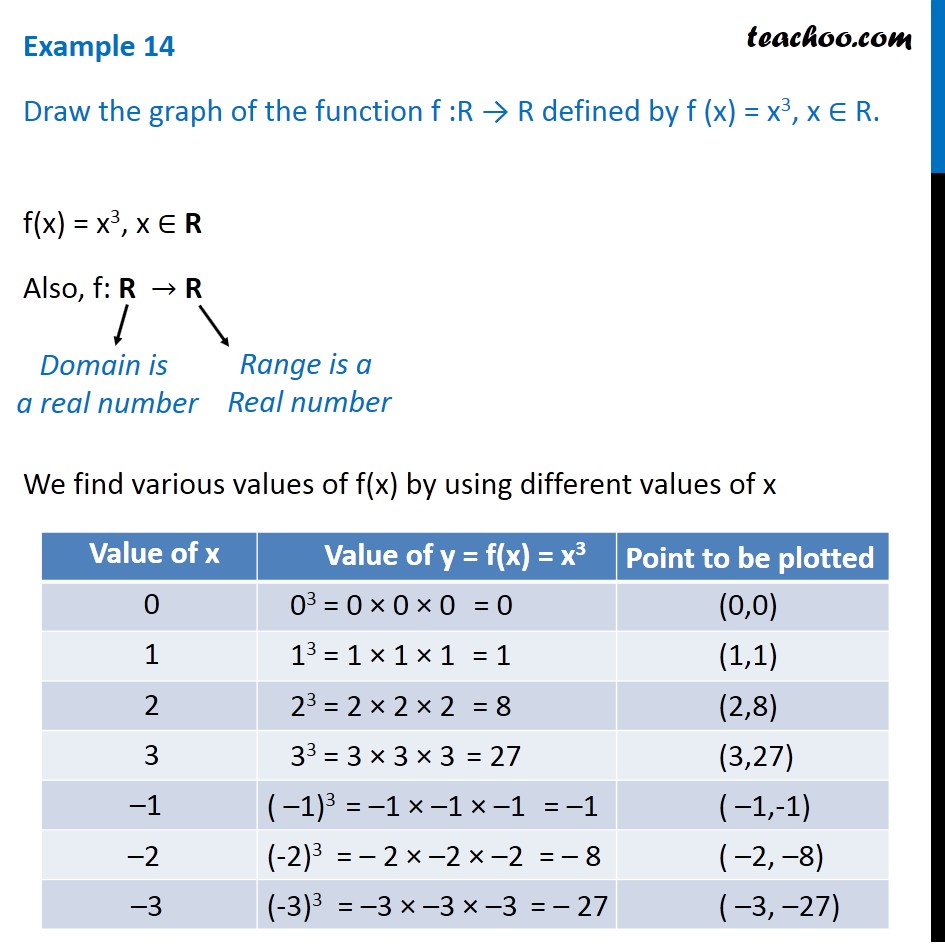



Example 14 Draw Graph Of F X X 3 Chapter 2 Class 11
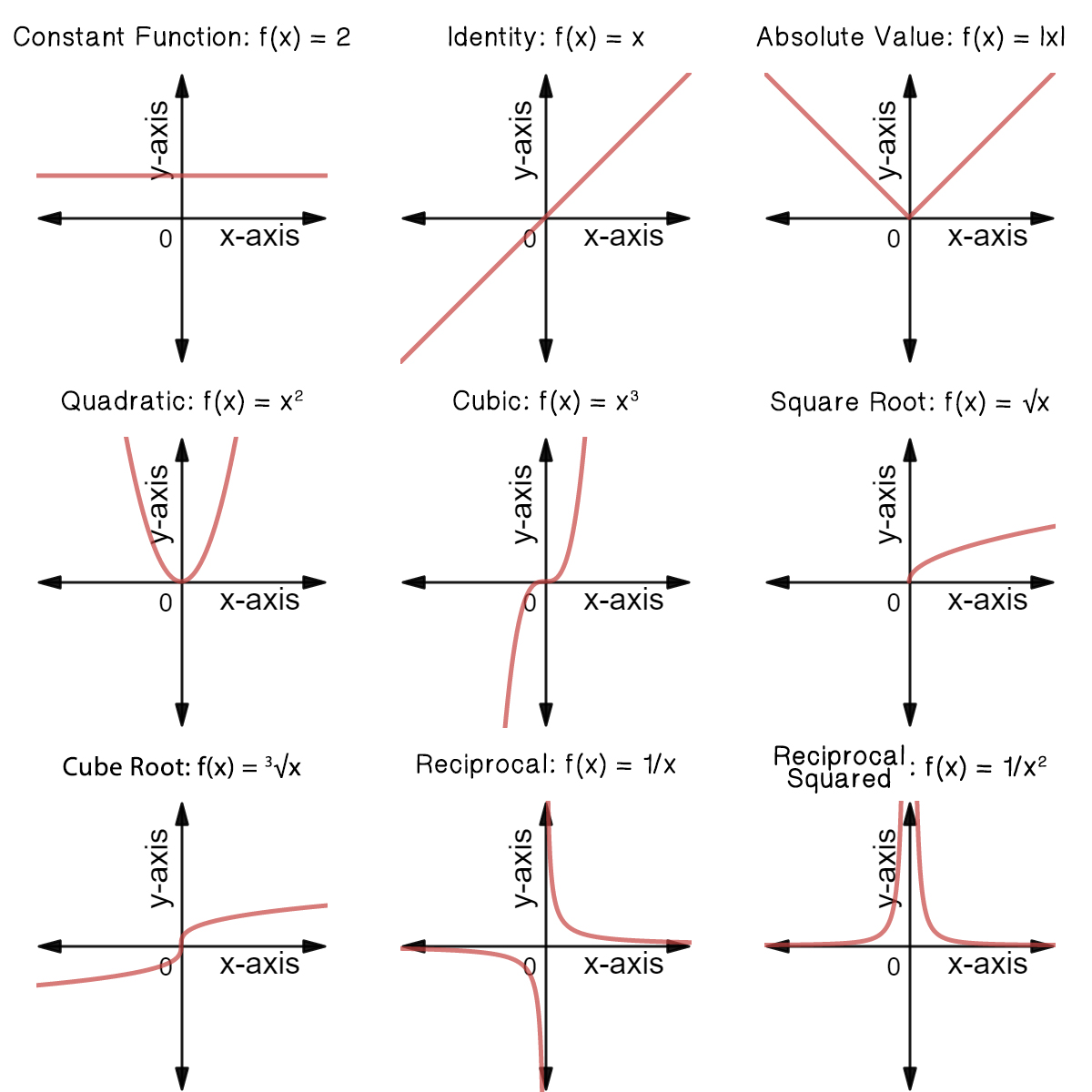



Classifying Common Functions Expii
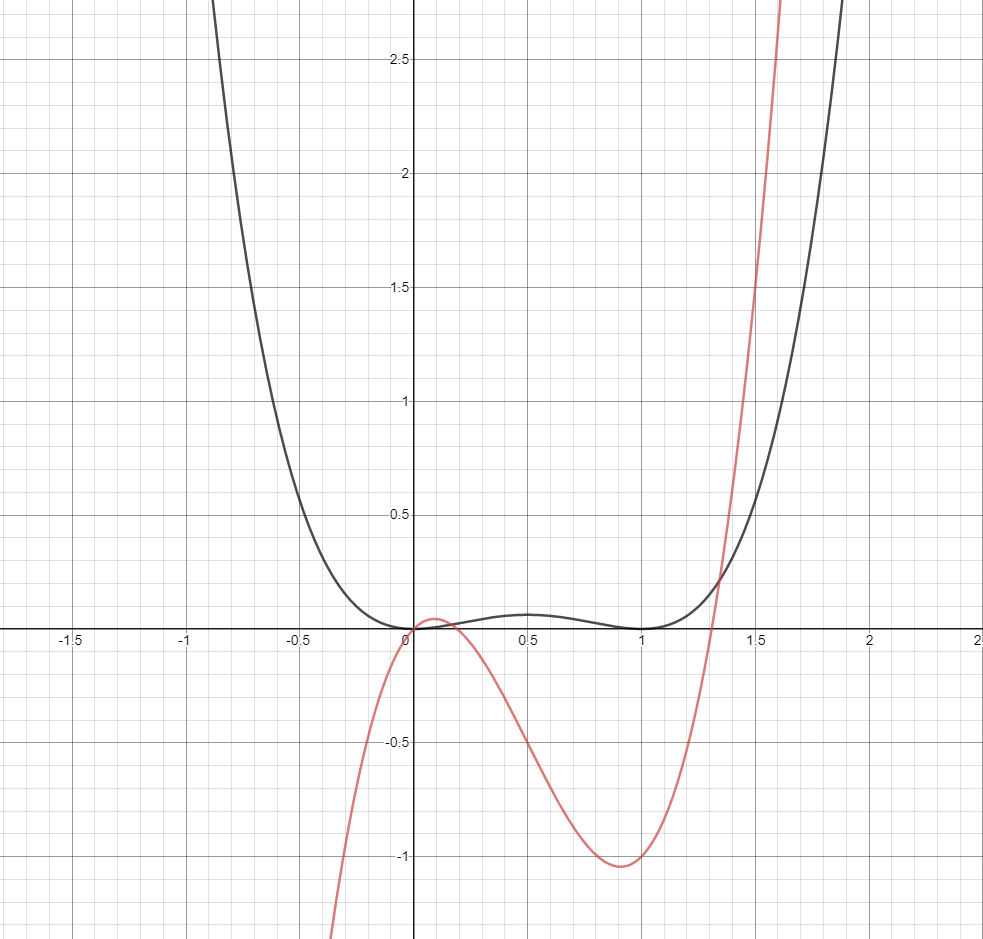



Find F X Compare The Graphs Of F And F And Use Them To Explain Why Your Answer Is Reasonable F X X 4 2x 3 X 2 Homework Help And Answers Slader
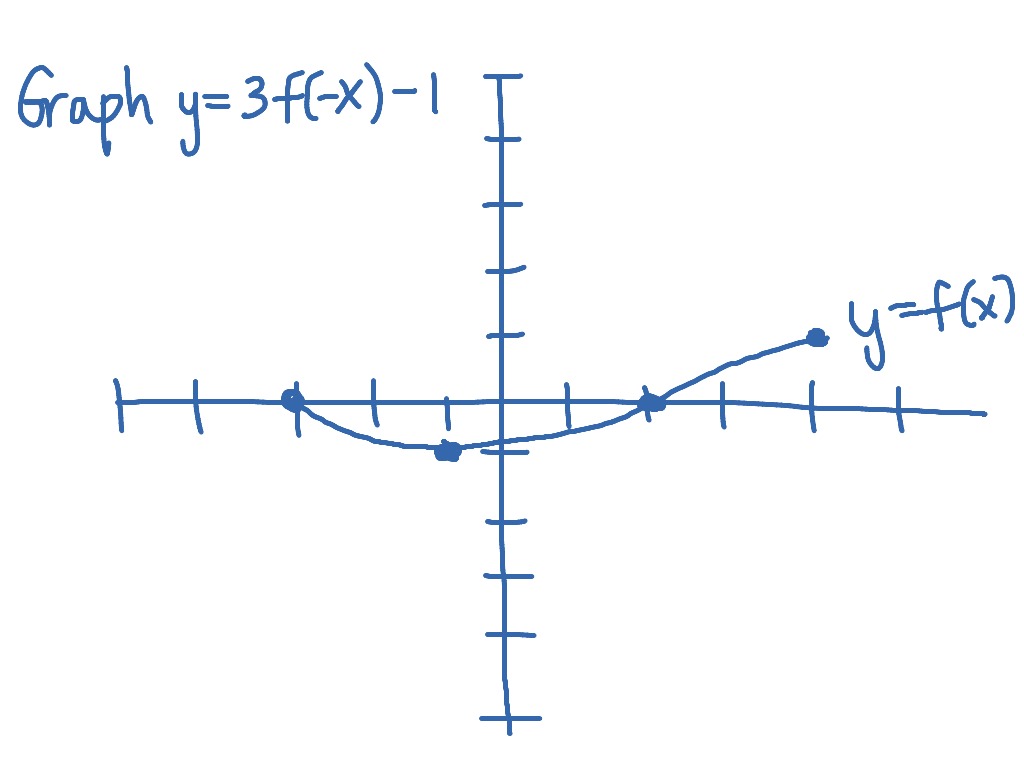



Graphing Y 3f X 1 From The Graph Of Y F X Math Showme
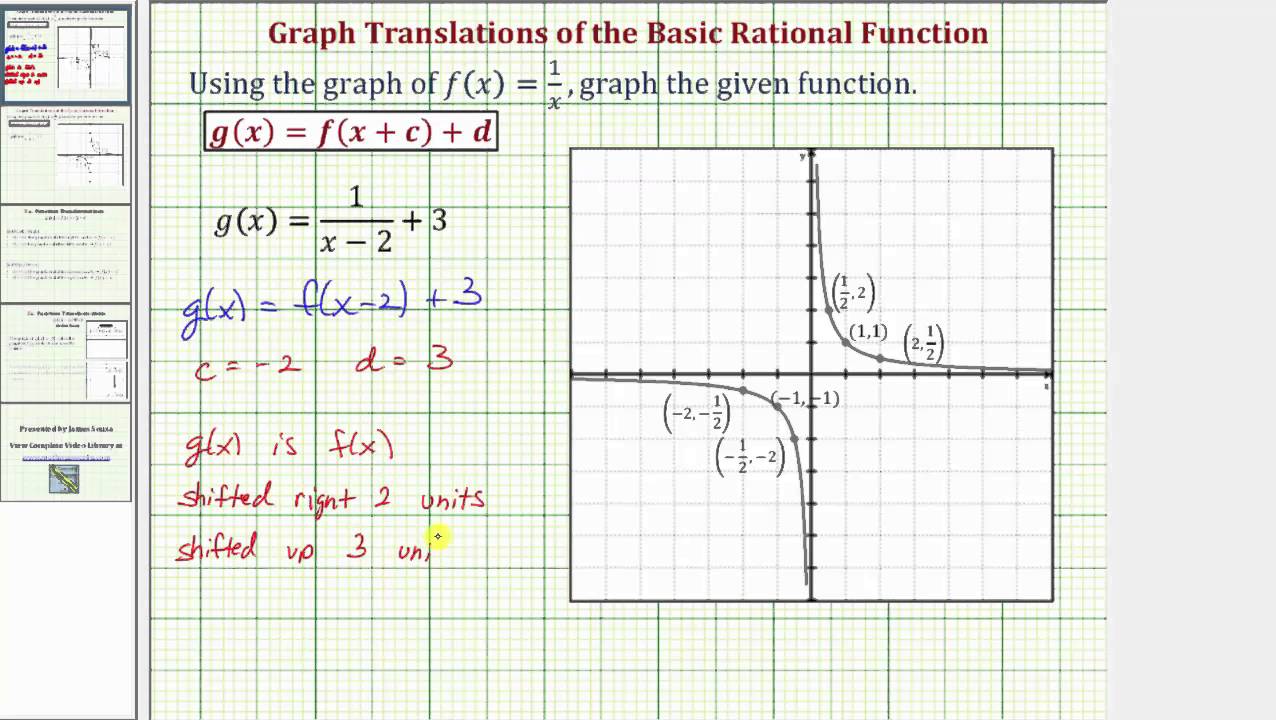



Ex 1 Graph Two Translations Of The Basic Rational Function F X 1 X Youtube




How To Graph A Quadratic Equation 10 Steps With Pictures




Finding Limits Graphically How To W 29 Examples
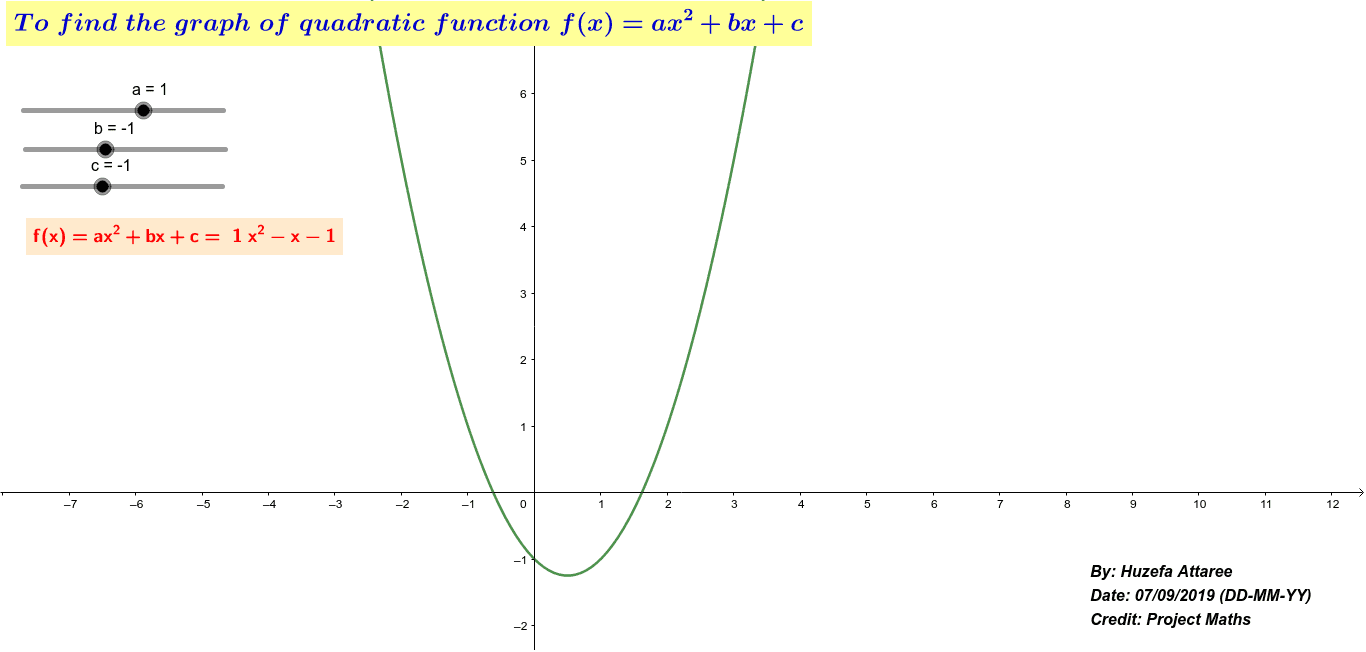



To Find The Graph Of Quadratic Function F X Ax 2 Bx C Geogebra



Graphing Square And Cube Root Functions Video Khan Academy




Functions Graph Interpreting Isaac Physics
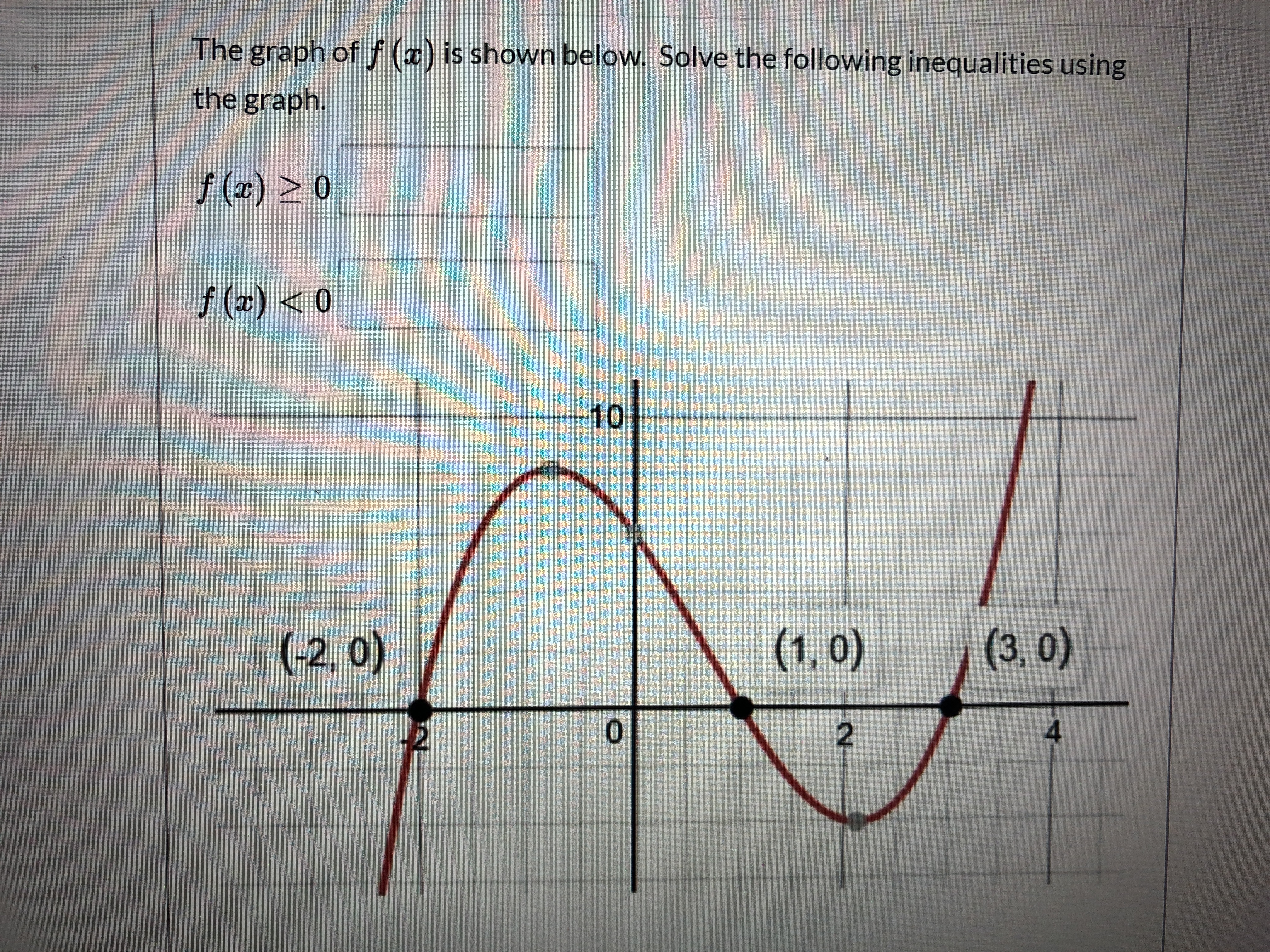



Answered The Graph Of F X Is Shown Below Bartleby
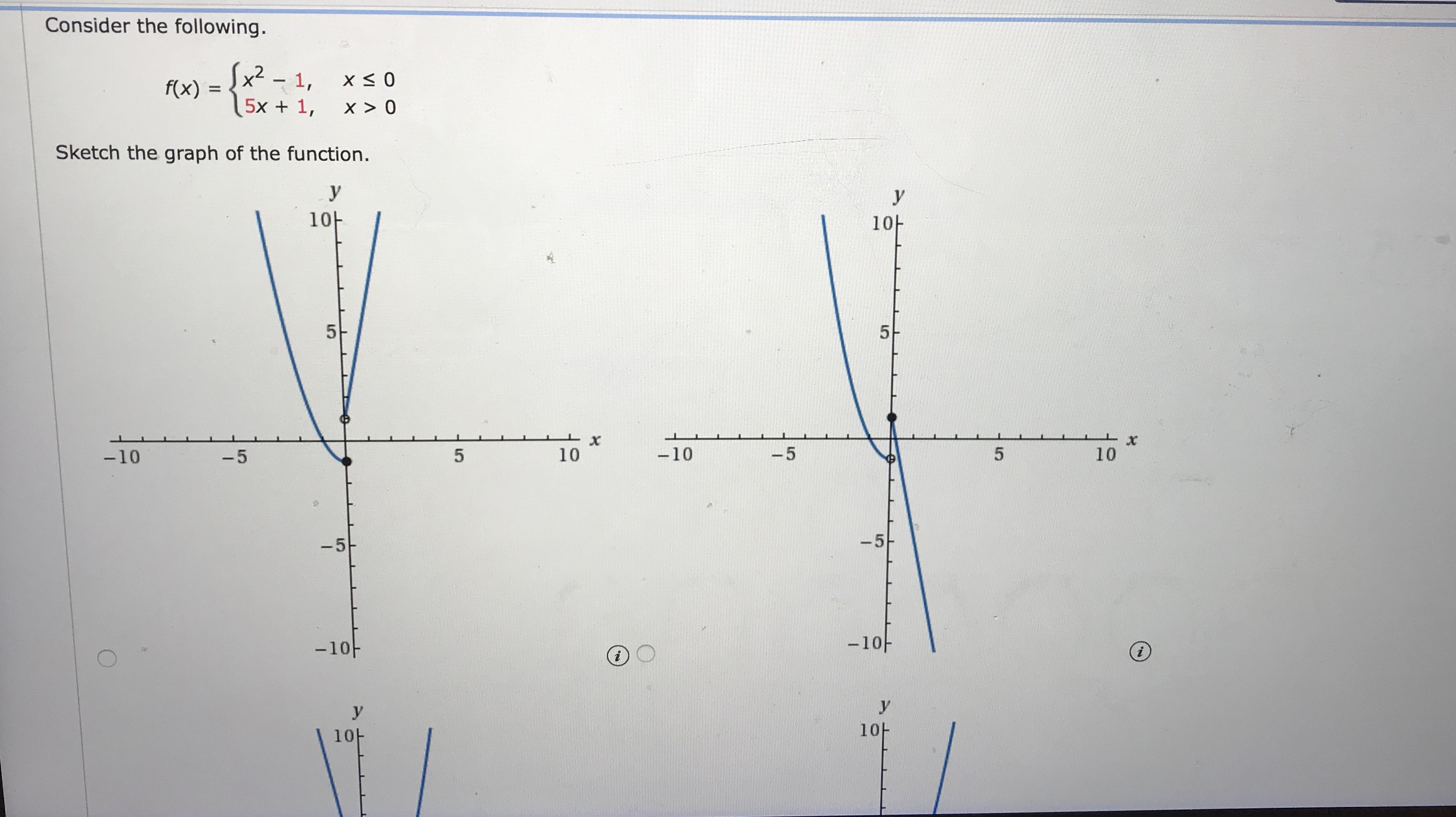



Answered Consider The Following X 1 F X 5x Bartleby



Drawing Graphs Of Y 1 F X And Y I1 F X I From Y F X Geogebra



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿