An odds ratio is simply the ratio of two sets of odds Increasing the odds ratio while holding a base odds constant corresponds to increasing the other odds, but may or may not be similar to the relative change in probability You may also want to ponder the difference between hazard and probability (see my earlier discussion where I make mention of handwaving;What does a relative risk of 25 mean? Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia from peterattiamdcom Is odds ratio a measure of risk?

Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar
Which is better odds ratio or relative risk
Which is better odds ratio or relative risk- Explanation and demonstration with simulated data of the difference between relative risk ratios and odds ratios, and how to extract them from a generalized linear model This post tries to explain the difference between odds ratios and relative risk ratios; Relative measures of effect are risk ratio (ie the ratio between two incidence proportions), incidence rate ratio (the ratio between two incidence rates), and OR (the ratio between two odds) The risk difference is an absolute measure of effect (ie the risk of the outcome in exposed individuals minus the risk of the same outcome in unexposed)



Www Jclinepi Com Article S05 4356 02 2 Pdf
The odds ratio should not be confused with relative risk or hazard ratios which might be close in certain cases, but are completely different measures Odds ratio vs Risk Ratio (Relative Risk) Odds ratios are not very intuitive to understand, but are sometimes used due to convenience in plugging them in other statisticsThe hazard ratio would be 2, indicating higher hazard of death from the treatment Hazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios 最も好ましい hazard ratio vs odds ratio vs relative risk Which is better odds ratio or relative risk but may or may not be similar to the relative change in probability You may also want to ponder the difference between hazard and probabilityThe risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions
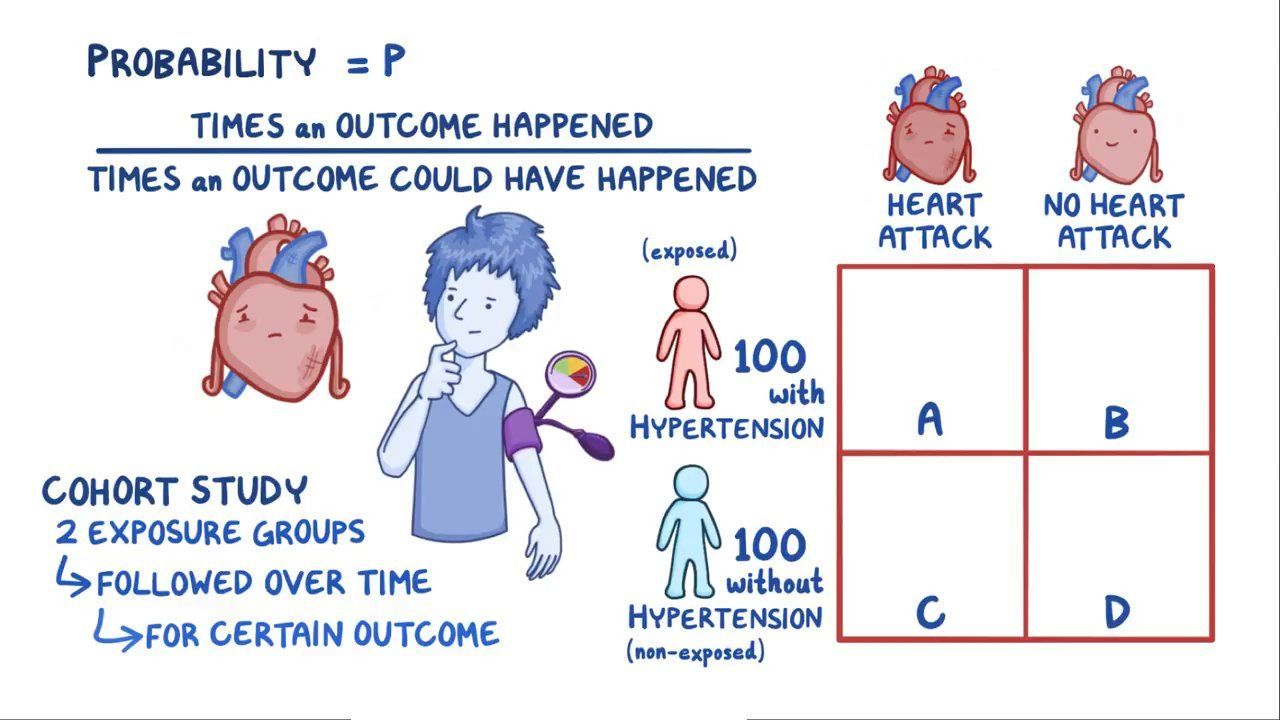
The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population,01 = 25This means that those in the control group were 25 times more likely to die than those in the treatment group The relative risk is interpreted in terms of the risk of the group in the numerator How do you interpret incidence risk ratio? How to Interpret Risk Ratios Since the relative risk is a simple ratio, errors tend to occur when the terms "more" or "less" are used Because it is a ratio and expresses how many times more probable the outcome is in the exposed group, the simplest solution is to incorporate the words "times the risk" or "times as high as" in your interpretation
In every other way the hazard ratio is similar to odds ratio and relative risk wherein treatment efficacy is denoted by a hazard ratio of less than 10 in prevention trials and a hazard ratio of more than 10 in treatment trials Table 3 Hazard ratio and timetoevent analysis 1You know the difference between risk and odds For instance, in the example in figure figure1, 1 , a 40% hazard reduction implies risk reductions of 25% and only 14% in the 1‐year and 2‐year mortality rates2ERA–EDTA Registry, Department of Medical Informatics, Academic Medical Center, University




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Who Saw This In The San Francisco Chronicle In The Past Week Ppt Download
As odds ratio and hazard ratio are the approximation to the relative risks, but they could be adjusted in multivariable settings When conducting aMeasures of effect Relative risks, odds ratios, risk difference, and 'number needed to treat' G Tripepi1, KJ Jager2, FW Dekker2,3, C Wanner4 and C Zoccali1 1CNRIBIM, Clinical Epidemiology and Physiopathology of Renal Diseases and Hypertension of Reggio Calabria, Reggio Calabria, Italy; Risk ratio = ratio of 2 cumulative incidence estimates = relative risk;



Jcm Free Full Text Risk Of Depression And Suicidality Among Diabetic Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Html



Arxiv Org Pdf 1510
The Difference Between Relative Risk and Odds Ratios The Risk ratios lack this symmetry, so it may be necessary to present 1 risk ratio for outcome Y and another for outcome not Relative risk is used to compare the risk in two different groups of people For example, the groups could beHazard ratio The hazard ratio in survival analysis is the effect of an exploratory?Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the likelihood of an event between two groups




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
After converting the odds ratio to a risk ratio, the actual risk is 14 (mortality is 14 times more likely in patients with ICU delirium compared to those without ICU delirium) Because the incidence rate in the nondelirium group is high, the odds ratio exaggerates the true risk demonstrated in the study Table 1 Relative risk (RR) vs Odds Ratio (OR) vs Hazard Ratio (HR) HRs are in tandem with survivorship curves, which show the temporal progression of some event within a group, whether that event is death, or contracting a diseaseThe absolute risk is the probability of an event in a sample or population of interest The relative risk (RR) is the risk of the event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group



1




Graphical Presentation Of Relative Measures Of Association The Lancet
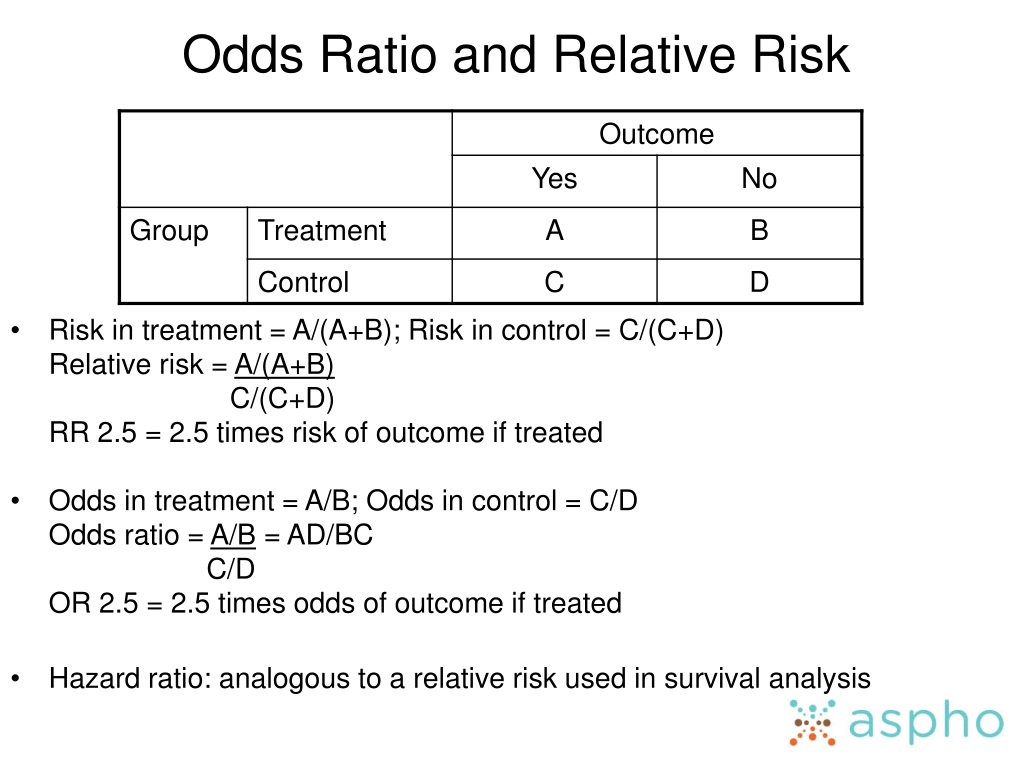
Odds Ratio Odds Ratio for comparing two proportions OR > 1 increased risk of group 1 compared to 2 OR = 1 no difference in risk of group 1 compared to 2 OR < 1 lower risk ("protective") in risk of group 1 compared to 2 In our example, p 1 = proportion of women receiving SAT p 2 = proportion of men receiving SAT OR pp pp pp pp = − − = − − 11 22 12 21 1Is still NOT the hazard ratio, as it is not a ratio of conditional probabilities Maybe the easiest way to understand that a hazard ratio cannot be equal to the relativerisk for any timetis to realize that eventually everybody dies, so the relative risk willapproach 1 with time, even though the hazard ratio is constantThis implausible scenario is shown in Table 5, where collapsed counts for low (or high) risk subjects only produce a 2 × 2 table with an odds ratios of 400



Forest Plot Showing The Pooled Odds Ratio Or Or Hazard Ratio Hr Of Download Scientific Diagram



9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science
When RR = 1, OR = 1Pute either the odds ratio or the relative risk to answer this question The odds ratio compares the relative odds of death in each group For women, the odds were exactly 2 to 1 against dying (154/308 05) For men, the odds were almost 5 to 1 in favor of death (709/142 4993) The odds ratio is 9986 (4993/05) There is a 10fold greater The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the placebo group



Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube




Ppt Point Estimation Odds Ratios Hazard Ratios Risk Differences Precision Powerpoint Presentation Id
May 03, In cohort A, imagingbased progressionfree survival was significantly longer in the olaparib group than in the control group (median, 74 months vs 36 months;Odds ratio, and when by equating the two statistics we are sometimes forcing OR to be something it is not Another statistic, which is often also perceived as a relative risk, is the hazard ratio (HR) We encounterSince all of the measures are ratios, either of probabilities or of odds, it is clearer and simpler to use the word ratio in describing each type Risk reflects the proportion of persons experiencing the event, so it follows that comparing two cumulative incidences is called a risk ratio A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equal An example with a control group and a therapy treatment group Treatment group 5 deaths, 95 survive Risk = 5/100 = 005




We Don T Have Them Yet Desantis Works To Get More Type Of Face Masks



Escholarship Umassmed Edu Cgi Viewcontent Cgi Article 1013 Context Liberia Peer
And how just a few letters in the code fitting a generalized linear model mean the difference between The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio • ericminikel The other day I was emailing with a statistical genetics colleague about a rare SNP associated with a phenotype I stated that the minor allele frequency (MAF) was 07% in cases and 01% in controls, for a risk ratio of 7 After clicking send, I felt a twinge of regretBoth the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds



Epidemiology Knowledge Amboss




Hydroxychloroquine And Mortality Risk Of Patients With Covid 19 A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Of Human Comparative Studies Medrxiv
Hazard Ratios vs Risk Ratios (or Relative Risk) Hazard ratio is frequently interpreted as risk ratio (or relative risk), but they are not technically the same However, if that helps you to understand hazard ratio then it is OK But keep in mind HR is not RRStart studying Risk Ratio, Odds Ratio, KaplanMeier, Survival Analysis, Hazard Analysis Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools While hazard ratios, relative risks, and odds ratios all show relative risk, there's plenty to distinguish them from one another, particularly around how they're calculated and interpreted That's why it's important to know which one is




Table I




Definition Of Risk Difference Definitionus
Variable on the hazard or risk of an event Hazard ratio can be considered as an estimate of relative risk, which is the risk of an event (or of developing a disease) relative to exposureRelative risk is a ratio of the probability of the event occurring in the exposed group versus the control (nonexposed) groupNow we don't gloss over the difference)Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literature Most readers perceive it as relative risk (RR), although most of them do not know why that




How To Tell The Difference Between A Hazard Ratio Relative Risk And Odds Ratio




đo Lư Ng Nh Hư Ng Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Ratio Hazard Ratio
In general If the risk ratio is 1 (or close to 1), it suggests no difference or little difference inIf the risks were 08 and 09, the odds ratio and relative risk will be 2 very different numbers OR = 044 and RR = 0 Relative risk vs Odds ratio Similarities They will always agree on the direction of comparison In our example above, both will agree that wine consumers have less heart disease than nonconsumers;StATS Odds ratio versus relative risk (created by ) Dear Professor Mean There is some confusion about the use of the odds ratio versus the relative risk Can you explain the difference between these two numbers?




Risk Ratios For Contagious Outcomes Journal Of The Royal Society Interface




Find An Example Of A Confidence Interval For A Chegg Com
Definition of risk ratio A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group It does so by dividing the risk (incidence proportion, attack rate) in group 1 by the risk (incidence proportion, attack rate) in group 2Start studying Applied Statistics Relative Risks, Odds Ratios, Hazard Ratios, NNT, NNH Part 1 Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and otherThis relative risk calculator allows you to perform a posthoc statistical evaluation of a set of risk data when the outcome of interest is the change in relative risk (the risk ratio) or the absolute risk difference (ARR) between an exposed/treatment group and a control group The Relative Merits of Risk Ratios and Odds Ratios the odds among men and women on the Titanic



Phdres Caregate Net Conferences Ay 13 14 ppt presentations Statistics 102 Pdf




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube
The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk isOdds Ratio = Odds / Odds Now that you have a general idea of what odds ratio and relative risk are you need to know when to use them They don't always just ask you to calculate one or the other Sometimes questions on Step 1 also require you to figure out which type of calculation is needed based on the situation In clinical trials and The relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1, meaning that the odds approaches the risk, and the odds ratio approaches the relative risk




Madhu Pai Md Phd Incidence Prevalence Odds Risk Rate Relative Risk Excess Risk Risk Reduction Hazard Confused When I Was A Phd Student Ucberkeleysph I Worked On A Handout




Long Term Risk Of Dementia Following Hospitalization Due To Physical Diseases A Multicohort Study Sipila Alzheimer S Amp Dementia Wiley Online Library
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsWhat are absolute risks, relative risks, odds ratios and hazard ratios?Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a r




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube
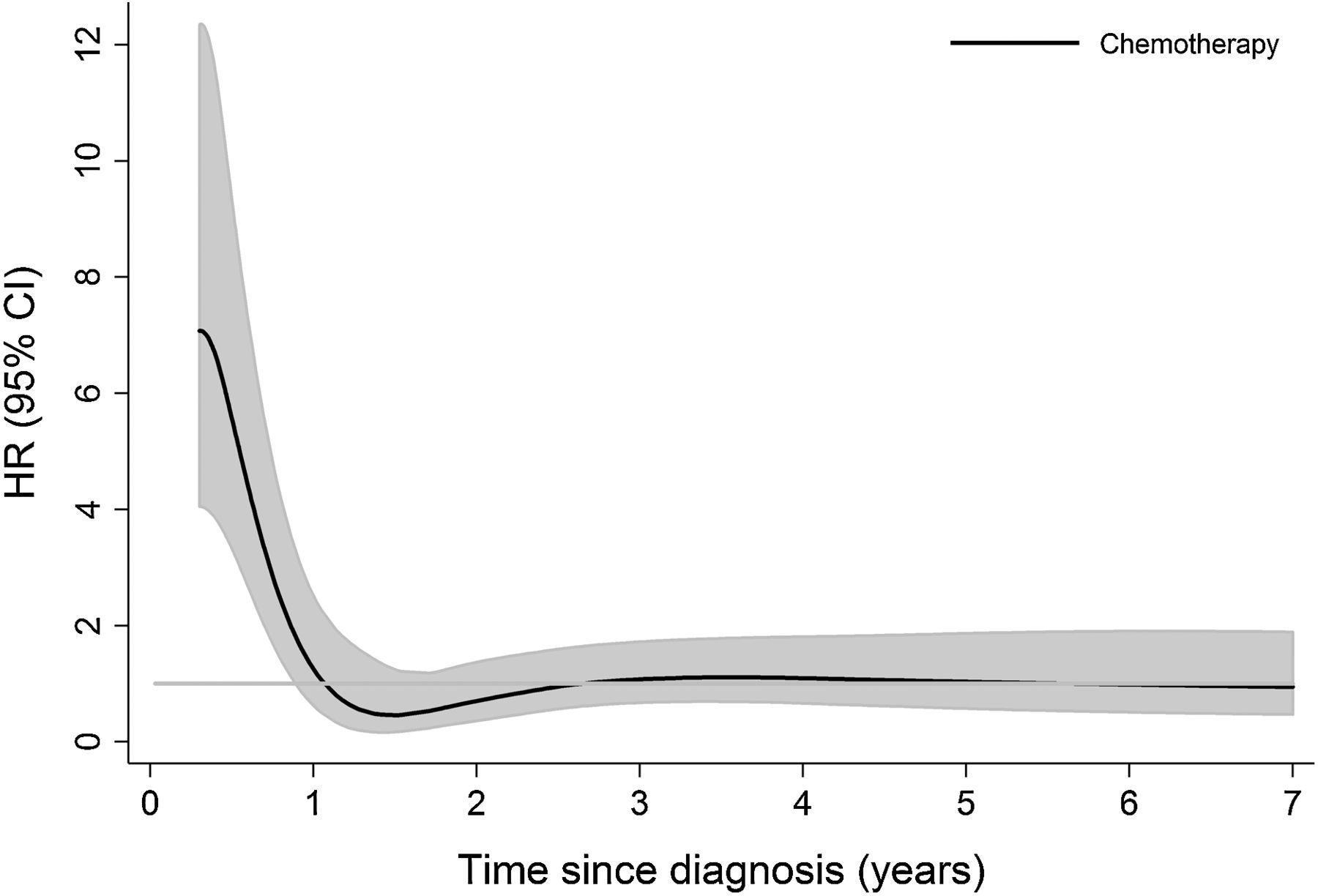



Hazard Ratio Plots With Non Linear Time Varying Effects In R Survival Analysis Datamethods Discussion Forum
Odds Ratio, Relative Risk, Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial #30 MarinStatsLectures How Compelling Is Your Writing?The method of presenting the results of clinical studies can affect their interpretation by clinicians2 and nonclinicians alike3,4 Therefore, it is important to understand the different ways in which results can be presented Absolute risk refers to the simple The odds ratio will estimate the average change in odds (the average odds ratio) among exposed individuals only when all individual odds ratios are equal and all individual outcome risks without exposure are equal 1;




Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk And




Biostatisticssummarypage



Who Saw This In The San Francisco Chronicle In The Past Week Ppt Download




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key




Who Saw This In The San Francisco Chronicle In The Past Week Ppt Download
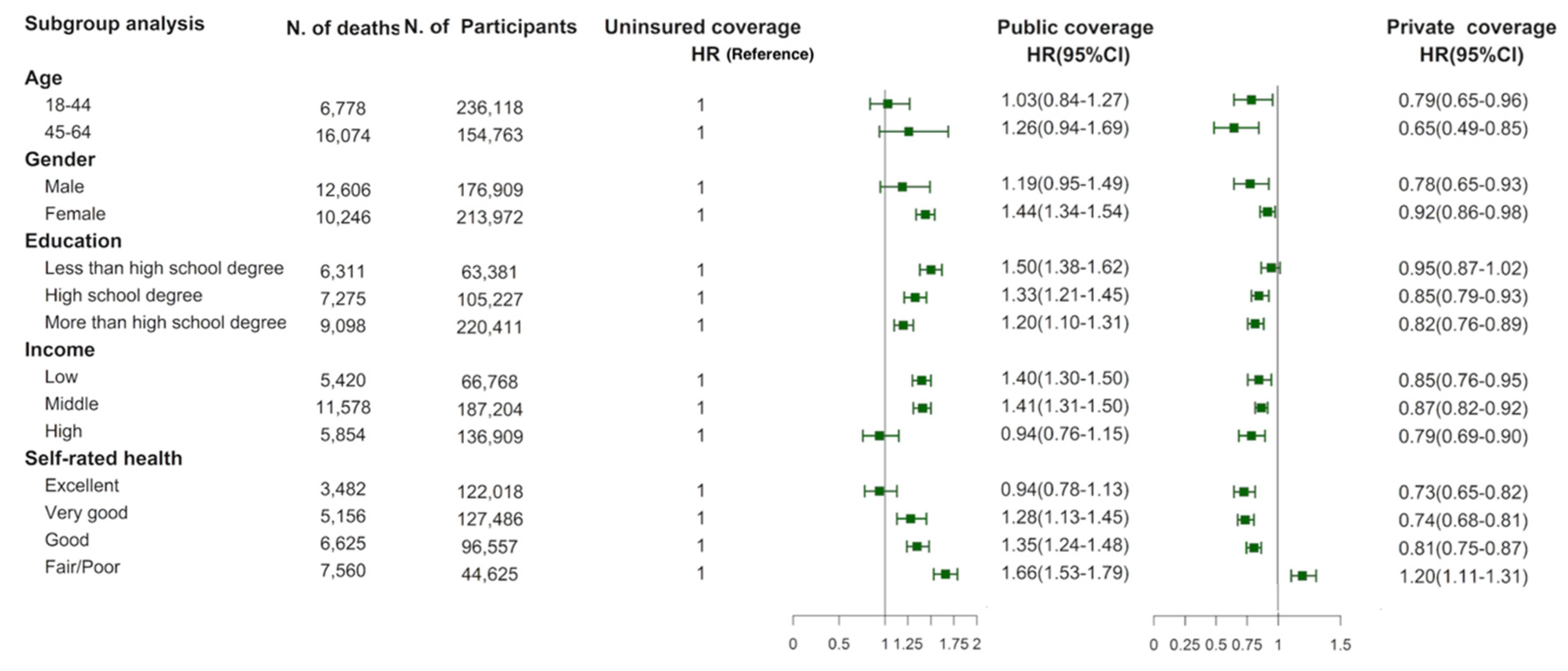



Ijerph Free Full Text The Association Between Health Insurance And All Cause Cardiovascular Disease Cancer And Cause Specific Mortality A Prospective Cohort Study Html




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk
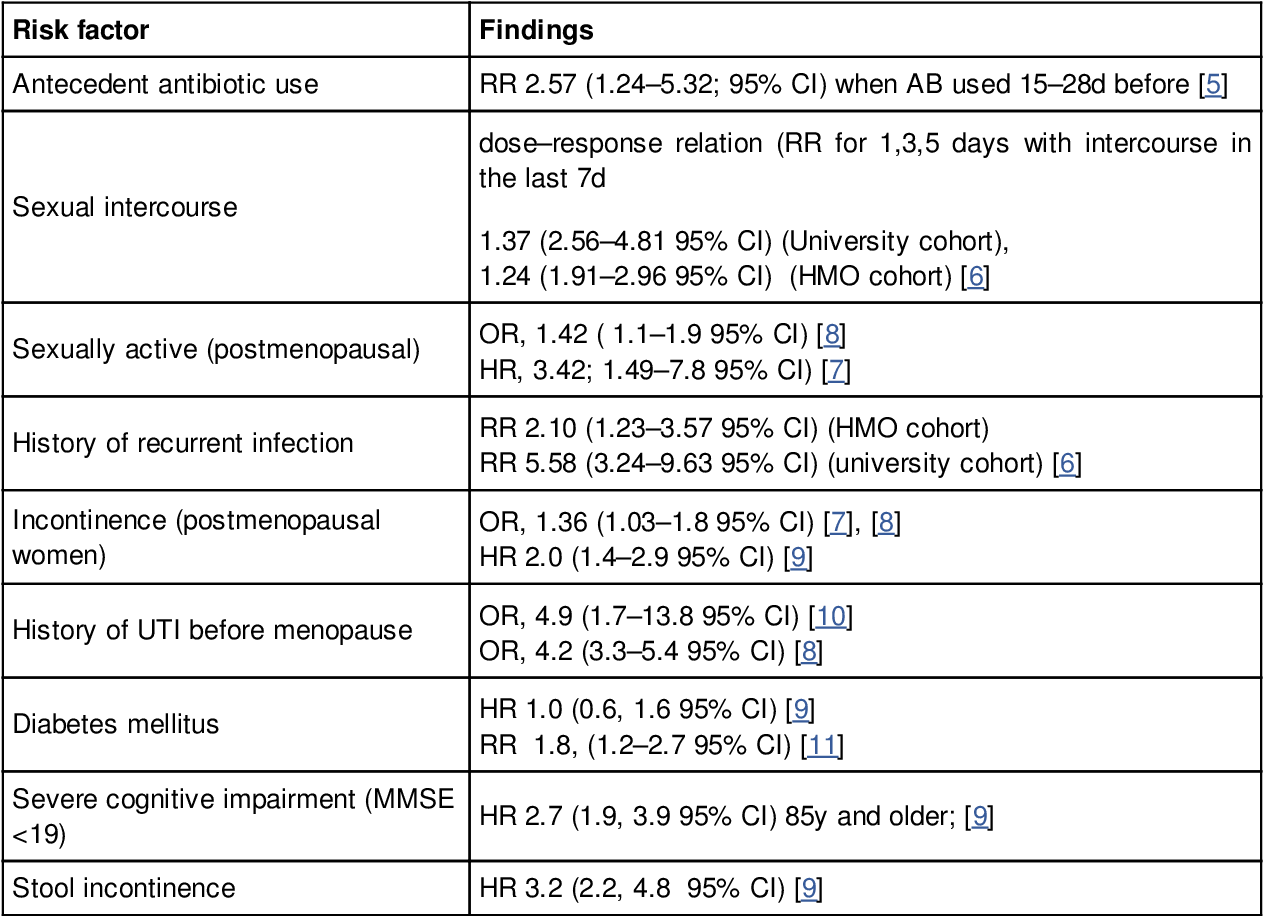



Table 1 From Diagnosis Of Uncomplicated Cystitis Uc Semantic Scholar



Hazard Ratio




Hazard Ratio In Clinical Trials Antimicrobial Agents And Chemotherapy




Hazard Ratio In Clinical Trials Antimicrobial Agents And Chemotherapy



Arxiv Org Pdf 2105
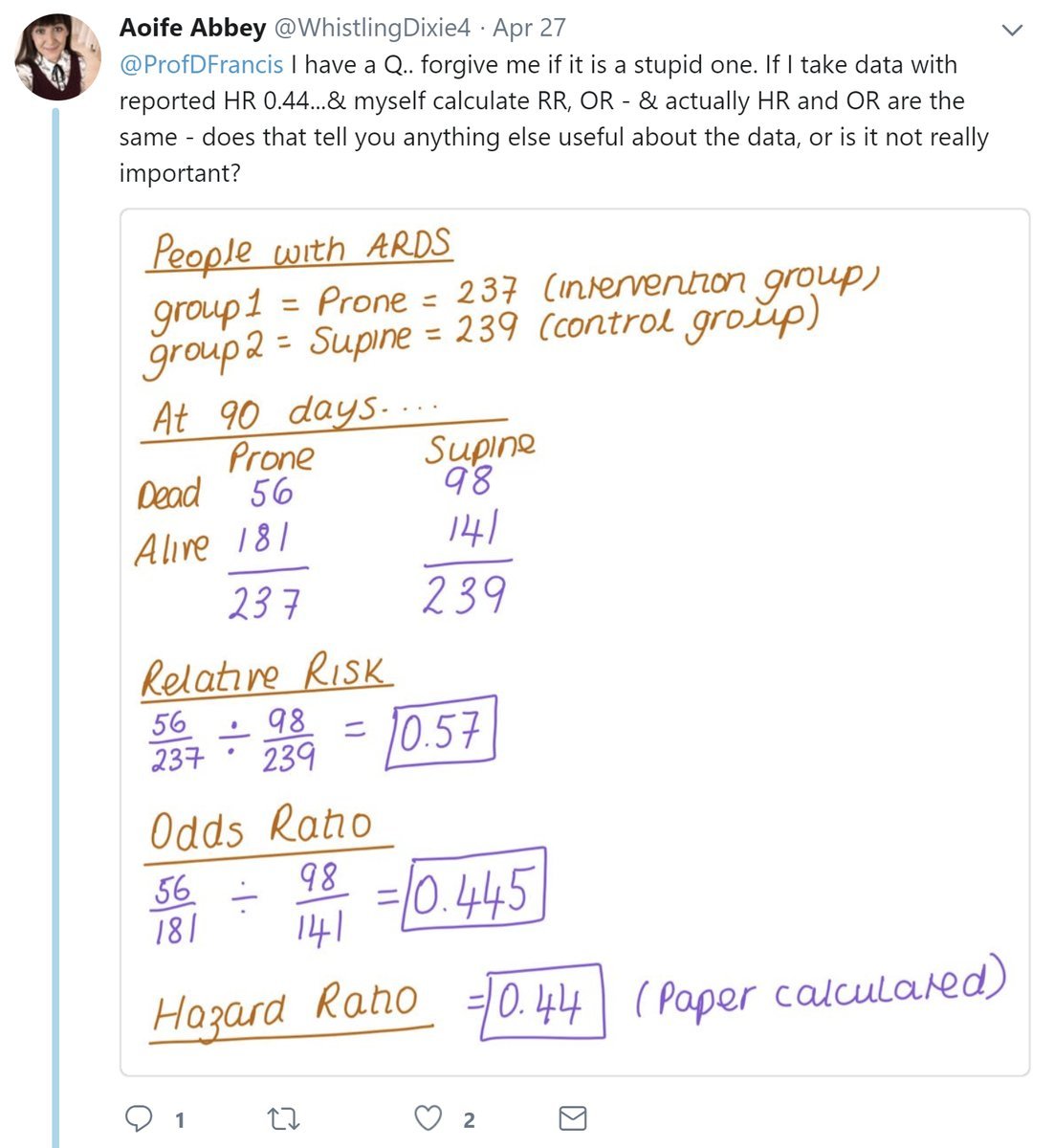



Prof Darrel Francis Mk Cardiofellows Great Again The Hazard Ratio Is In A Way The Best Thing We Could Calculate Because It Looks Along Every Instant In Time And



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood




Estimated Relative Risk Odds Ratio Or Hazard Ratio With 95 Ci For 4 Download Scientific Diagram



Academic Oup Com Ije Article Pdf 24 2 464 24 2 464 Pdf




Scielo Brasil Significant Association Between Osteoporosis And Hearing Loss A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Significant Association Between Osteoporosis And Hearing Loss A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Odds Ratios Relative Risks Or Hazard Ratios From Studies Reporting Download Table




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Hazard Ratio In Clinical Trials Antimicrobial Agents And Chemotherapy



Plos One Association Between Diabetes Mellitus And Active Tuberculosis A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis



How To Read A Forest Plot Cochrane Uk



Www Ahajournals Org Doi Pdf 10 1161 Circheartfailure 116 Download True



Www Jclinepi Com Article S05 4356 02 2 Pdf



Plos One Risk Of Cardiovascular Disease From Antiretroviral Therapy For Hiv A Systematic Review



1



Ppt Header Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Ppt Measures Of Association Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



Pregnancy Associated Plasma Protein A As A Predictor Of All Cause Mortality And Cardiovascular Events In Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease A Meta Analysis Of Prospective Studies




Global Brain Perfusion And The Risk Of Transient Ischemic Attack And Ischemic Stroke The Rotterdam Study Journal Of The American Heart Association




Retrospective Cohort Study Wikipedia



Odds Ratio Video Explanation Osmosis



Relative Risk



Beaumont Cloud Cme Com Launchscorm Aspx Caseid 112 Userid 0 Video True




Genetic Risk Of Dementia Mitigated By Cognitive Reserve A Cohort Study Dekhtyar 19 Annals Of Neurology Wiley Online Library
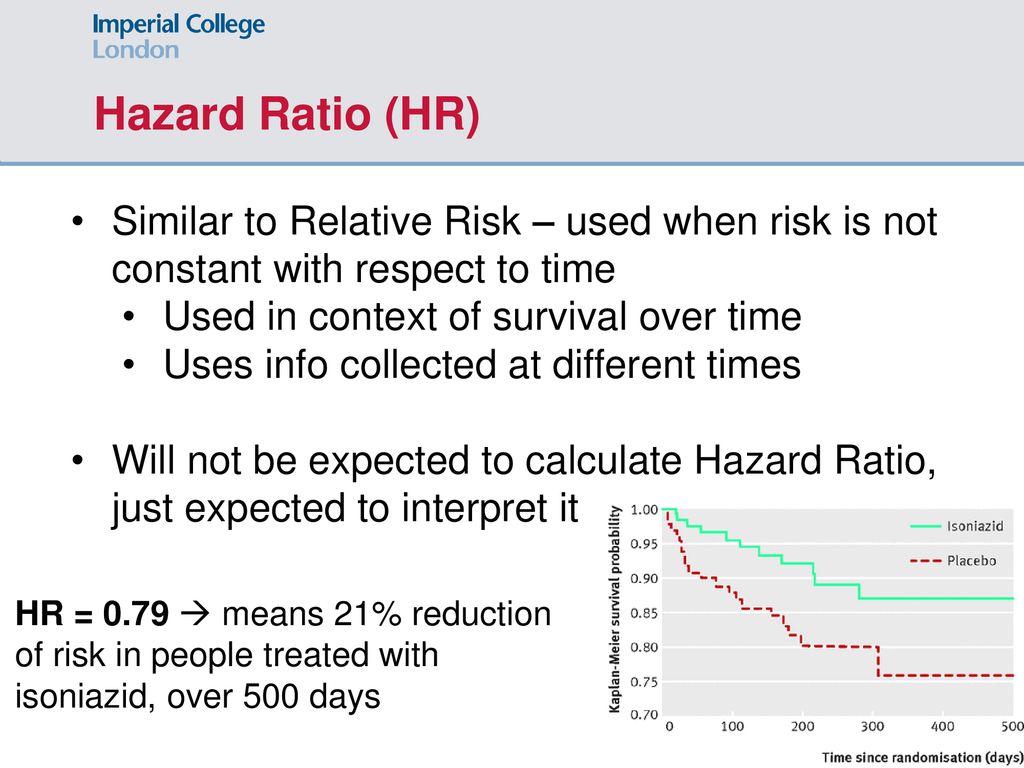



Data Analysis For The Bsc Year Ppt Download
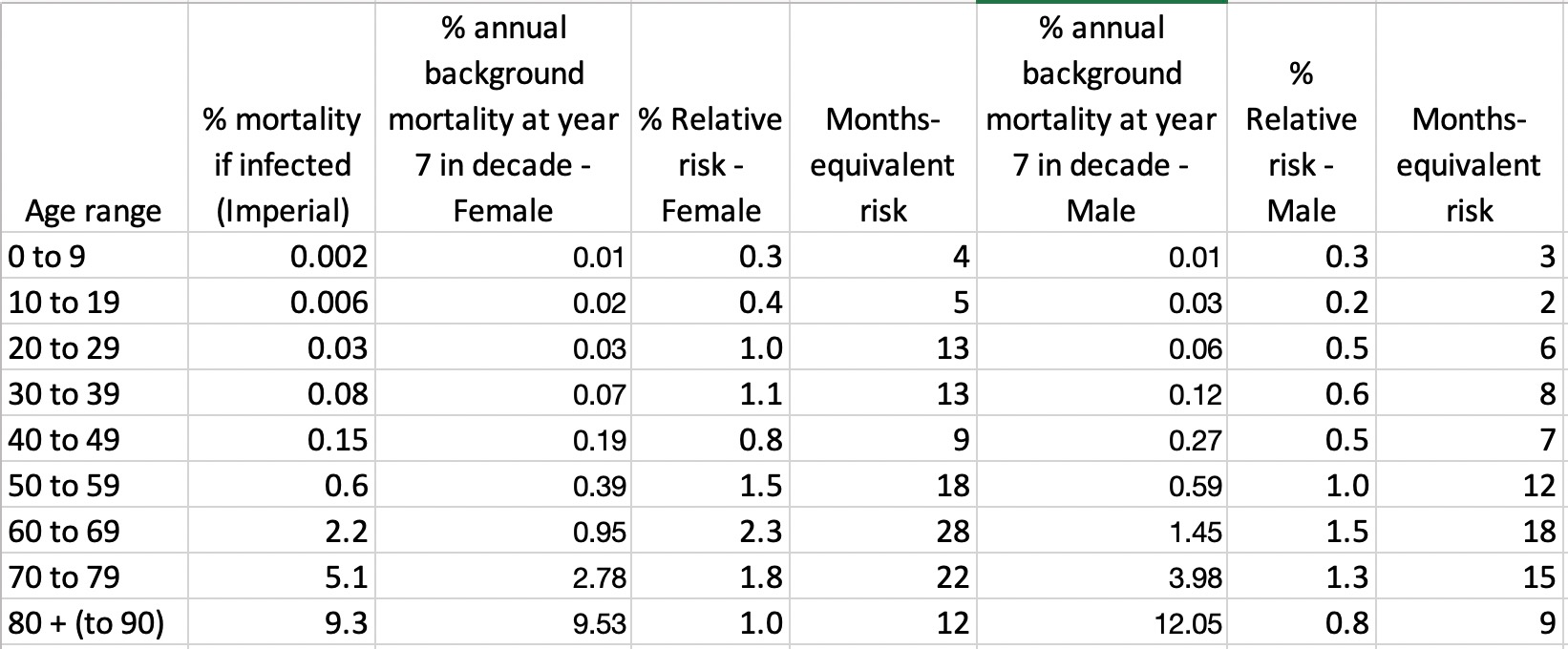



How Much Normal Risk Does Covid Represent By David Spiegelhalter Wintoncentre Medium




Against All Odds Improving The Understanding Of Risk Reporting British Journal Of General Practice
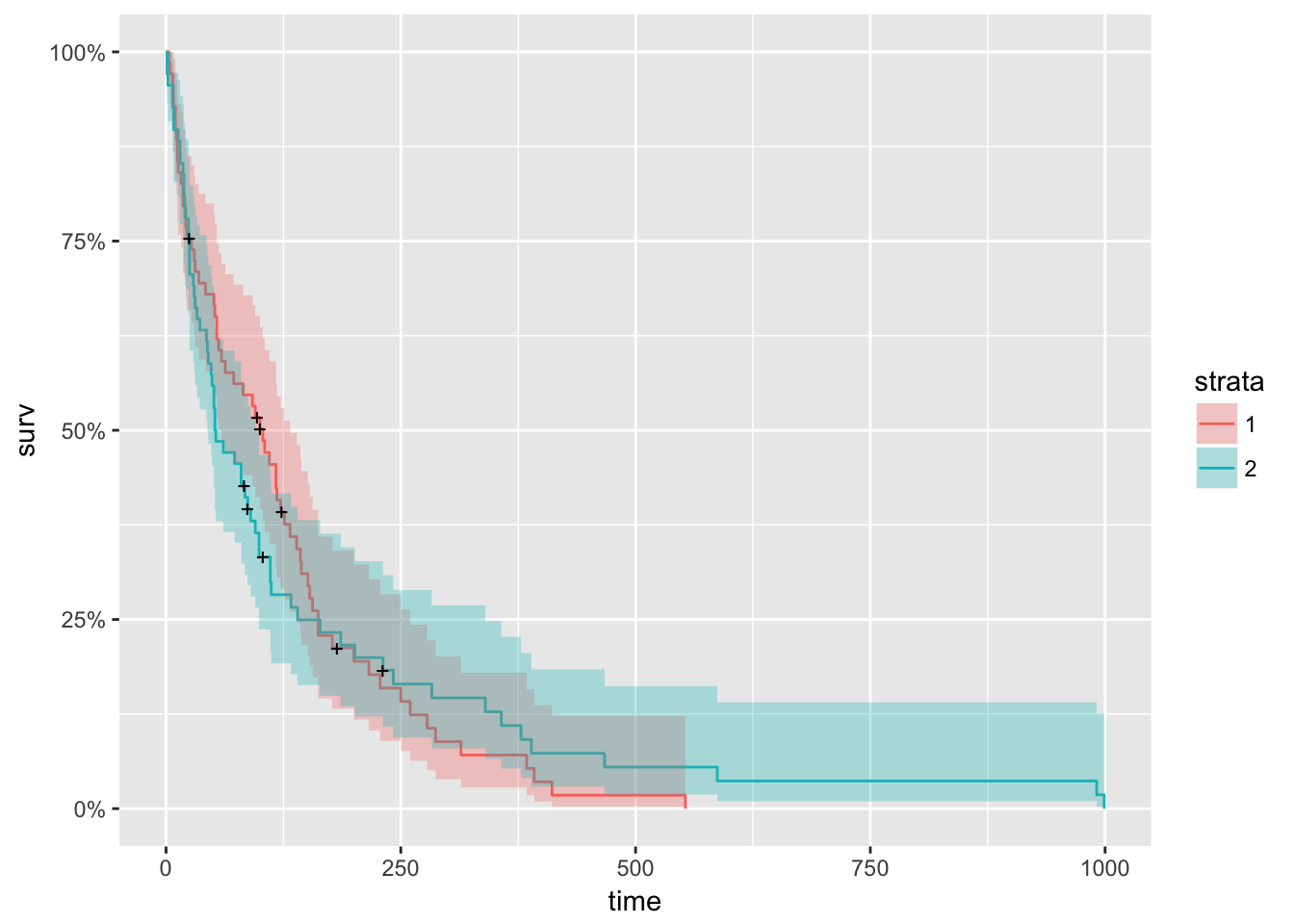



Survival Analysis With R R Views
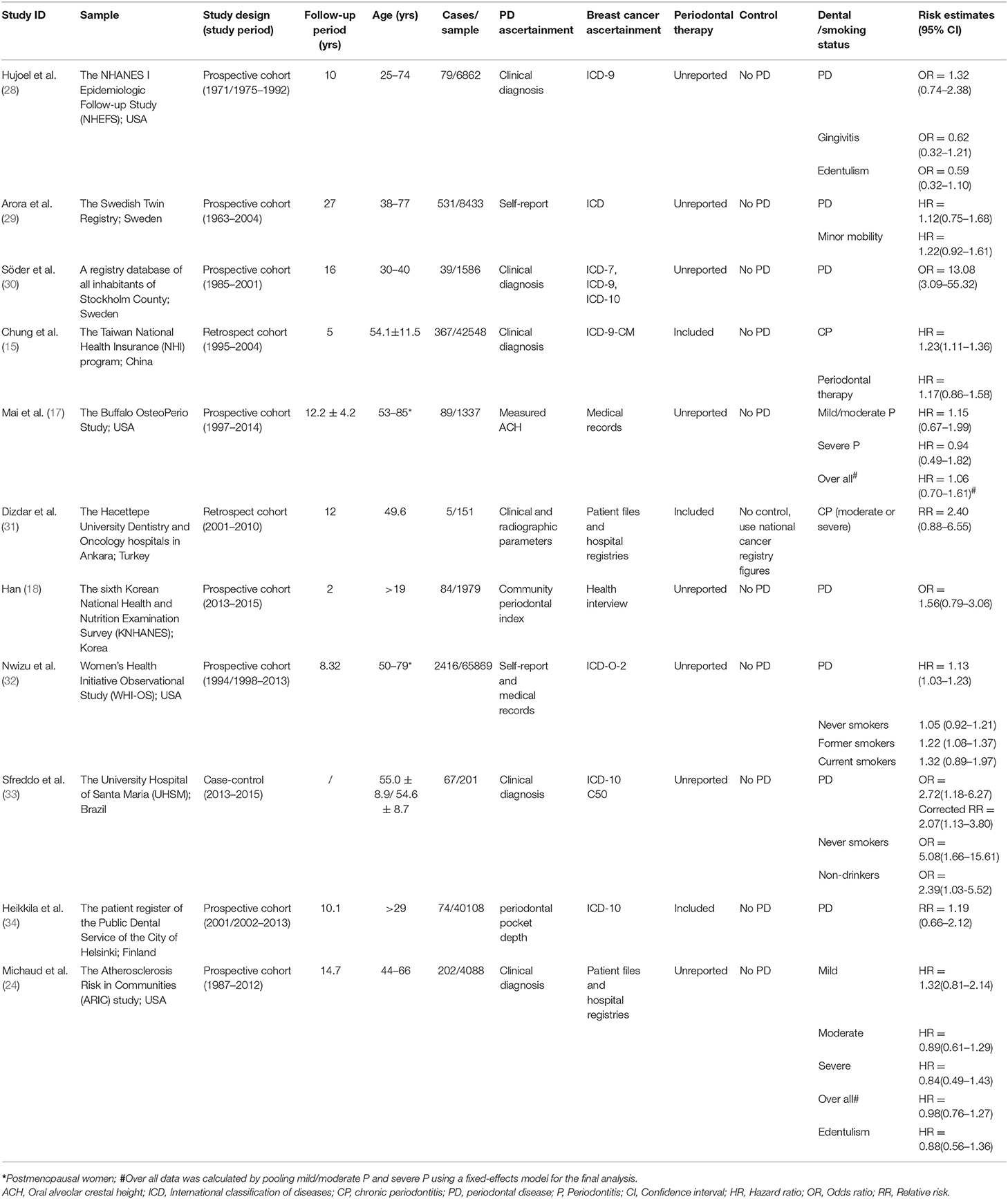



Frontiers Periodontal Disease And Breast Cancer A Meta Analysis Of 1 73 162 Participants Oncology



Beaumont Cloud Cme Com Launchscorm Aspx Caseid 112 Userid 0 Video True
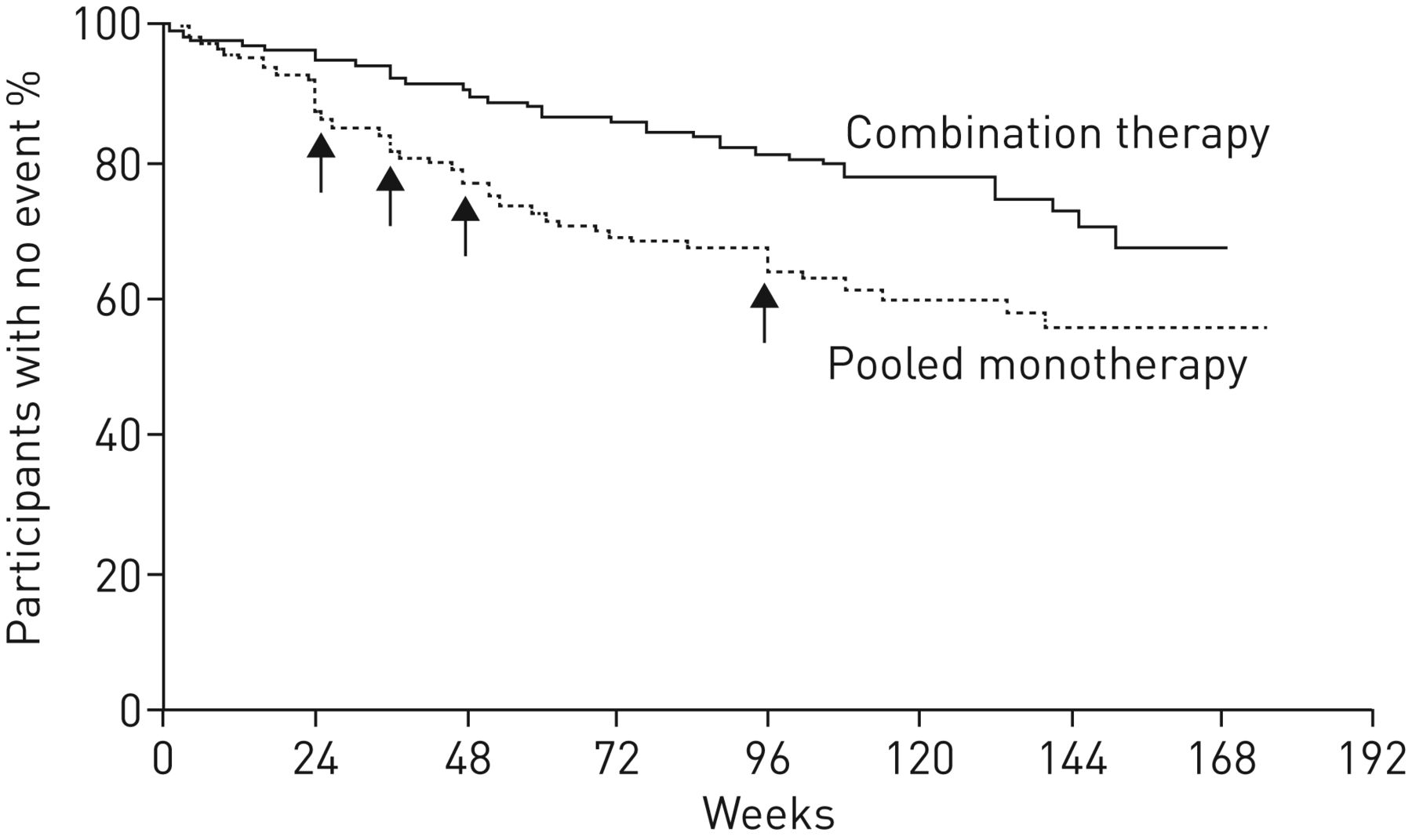



Interpreting Risk Reduction In Clinical Trials For Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension European Respiratory Society



2



Epidemiology Stepwards



Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies




Scielo Brasil Survival Analysis Kaplan Meier Curves A Method To Predict The Future Survival Analysis Kaplan Meier Curves A Method To Predict The Future
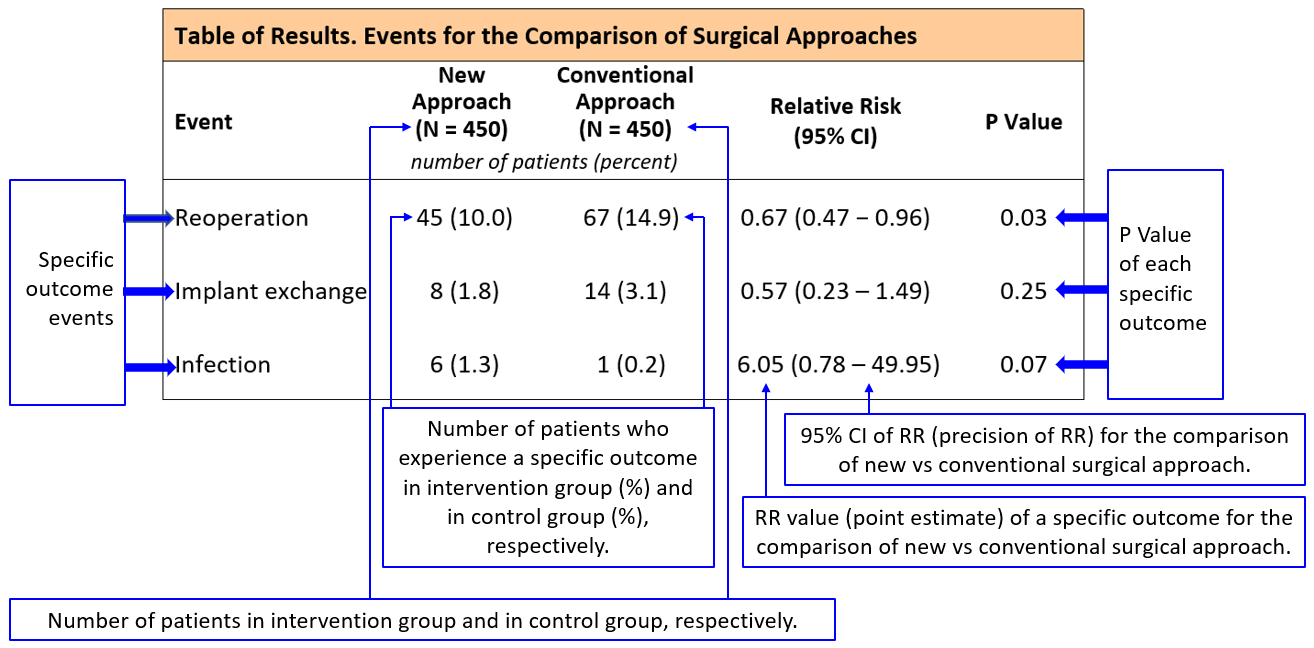



Interpreting Results From Randomized Trials




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




The Effects Of Diabetes On The Risks Of Major Cardiovascular Diseases And Death In The Asia Pacific Region Diabetes Care




Risk Of All Cause Mortality And Cardiovascular Disease Associated With Secondhand Smoke Exposure A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis International Journal Of Cardiology




Linear Combinations Of Estimators Logistic Regression Coefficient Of Determination
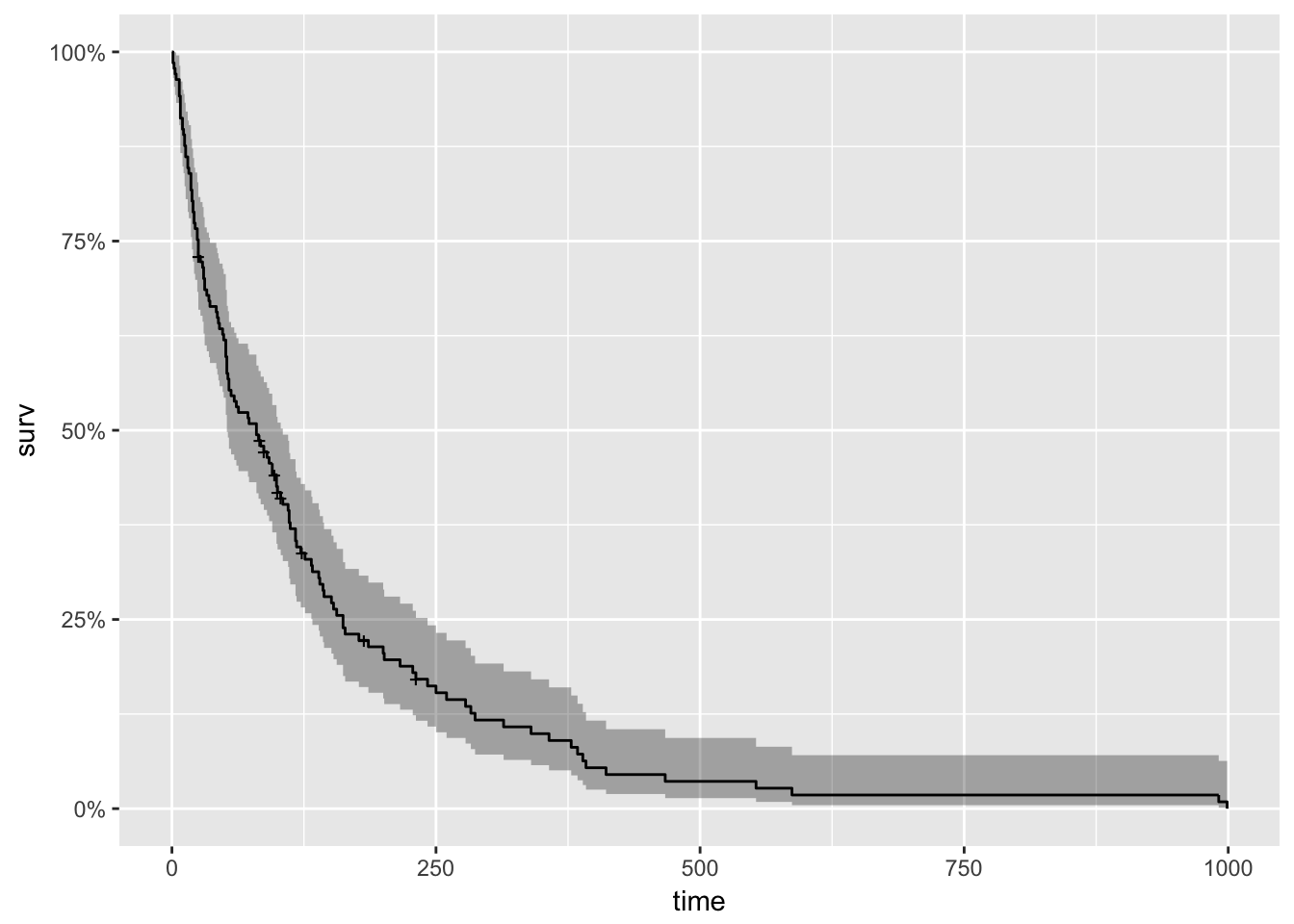



Survival Analysis With R R Views




Risk Of Kidney Failure Death And Cardiovascular Events After Lower Limb Complications In Patients With Ckd Kidney International Reports
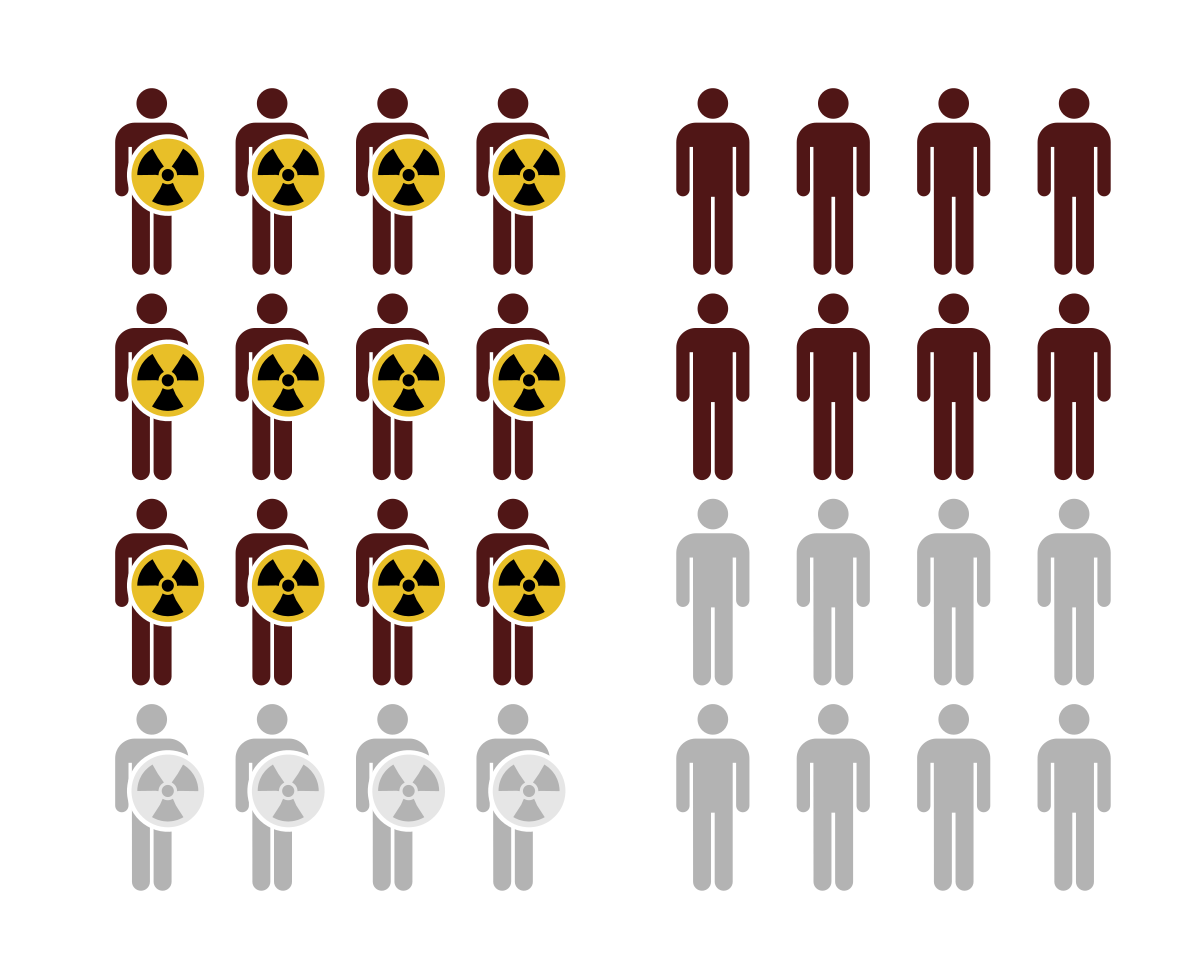



Number Needed To Harm Wikipedia




Ppt Measures Of Association Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Onlinelibrary Wiley Com Doi Pdf 10 1002 Psb 62




Pdf What Are Hazard Ratios




Degree Of Serotonin Reuptake Inhibition Of Antidepressants And Ischemic Risk Neurology




How To Tell The Difference Between A Hazard Ratio Relative Risk And Odds Ratio



Www Medrxiv Org Content 10 1101 21 02 02 v3 Full Pdf




Risk Thresholds For Alcohol Consumption Combined Analysis Of Individual Participant Data For 599 912 Current Drinkers In Prospective Studies The Lancet




Assessing Heterogeneity Of Treatment Effect Estimating Patient Specific Efficacy And Studying Variation In Odds Ratios Risk Ratios And Risk Differences Statistical Thinking



Epidemiology Stepwards




Increased Risk Of Colorectal Cancer In Individuals With A History Of Serrated Polyps Gastroenterology




Risk Ratios For Contagious Outcomes Journal Of The Royal Society Interface
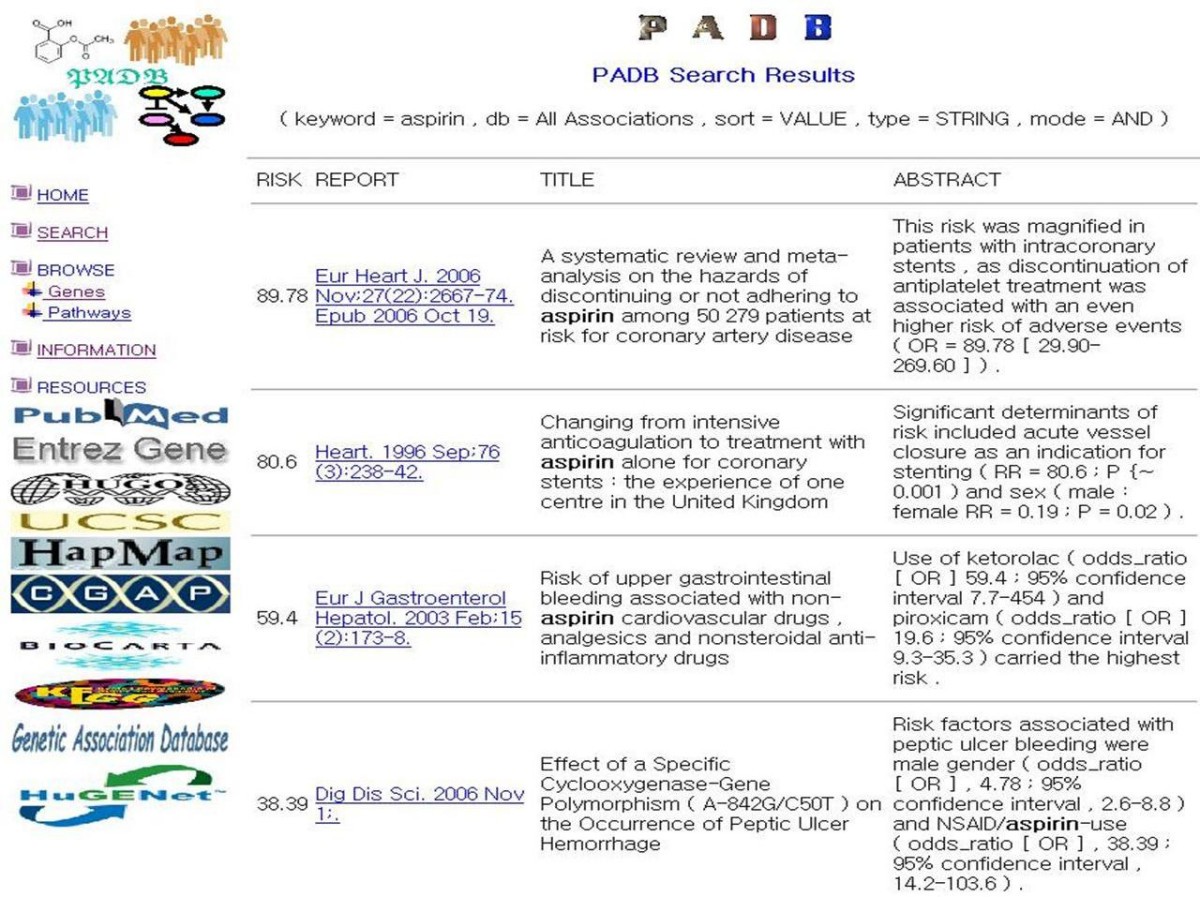



Padb Published Association Database Bmc Bioinformatics Full Text



Http Aspirekpco Weebly Com Uploads 1 5 9 3 Session 6 Statistical Interpretation 19 Pdf




Sedentary Time And Its Association With Risk For Disease Incidence Mortality And Hospitalization In Adults A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Annals Of Internal Medicine Vol 162 No 2




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



Www Cebm Ox Ac Uk Files Data Extraction Tips Blog 10 Pdf



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿